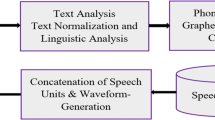
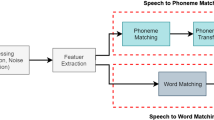
Abstract
Speech technologies such as text-to-speech (TTS) and speech-to-text (STT) are becoming increasingly applicable. Significant improvements in their quality are driven by advancements in deep machine learning. The ability of devices to deeply understand human speech and generate appropriate responses is a hallmark of AI capabilities. Developing speech technology requires extensive speech and language resources, which is why many languages with smaller speaker bases lag behind widely spoken languages in the development of speech technologys. Prior to the deep learning (DL) paradigm, hidden Markov models (HMM) and probabilistic approaches dominated speech technology development. This paper reviews the challenges and solutions in TTS and STT development for Serbian, highlighting the transition from HMM to DL. It also explores the future prospects of speech technology development for under-resourced languages and its role in preserving these languages.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delić, V., et al.: Speech technology progress based on new machine learning paradigm. Computational Intelligensce and Neuroscience, Wiley, Article 4368036, 19 pages (2019)
Besacier, L., Barnard, E., Karpov, A., Schultz, T.: Automatic speech recognition for under-resourced languages: a survey. Speech Commun. 56, 85–100 (2014)
Swietojanski, P., Ghoshal, A., Renals, S.: Unsupervised crosslingual knowledge transfer in DNN-based LVCSR. In: Workshop SLT, pp. 246–251. IEEE, Miami, FL, USA (2012)
Tan, X., Qin, T., Soong, F., Liu, T.Y.: A Survey on Neural Speech Synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.15561 (2021)
Dutoit, T.: High Quality Text-To-Speech Synthesis of the French Language. Ph.D. dissertation. Supervised by Prof. Henri Leich. Faculté Polytechnique de Mons. (1993)
Teranishi R., Umeda N.: Use of pronouncing dictionary in speech synthesis experiments. In: Reports of the Sixth International Congress on Acoustics, vol. 2, pp. 155–158 (1968)
Hallahan, W.I.: DECtalk Software: text-to-speech technology and implementation. Digit. Tech. J. 7(4), 5–19 (1995)
Dutoit, T.: An Introduction to Text-to-Speech Synthesis. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London (1999)
Van Santen, J.: Assignment of segmental duration in text-to-speech synthesis. Comput. Speech Lang. 8(2), 95–128 (1994)
Sejnowski, T., Rosenberg, C.R.: Parallel networks that learn to pronounce English text. Complex Syst.1, 145–168 (1987)
McCulloch, N., Bedworth, M., Bridle J.: NETspeak – a re-implementation of NETtalk. Comput. Speech Lang. 2, 289–301 (1987)
Ronanki, S.: Prosody Generation for Text-to-Speech Synthesis. Ph.D. thesis, University of Edinburgh (2019)
Sagisaka, Y., Kaiki, N., Iwahashi, N., Mimura, K.: ATR v-TALK speech synthesis system. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, pp. 483–486 (1992)
Donovan, R.E., Eide, E.: The IBM trainable speech synthesis system. In: Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP 98), p. 4, ISCA, Sydney, Australia (1998)
Hunt A.J., Black A.W.: Unit selection in a concatenative speech synthesis system using a large speech database. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 373–376. IEEE, Atlanta, GA, USA (1996)
Yoshimura, T., Tokuda, K., Masuko, T., Kobayashi, T., Kitamura T.: Simultaneous modeling of spectrum, pitch and duration in HMM-based speech synthesis, In: Proceedings of the 6th EUROSPEECH, pp. 2347–2350. Budapest, Hungary (1999)
Yamagishi, J., Kobayashi, T., Nakano, Y., Ogata, K., Isogai J.: Analysis of speaker adaptation algorithms for HMM-based speech synthesis and a constrained SMAPLR adaptation algorithm. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 17(s1), 66–83 (2009)
Yamagishi, J., Onishi, K., Masuko, T., Kobayashi, T.: Modeling of various speaking styles and emotions for HMM-based speech synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 10th EUROSPEECH, pp. 2461–2464. Geneva, Switzerland (2003)
Qian, Y., Liang, H., Soong, F.K.: A cross-language state sharing and mapping approach to bilingual (Mandarin-English) TTS. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 17(6), 1231–1239 (2009)
Tokuda, K., Nankaku, Y., Toda, T., Zen, H., Yamagishi, J., Oura, K.: Speech synthesis based on hidden markov models. Proc. IEEE 101(5), 1234–1252 (2013)
Yan, Z.-J., Qian, Y., Soong, F.K.: Rich-context unit selection (RUS) approach to high quality TTS. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 4798–4801. IEEE (2010)
Qian, Y., Soong, F.K., Yan, Z.J.: A unified trajectory tiling approach to high quality speech rendering. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(2), 280–290 (2013)
Weijters, T., Thole, J.: Speech synthesis with artificial neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 1764–1769, San Francisco, CA, USA (1993)
Zen, H., Senior, A., Schuster, M.: Statistical parametric speech synthesis using deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the ICASSP, pp. 7962–7966. IEEE (2013)
Fan, Y., Qian, Y., Xie, F.L., Soong, F.K.: TTS synthesis with bidirectional LSTM based recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of 15th INTERSPEECH, pp. 1964–1968. ISCA, Singapore (2014)
Saito, Y., Takamichi, S., Saruwatari, H.: Statistical parametric speech synthesis incorporating generative adversarial networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 26(1), 84–96 (2018)
Wu, Z., King, S.: Improving trajectory modelling for DNN-based speech synthesis by using stacked bottleneck features and minimum generation error training. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 24(7), 1255–1265 (2016)
Fan, Y., Qian, Y., Soong, F.K., He, L.: Multi-speaker modeling and speaker adaptation for DNN-based TTS synthesis. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 4475–4479. IEEE (2015)
Wu, Z., Swietojanski, P., Veaux, C., Renals, S., King, S.: A study of speaker adaptation for DNN-based speech synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 16th INTERSPEECH, pp. 879–883, Dresden (2015)
Hojo, N., Ijima, Y., Mizuno, H.: An investigation of DNN-based speech synthesis using speaker codes. In: Proceedings of the 17th INTERSPEECH 2016, pp. 2278–2282. San Francisco, USA (2016)
Fan, Y., Qian, Y., Soong, F.K., He, L.: Multi-speaker modeling and speaker adaptation for DNN-based TTS synthesis. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 4475–4479. Brisbane, Australia (2015)
Brave, S., Nass, C.: Emotion in human-computer interaction. In: Sears, A., Jacko, J.A. (eds.) Human-Computer Interaction Fundamentals, pp. 53–68, CRC, Boca Raton, USA (2009)
Yamagishi, J., Onishi, K., Masuko, T., Kobayashi, T.: Modeling of various speaking styles and emotions for HMM-based speech synthesis. In: 8th EUROSPEECH, Geneva, Switzerland (2003)
Eyben, F., et al.: Unsupervised clustering of emotion and voice styles for expressive TTS. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 4009–4012. IEEE (2012)
Aihara, R., Takashima, R., Takiguchi, T., Ariki, Y.: GMM-based emotional voice conversion using spectrum and prosody features. Am. J. Signal Process. 2(5), 134–138 (2012)
Lorenzo-Trueba, J., Henter, G.E., Takaki, S., Yamagishi, J., Morino, Y., Ochiai, Y.: Investigating different representations for modeling and controlling multiple emotions in DNN-based speech synthesis. Speech Commun. 99, 135–143 (2018)
Luo, Z., Chen, J., Takiguchi, T., Ariki, Y.: Emotional voice conversion with adaptive scales F0 based on wavelet transform using limited amount of emotional data. In: Proceedings of the 18th INTERSPEECH, pp. 3399–3403. ISCA (2017)
Ming, H., Huang, D., Xie, L., Wu, J., Dong, M., Li, H.: Deep bidirectional LSTM modeling of timbre and prosody for emotional voice conversion. In: Proceedings of the 17th INTERSPEECH 2016, pp. 2453–2457. ISCA (2016)
An, S., Ling, Z., Dai, L.: Emotional statistical parametric speech synthesis using LSTM-RNNS. In: Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Samit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), pp. 1613–1616, IEEE (2017)
Skerry-Ryan, R., et al.: Towards end-to-end prosody transfer for expressive speech synthesis with Tacotron. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 4693–4702. PMLR (2018)
Wu, P., Ling, Z., Liu, L., Jiang, Y., Wu, H., Dai, L.: End-to-end emotional speech synthesis using style tokens and semisupervised training. In: Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Samit and Conf. (APSIPA ASC), pp. 623–627. IEEE (2019)
Zhou, K., Sisman, B., Rana, R., Schuller, B.W., Li, H.: Speech synthesis with mixed emotions. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 14(4), 3120–3134 (2022)
Van den Oord, A., Dieleman, S., Zen, H., et al.: WaveNet: a generative model for raw audio. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.03499 12 (2016)
Van den Oord, A., et al.: Parallel WaveNet: fast high- fidelity speech synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 3915–3923. Stockholm, Sweden (2018)
Arik, S.O., et al.: Deep voice: real-time neural text-to-speech. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 195–204. PMLR, Sydney, Australia (2017)
Wang, Y., et al.: Tacotron: towards end-to-end speech synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 18th INTERSPEECH 2017, pp. 4006–4010. ISCA, Stockholm, Sweden (2017)
Shen, J., et al.: Natural TTS synthesis by conditioning WaveNet on MEL spectrogram predictions. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 4779–4783. Calgary, Canada (2018)
Ping, W., Peng, K., Gibiansky, A., et al.: Deep voice 3: scaling text-to-speech with convolutional sequence learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.07654 (2017)
Arik, S.Ö, Chen, J., Peng, K., Ping, W., Zhou, Y.: Neural voice cloning with a few samples. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31, 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 10040–10050, Montreal, Canada (2018)
Nachmani, E., Polyak, A., Taigman, Y., Wolf, L.: Fitting new speakers based on a short untranscribed sample. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 3680–3688. Stockholm, Sweden (2018)
Akuzawa, K., Iwasawa, Y., Matsuo, Y.: Expressive speech synthesis via modeling expressions with variational autoencoder. In: Proceedings of the 19th INTERSPEECH, pp. 3067–3071. ISCA, Hyderabad, India (2018)
Ren, Y., et al.: Fastspeech: fast, robust and controllable text to speech. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. systems 32 (2019)
Ren, Y., et al.: Fastspeech 2: Fast and high-quality end-to-end text to speech. Preprint arXiv:2006.04558 (2020)
Nosek, T., Suzić, S., Sečujski, M., Stanojev, V., Pekar, D., Delić, V.: End-to-end speech synthesis for the Serbian language based on Tacotron. In: Karpov, A. Delić, V., (eds.) SPECOM 2024, LNAI Part I - 15299, Springer, Heidelberg, Belgrade, Serbia (2024)
Wang, C., et al.: Neural Codec Language Models are Zero-Shot Text to Speech Synthesizers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.02111 (2023)
Zhang, Z., et al.: Speak foreign languages with your own voice: Cross-lingual neural codec language modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.03926 (2023)
Han, B., et al.: VALL-E R: Robust and Efficient Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech Synthesis via Monotonic Alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.07855 (2024)
Meng, L., et al.: Autoregressive Speech Synthesis without Vector Quantization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.08551 (2024)
Casanova, E., Weber, J., Shulby, C., Candido Junior, A., Gölge, E., Antonelli Ponti, M.: YourTTS: Towards Zero-Shot Multi-Speaker TTS and Zero-Shot Voice Conversion for everyone. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.02418 (2024)
Kong, J., Kim, J., Bae, J.: HiFi-GAN: generative adversarial networks for efficient and high fidelity speech synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.05646 (2020)
Prenger, R., Valle, R., Catanzaro, B.: WaveGlow: A Flow-based Generative Network for Speech Synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.00002 (2018)
Casanova, E., et al.: XTTS: a Massively Multilingual Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech Model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.04904 (2024)
Sečujski, M., Obradović, R., Pekar, D., Jovanov, Lj., Delić, V.: AlfaNum system for speech synthesis in Serbian language. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference Text, Speech and Dialogue (TSD 2002), pp. 237–244. Brno, Czech Republic (2002)
Pakoci, E., Mak, R.: HMM-based speech synthesis for the Serbian language. In: Proceedings of the 56th ETRAN, vol. TE4, pp. 1–4. Zlatibor, Serbia (2012)
Delić, T., Sečujski, M., Suzić, S.: A review of serbian parametric speech synthesis based on deep neural networks. TELFOR J. 9(1), 32–37 (2017)
Sečujski, M., Pekar, D., Suzić, S., Smirnov, A., Nosek, T.: Speaker/style-dependent neural network speech synthesis based on speaker/style embedding. J. Univ. Comput. Sci. 26(4), 434–453 (2020)
Suzić, S., Sečujski, M., Nosek, T., Delić, V., Pekar, D.: HiFi-GAN based text-to-speech synthesis in Serbian. In: Proceedings of 30th EUSIPCO, pp. 2231–2235, Belgrade, Serbia (2022)
Sakai, T., Doshita, S.: Phonetic Typewriter. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 33, 1664 (1961)
Davis, K.H., Biddulph, R., Balashek, S.: Automatic recognition of spoken digits. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 24, 637–642 (1952)
Vintsyuk, T.K.: Speech discrimination by dynamic programming. Cybern. Syst. Anal. 4, 52–57 (1972)
Sakoe, H., Chiba, S.: Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 26, 43–49 (1978)
Atal, B.S., Hanauer, S.L.: Speech analysis and synthesis by linear prediction of the speech wave. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 50, 637–655 (1971)
Jelinek, F., Bahl, L., Mercer, R.: Design of a linguistic statistical decoder for the recognition of continuous speech. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 21, 250–256 (1975)
Klatt, D.H.: Review of the ARPA speech understanding project. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 62, 1345–1366 (1977)
Jelinek, F.: Continuous speech recognition by statistical methods. Proc. IEEE 64, 532–556 (1976)
Levinson, S.E., Rabiner, L.R., Sondhi, M.M.: An Introduction to the application of the theory of probabilistic functions of a markov process to automatic speech recognition. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 62, 1035–1074 (1983)
Juang, B.-H.: Maximum-likelihood estimation for mixture multivariate stochastic observations of markov chains. AT&T Tech. J. 64, 1235–1249 (1985)
Juang, B.-H., Levinson, S., Sondhi, M.: Maximum likelihood estimation for multivariate mixture observations of Markov chains. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory 32, 307–309 (1986)
Lee, K.-F.: Context-independent phonetic hidden Markov models for speaker-independent continuous speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 38, 599–609 (1990)
Young, S.J., Woodland, P.C.: State clustering in hidden Markov model-based continuous speech recognition. Comput. Speech Lang. 8, 369–383 (1994)
Mermelstein, P.: Distance measures for speech recognition, psychological and instrumental. Pattern Recogn. Artif. Intell. 374–388 (1976)
Hermansky, H.: Perceptual linear predictive (PLP) analysis of speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87, 1738–1752 (1990)
Viikki, O., Laurila, K.: Cepstral domain segmental feature vector normalization for noise robust speech recognition. Speech Commun. 25, 133–147 (1998)
Prasad, N.V., Umesh, S.: Improved cepstral mean and variance normalization using Bayesian framework. In: IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, pp. 156–161. IEEE, Olomouc, Czech Republic (2013)
Rehr, R., Gerkmann, T.: Cepstral noise subtraction for robust automatic speech recognition. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 375–378. IEEE, South Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (2015)
Hermansky, H., Morgan, N.: RASTA processing of speech. IEEE Trans. on Speech Audio Processing 2, 578–589 (1994)
Bahl, L., Brown, P., De Souza, P., Mercer, R.: Maximum mutual information estimation of hidden Markov model parameters for speech recognition. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 49–52. IEEE, Tokyo, Japan (1986)
Valtchev, V., Odell, J.J., Woodland, P.C., Young, S.J.: MMIE training of large vocabulary recognition systems. Speech Commun. 22, 303–314 (1997)
Juang, B.-H., Hou, W., Lee, C.-H.: Minimum classification error rate methods for speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 5, 257–265 (1997)
Povey, D., Woodland, P.C.: Minimum phone error and i-smoothing for improved discriminative training. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. I-105-I–108. IEEE, Orlando, FL, USA (2002)
Ng, A.Y., Jordan, M.I.: On discriminative vs. generative classifiers: a comparison of logistic regression and naive Bayes. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems: Natural and Synthetic, pp. 841–848. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA (2001)
Macherey, W.: Discriminative training and acoustic modeling for automatic speech recognition. Ph.D. Thesis, Aachen Techn. Hochsch (2010)
Baker, J.: The DRAGON system–An overview. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 23, 24–29 (1975)
Bahl, L.R., Jelinek, F., Mercer, R.L.: A maximum likelihood approach to continuous speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. PAMI-5, 179–190 (1983)
Chen, S.F., Goodman, J.: An empirical study of smoothing techniques for language modeling. Comput. Speech Lang. 13, 359–393 (1999)
Goodman, J.T.: A bit of progress in language modeling. Comput. Speech Lang. 15, 403–434 (2001)
Lippmann, R.P.: Review of neural networks for speech recognition. Neural Comput. 1, 1–38 (1989)
Bourlard, H.A., Morgan, N.: Connectionist Speech Recognition: a Hybrid Approach. Springer, US, Boston, MA (1994)
Mohamed, A., Dahl, G.E., Hinton, G.E.: Deep belief networks for phone recognition. In: NIPS Workshop on Deep Learning for Speech Recognition and Related Applications, pp. 1–9. Vancouver, BC, Canada (2009)
Dahl, G.E., Dong Yu, Li Deng, Acero, A.: Context-dependent pre-trained deep neural networks for large-vocabulary speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Audio, Speech, Lang. Process. 20, 30–42 (2012)
Graves, A., Fernández, S., Gomez, F., Schmidhuber, J.: Connectionist temporal classification: labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 369–376. ACM Press, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania (2006)
Maas, A., Xie, Z., Jurafsky, D., Ng, A.: Lexicon-free conversational speech recognition with neural networks. In: Proceedings Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 345–354. Denver, Colorado (2015)
Bahdanau, D., Chorowski, J., Serdyuk, D., Brakel, P., Bengio, Y.: End-to-end attention-based large vocabulary speech recognition. In: Proceedings of ICASSP, pp. 4945–4949. Shanghai (2016)
Karita, S., et al.: A comparative study on transformer vs RNN in speech applications. In: Automatic speech recognition and understanding workshop (ASRU), pp. 449–456. IEEE, SG, Singapore (2019)
Zhu, H., Wang, L., Cheng, G., Wang, J., Zhang, P., Yan, Y.: Wav2vec-S: semi-supervised pre-training for low-resource ASR. In: Proceedings of the 23th INTERSPEECH, pp. 4870–4874. ISCA (2022)
Schneider, S., Baevski, A., Collobert, R., Auli, M.: wav2vec: Unsupervised pre-training for speech recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.05862 (2019)
Radford, A., Kim, J.W., Xu, T., Brockman, G., McLeavey, C., Sutskever, I.: Robust speech recognition via large-scale weak supervision. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 28492–28518 (2023)
Suzić, S., Ostrogonac, S., Pakoci, E., Bojanić, M.: Building a speech repository for a Serbian LVCSR system. Telfor J. 6(2), 109–114 (2014)
Nosek, T., Suzić, S., Delić, V., Sečujski, M.: Cross-lingual text-to-speech with prosody embedding. In: Proceedings of IWSSIP, 5 pages (2023)
Pakoci, E.T., Popović, B.Z.: Recurrent neural networks and morphological features in language modeling for Serbian. In: 29th Telecommunication Forum (TELFOR), 8 pages. IEEE (2021)
Delić, V., Sečujski, M., Sedlar, N.V., Mišković, D., Mak, R., Bojanić, M.: How speech technologies can help people with disabilities. In: Ronzhin, A., Potapova, R., Delić, V. (eds.) 16th SPECOM 2014, LNAI, vol. 8773, pp. 243–250. Springer. Novi Sad, Serbia (2014)
Delić, V., et al.: Central audio-library of the university of Novi Sad. In: Proceedings of the Intelligent Distributed Computing XIII, pp. 467–476. Springer International Publishing (2020)
Pakoci, E., Pekar, D., Popović, B., Sečujski, M., Delić, V.: Overcoming data sparsity in automatic transcription of dictated medical findings. In: Proceedings of the 30th EUSIPCO, pp. 454–458. IEEE (2022)
Popović, B., Pakoci, E., Jakovljević, N., Kočiš, G., Pekar, D.: Voice assistant application for the Serbian language. In: 23rd Telecommunication Forum (TELFOR), pp. 858–861. IEEE (2015)
Reitmaier, T., et al: Opportunities and challenges of automatic speech recognition systems for low-resource language speakers. In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, p. 17 (2022)
Mu, Z., Yang, X., Dong, Y.: Review of end-to-end speech synthesis technology based on deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.09995 (2021)
Ogayo, P., Neubig, G., Black, A.W.: Building TTS systems for low resource languages under resource constraints. In: Proceedings Speech for Social Good Workshop, p. 5 (2022)
Jimerson, R., Liu, Z., Prud’Hommeaux, E.: An (unhelpful) guide to selecting the best ASR architecture for your under-resourced language. In: Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Comp. Linguistics (Vol. 2 Short Papers), pp. 1008–1016 (2023)
Baevski, A., Zhou, Y., Mohamed, A., Auli, M.: Wav2vec 2.0: a framework for self-supervised learning of speech representations. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 12449–12460 (2020)
Popović, B.Z., Pakoci, E.T., Pekar, D.J.: Transfer learning for domain and environment adaptation in Serbian ASR. Telfor Journal 12(2), 110–115 (2020)
Delić, V.D., Pekar, D.J., Sečujski, M.S., Popović, B.Z., Pakoci, E.T., Suzić, S.B.: Development of speech technology for Serbian and its applications. In: Proceedings of the First Serbian International Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence, p. 7. Kragujevac, Serbia (2022)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Science Fund of the Republic of Serbia, Grant No. 7449, Multimodal multilingual human-machine speech communication, AI-SPEAK, and by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation (Contract No. 451–03-65/2024–03/200156) and the Faculty of Technical Sciences, University of Novi Sad through project “Scientific and Artistic Research Work of Researchers in Teaching and Associate Positions at the Faculty of Technical Sciences, University of Novi Sad” (No. 01–3394/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sečujski, M. et al. (2025). Retrospective and Perspectives of TTS & STT Technology Development and Implementation for South Slavic Under-Resourced Languages. In: Karpov, A., Delić, V. (eds) Speech and Computer. SPECOM 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 15299. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-77961-9_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-77961-9_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-77960-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-77961-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)