Abstract
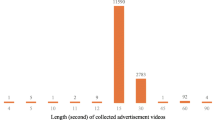
Ad designers often use sequences of shots in video ads, where frames are similar within a shot but vary across shots. These visual variations, along with changes in auditory and narrative cues, can interrupt viewers’ attention. In this paper, we address the underexplored task of applying multimodal feature extraction techniques to marketing problems. We introduce the “AttInfaForAd” dataset, containing 111 baby product video ads with visual ground truth labels indicating points of interest in the first, middle, and last frames of each shot, identified by 75 shoppers. We propose attention interruption measures and use multimodal techniques to extract visual, auditory, and linguistic features from video ads. Our feature-infused model achieved the lowest mean absolute error and highest R-square among various machine learning algorithms in predicting shopper attention interruption. We highlight the significance of these features in driving attention interruption. By open-sourcing the dataset and model code, we aim to encourage further research in this crucial area. (Dataset and model code available at https://github.com/ostadabbas/Baby-Product-Video-Ads).
W. Xie and L. Luan—Contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S.T.: The Language of the Creative Person: Validating the Use of Linguistic Analysis to Assess Creativity. San Jose State University (2021)
Al-Mosaiwi, M., Johnstone, T.: In an absolute state: Elevated use of absolutist words is a marker specific to anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation. Clinical psychological science 6(4), 529–542 (2018)
Alemdag, E., Cagiltay, K.: A systematic review of eye tracking research on multimedia learning. Computers & Education 125, 413–428 (2018)
Baele, S.J., Sterck, O.C.: Diagnosing the securitisation of immigration at the eu level: A new method for stronger empirical claims. Political Studies 63(5), 1120–1139 (2015)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32 (2001)
Burkhardt, H.A., Alexopoulos, G.S., Pullmann, M.D., Hull, T.D., Areán, P.A., Cohen, T.: Behavioral activation and depression symptomatology: longitudinal assessment of linguistic indicators in text-based therapy sessions. J. Med. Internet Res. 23(7), e28244 (2021)
Drewes, H., Pfeuffer, K., Alt, F.: Time-and space-efficient eye tracker calibration. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM symposium on eye tracking research & applications. pp. 1–8 (2019)
Everdell, I.: The Relationship Between Bottom-Up Saliency and Gaze Behaviour During Audiovisual Speech Perception. Ph.D. thesis (2009)
Freedman, D.A.: Statistical Models: Theory and Practice. cambridge University Press (2009)
Friedman, J.H.: Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics pp. 1189–1232 (2001)
Green, M.C., Brock, T.C.: The role of transportation in the persuasiveness of public narratives. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 79(5), 701 (2000)
Grewal, R., Gupta, S., Hamilton, R.: Marketing insights from multimedia data: Text, image, audio, and video (2021)
Hearst, M.A., Dumais, S.T., Osuna, E., Platt, J., Scholkopf, B.: Support vector machines. IEEE Intelligent Systems and Their Applications 13(4), 18–28 (1998)
Hoerl, A.E., Kennard, R.W.: Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 12(1), 55–67 (1970)
Huang, Q., Veeraraghavan, A., Sabharwal, A.: Tabletgaze: Dataset and analysis for unconstrained appearance-based gaze estimation in mobile tablets. Mach. Vis. Appl. 28, 445–461 (2017)
Johnsen, J.A.K., Vambheim, S.M., Wynn, R., Wangberg, S.C.: Language of motivation and emotion in an internet support group for smoking cessation: explorative use of automated content analysis to measure regulatory focus. Psychology research and behavior management pp. 19–29 (2014)
Kastrati, A., Płomecka, M.B., Pascual, D., Wolf, L., Gillioz, V., Wattenhofer, R., Langer, N.: Eegeyenet: a simultaneous electroencephalography and eye-tracking dataset and benchmark for eye movement prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.05100 (2021)
Kellaris, J.J., Cox, A.D., Cox, D.: The effect of background music on ad processing: A contingency explanation. J. Mark. 57(4), 114–125 (1993)
Kirillov, A., Mintun, E., Ravi, N., Mao, H., Rolland, C., Gustafson, L., Xiao, T., Whitehead, S., Berg, A.C., Lo, W.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R.: Segment anything. arXiv:2304.02643 (2023)
Krafka, K., Khosla, A., Kellnhofer, P., Kannan, H., Bhandarkar, S., Matusik, W., Torralba, A.: Eye tracking for everyone. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 2176–2184 (2016)
Luan, L., Liu, W., Zhang, R., Hu, S.: Introducing cognitive psychology in film studies: Redefining affordance. International Journal of Education and Humanities 2(3), 70–78 (2022)
Luke, S.G., Christianson, K.: The provo corpus: A large eye-tracking corpus with predictability norms. Behav. Res. Methods 50, 826–833 (2018)
Machajdik, J., Hanbury, A.: Affective image classification using features inspired by psychology and art theory. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM international conference on Multimedia. pp. 83–92 (2010)
Masciocchi, C.M., Mihalas, S., Parkhurst, D., Niebur, E.: Everyone knows what is interesting: Salient locations which should be fixated. J. Vis. 9(11), 25–25 (2009)
Matz, S.C., Segalin, C., Stillwell, D., Müller, S.R., Bos, M.W.: Predicting the personal appeal of marketing images using computational methods. J. Consum. Psychol. 29(3), 370–390 (2019)
McCullough, M.E., Root, L.M., Cohen, A.D.: Writing about the benefits of an interpersonal transgression facilitates forgiveness. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 74(5), 887 (2006)
Mejova, Y., Zhang, A.X., Diakopoulos, N., Castillo, C.: Controversy and sentiment in online news. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.8152 (2014)
Mele, M.L., Federici, S.: Gaze and eye-tracking solutions for psychological research. Cogn. Process. 13, 261–265 (2012)
Opoku, R.A., Hultman, M., Saheli-Sangari, E.: Positioning in market space: The evaluation of swedish universities’ online brand personalities. J. Mark. High. Educ. 18(1), 124–144 (2008)
Overgoor, G., Rand, W., van Dolen, W., Mazloom, M.: Simplicity is not key: Understanding firm-generated social media images and consumer liking. Int. J. Res. Mark. 39(3), 639–655 (2022)
Palazzi, A., Abati, D., Solera, F., Cucchiara, R., et al.: Predicting the driver’s focus of attention: the dr (eye) ve project. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(7), 1720–1733 (2018)
Pieters, R., Wedel, M.: Attention capture and transfer in advertising: Brand, pictorial, and text-size effects. J. Mark. 68(2), 36–50 (2004)
Pieters, R., Wedel, M., Batra, R.: The stopping power of advertising: Measures and effects of visual complexity. J. Mark. 74(5), 48–60 (2010)
Rosenblatt, F.: Principles of neurodynamics. perceptrons and the theory of brain mechanisms. Tech. rep., Cornell Aeronautical Lab Inc Buffalo NY (1961)
Schweitzer, S., Waytz, A.: Language as a window into mind perception: How mental state language differentiates body and mind, human and nonhuman, and the self from others. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 150(8), 1642 (2021)
Van der Stigchel, S., Theeuwes, J.: The relationship between covert and overt attention in endogenous cuing. Perception & Psychophysics 69(5), 719–731 (2007)
Theeuwes, J.: Top-down and bottom-up control of visual selection. Acta Physiol. (Oxf) 135(2), 77–99 (2010)
Wedel, M., Pieters, R., et al.: Eye tracking for visual marketing. Foundations and Trends® in Marketing 1(4), 231–320 (2008)
Xiao, L., Kim, H.j., Ding, M.: An introduction to audio and visual research and applications in marketing. Review of Marketing Research 10, 213–253 (2013)
Xie, W., Lee, M.H., Chen, M., Han, Z.: Understanding consumers’ visual attention in mobile advertisements: An ambulatory eye-tracking study with machine learning techniques. Journal of Advertising pp. 1–19 (2023)
Zhang, S., Lee, D., Singh, P.V., Srinivasan, K.: What makes a good image? airbnb demand analytics leveraging interpretable image features. Manage. Sci. 68(8), 5644–5666 (2022)
Zhang, X., Sugano, Y., Fritz, M., Bulling, A.: Mpiigaze: Real-world dataset and deep appearance-based gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(1), 162–175 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xie, W., Luan, L., Zhu, Y., Bart, Y., Ostadabbas, S. (2025). Multimodal Drivers of Attention Interruption to Baby Product Video Ads. In: Antonacopoulos, A., Chaudhuri, S., Chellappa, R., Liu, CL., Bhattacharya, S., Pal, U. (eds) Pattern Recognition. ICPR 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15328. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78104-9_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78104-9_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-78103-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-78104-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)