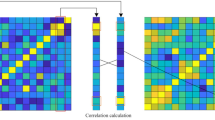
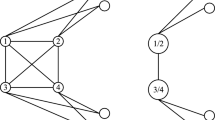
Abstract
Human brain is a complex organ that consists of billions of neurons and trillions of connections among the neurons. To describe the correlations among the time series of the brain regions, we model the brain as a functional brain network to diagnose psychosis. However, traditional methods of functional brain network construction are usually noisy and do not consider the causal relationships among brain regions. To obtain the causal relationships and improve diagnosis interpretability, we propose a directed brain network Transformer (DBNT) for psychiatric diagnosis. First, the causal relationships in the blood-oxygen-level-dependent time series of brain regions are extracted to generate a directed brain network. Then, the feature encoding method is proposed to obtain local and global features of the brain networks by using the DBNT. Experimental results demonstrate that the accuracy of DBNT increases by 8.1% and 6.4% compared to state-of-the-art methods on two large-scale brain network datasets. DBNT also highlights the brain regions associated with psychosis and provides interpretation for diagnosis.
Supported by the Program of Yunnan Key Laboratory of Intelligent Systems and Computing (202405AV340009) and Yunnan Fundamental Research Project (202401AT070462).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
https://fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org/indi/abide/
- 2.
http://fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org/indi/adhd200/
References
Bannadabhavi, A., Lee, S., Deng, W., Ying, R., Li, X.: Community-aware transformer for autism prediction in fmri connectome. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. pp. 287–297 (2023)
Bellec, P., Chu, C., Chouinard-Decorte, F., Benhajali, Y., Margulies, D.S., Craddock, R.C.: The neuro bureau adhd-200 preprocessed repository. NeuroImage pp. 275–286 (2017)
Canario, E., Chen, D., Biswal, B.: A review of resting-state fmri and its use to examine psychiatric disorders. Psychoradiology 1(1), 42–53 (2021)
Craddock, C., Benhajali, Y., Chu, C., Chouinard, F., Evans, A., Jakab, A., Khundrakpam, B.S., Lewis, J.D., Li, Q., Milham, M.: The neuro bureau preprocessing initiative: open sharing of preprocessed neuroimaging data and derivatives. Front. Neuroinform. 7(27), 5 (2013)
Craddock, R.C., James, G.A., Holtzheimer, P.E., III., Hu, X.P., Mayberg, H.S.: A whole brain fmri atlas generated via spatially constrained spectral clustering. Hum. Brain Mapp. 33(8), 1914–1928 (2012)
Cui, H., Dai, W., Zhu, Y., Kan, X., Gu, A.A.C., Lukemire, J., Zhan, L., He, L., Guo, Y., Yang, C.: Braingb: A benchmark for brain network analysis with graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 42(2), 493–506 (2022)
Cui, H., Dai, W., Zhu, Y., Yang, C.: Interpretable graph neural networks for connectome-based brain disorder analysis. In: Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. p. 375-385 (2022)
Dai, W., Cui, H., Kan, X., Guo, Y., van Rooij, S., Yang, C.: Transformer-based hierarchical clustering for brain network analysis. In: Proceedings of The IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. pp. 1–5 (2023)
Delvigne, V., Wannous, H., Vandeborre, J.P., Ris, L.: Spatio-temporal analysis of transformer based architecture for attention estimation from eeg. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Pattern Recognition. pp. 1076–1082 (2022)
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
Kan, X., Cui, H., Lukemire, J., Yang, C.: Fbnetgen: Task-aware gnn-based fmri analysis via functional brain network generation. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning. pp. 618–637 (2022)
Kan, X., Dai, W., Yang, C.J.: Brain network transformer. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2022)
Kawahara, J., Brown, C.J., Miller, S.P., Booth, B.G., Chau, V., Grunau, R.E., Zwicker, J.G.: Brainnetcnn: Convolutional neural networks for brain networks; towards predicting neurodevelopment. Neuroimage 146, 1038–1049 (2017)
Kreuzer, D., Beaini, D., Hamilton, W., Létourneau, V., Tossou, P.: Rethinking graph transformers with spectral attention. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. vol. 34, pp. 21618–21629 (2021)
Krystal, J.H.: Psychiatric disorders: diagnosis to therapy. Cell 157(1), 201–214 (2014)
Li, L., Duan, L., Wang, J., He, C., Chen, Z., Xie, G., Deng, S., Luo, Z.: Memory-enhanced transformer for representation learning on temporal heterogeneous graphs. Data Science and Engineering 8(2), 98–111 (2023)
Li, X., Zhou, Y., Dvornek, N., Zhang, M., Gao, S., Zhuang, J., Scheinost, D., Staib, L.H., Ventola, P., Duncan, J.S.: Braingnn: Interpretable brain graph neural network for fmri analysis. Med. Image Anal. 74, 102233 (2021)
Scangos, K.W., State, M.W., Miller, A.H., Baker, J.T.: New and emerging approaches to treat psychiatric disorders. Nat. Med. 29(2), 317–333 (2023)
Scheltens, P., De Strooper, B., Kivipelto, M., Holstege, H., Chételat, G., Teunissen, C.E., Cummings, J., van der Flier, W.M.: Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet 397(10284), 1577–1590 (2021)
Shojaie, A., Fox, E.B.: Granger causality: A review and recent advances. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application 9, 289–319 (2022)
Tong, Y., Li, Z., Huang, H., Gao, L., Xu, M., Hu, Z.: Research of spatial context convolutional neural networks for early diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease. The Journal of Supercomputing pp. 1–19 (2023)
Tu, Z., Talebi, H., Zhang, H., Yang, F., Milanfar, P., Bovik, A., Li, Y.: Maxvit: Multi-axis vision transformer. In: Proceedings of European conference on computer vision. pp. 459–479 (2022)
Velickovic, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Liò, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks. In: Proceedings of The International Conference on Learning Representations (2018)
Wu, Q., Lei, H., Mao, T., Deng, Y., Zhang, X., Jiang, Y., Zhong, X.: Test-retest reliability of resting brain small-world network properties across different data processing and modeling strategies. Brain Sci. 13(5), 825 (2023)
Xia, M., Wang, J., He, Y.: Brainnet viewer: a network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS ONE 8(7), 689–699 (2013)
Yu, Y., Kan, X., Cui, H., Xu, R., Zheng, Y., Song, X., Zhu, Y., Zhang, K.: Deep dag learning of effective brain connectivity for fmri analysis. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. pp. 1–5 (2023)
Zhang, R., Volkow, N.D.: Seasonality of brain function: role in psychiatric disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 13(1), 65 (2023)
Zhdanov, M., Steinmann, S., Hoffmann, N.: Investigating brain connectivity with graph neural networks and gnnexplainer. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Pattern Recognition. pp. 5155–5161 (2022)
Zheng, K., Yu, S., Chen, B.: Ci-gnn: A granger causality-inspired graph neural network for interpretable brain network-based psychiatric diagnosis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.01642 (2023)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhu, X., Qi, Z., Yue, K., Su, Y., Duan, L. (2025). Directed Brain Network Transformer for Psychiatric Diagnosis. In: Antonacopoulos, A., Chaudhuri, S., Chellappa, R., Liu, CL., Bhattacharya, S., Pal, U. (eds) Pattern Recognition. ICPR 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15311. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78195-7_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78195-7_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-78194-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-78195-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)