Abstract
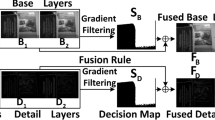
Multi-focus image fusion (MFIF) explores the positioning and reorganization of the focused parts from the input images. Focused and defocused parts have similar representations in color, contour and other appearance information, which degrades the fusion quality due to the influence of these redundant information. Currently, most MFIF methods have not identified an effective way to remove redundant information before fusion stage. Thus, in this paper, we introduce a structural map extraction strategy for multi-focus image fusion. Compared to the source image, structural map reduces redundant information, and the clearer parts of the image retain more abundant structural features. Consequently, the differences between focused part and defocused part become more pronounced based on the extracted structural map. Specifically, the proposed fusion method adopts a two-stage training strategy. Firstly, the structural map is extracted by the proposed structural map extraction network (SMENet) from the source images. Secondly, the structural map is thus applied to train the decision map generation network (DMGNet) to obtain the decision map which is utilized to generate the final fusion image. Qualitative and quantitative experiments on three public datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method, compared with the advanced image fusion algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The threshold is set to 0.5 [1].
- 2.
The threshold is set to \(0.002\times H\times W\). Among them, H and W are the height and width of the source image, respectively.
- 3.
The window size of the filter is set to 5, and the smoothness is set to 1.
- 4.
Due to space limitations, the qualitative and quantitative experimental results on the MFFW dataset have been included in the supplementary materials.
- 5.
Due to page constraints, the ablation experiments on the MFFW and MFI-WHU datasets are included in the supplementary materials.
References
Wang, Z., Li, X., Duan, H., Zhang, X.: A self-supervised residual feature learning model for multifocus image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 4527–4542 (2022)
Li, X., Li, Y., Chen, H., Peng, Y., Chen, L., Wang, M.: Ritfusion: Reinforced interactive transformer network for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 73, 1–16 (2024)
Da Cunha, A.L., Zhou, J., Do, M.N.: The nonsubsampled contourlet transform: Theory, design, and applications. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(10), 3089–3101 (2006)
Easley, G., Labate, D., Lim, W.-Q.: Sparse directional image representations using the discrete shearlet transform. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 25(1), 25–46 (2008)
Zhang, Q., Wang, F., Luo, Y., Han, J.: Exploring a unified low rank representation for multi-focus image fusion. Pattern Recogn. 113, 107752 (2021)
Liu, Yu., Liu, S., Wang, Z.: Multi-focus image fusion with dense sift. Information Fusion 23, 139–155 (2015)
Yu Liu, Xun Chen, Hu Peng, and Zengfu Wang. Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Information Fusion, 36:191–207, 2017.
Boyuan Ma, Yu., Zhu, X.Y., Ban, X., Huang, H., Mukeshimana, M.: Sesf-fuse: an unsupervised deep model for multi-focus image fusion. Neural Comput. Appl. 33, 5793–5804 (2021)
Xingyu, H., Jiang, J., Liu, X., Ma, J.: Zmff: Zero-shot multi-focus image fusion. Information Fusion 92, 127–138 (2023)
Cheng Ma, Yongming Rao, Yean Cheng, Ce Chen, Jiwen Lu, and Jie Zhou. Structure-preserving super resolution with gradient guidance. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 7769–7778, 2020
Yuan Tian, Guo Lu, Yichao Yan, Guangtao Zhai, Li Chen, and Zhiyong Gao. A coding framework and benchmark towards low-bitrate video understanding. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024
Han, X., Ma, J., Jiang, J., Guo, X., Ling, H.: U2fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(1), 502–518 (2022)
Cheng, C., Tianyang, X., Xiao-Jun, W.: Mufusion: A general unsupervised image fusion network based on memory unit. Information Fusion 92, 80–92 (2023)
Guo, X., Nie, R., Cao, J., Zhou, D., Mei, L., He, K.: Fusegan: Learning to fuse multi-focus image via conditional generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 21(8), 1982–1996 (2019)
Zhang, H., Le, Z., Shao, Z., Han, X., Ma, J.: Mff-gan: An unsupervised generative adversarial network with adaptive and gradient joint constraints for multi-focus image fusion. Information Fusion 66, 40–53 (2021)
Cheng, C., Xiao-Jun, W., Tianyang, X., Chen, G.: Unifusion: A lightweight unified image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–14 (2021)
Xiao, B., Bocheng, X., Bi, X., Li, W.: Global-feature encoding u-net (geu-net) for multi-focus image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 163–175 (2021)
Zhou Wang, A.C. Bovik, H.R. Sheikh, and E.P. Simoncelli. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 13(4):600–612, 2004
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollár, P., Zitnick, C.L.: Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 740–755. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Yi Wu, Jongwoo Lim, and Ming-Hsuan Yang. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2013
Nejati, M., Samavi, S., Shirani, S.: Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary-based sparse representation. Information Fusion 25, 72–84 (2015)
Xiao, B., Bocheng, X., Bi, X., Li, W.: Global-feature encoding u-net (geu-net) for multi-focus image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 163–175 (2021)
Xilai Li, Xiaosong Li, Haishu Tan, and Jinyang Li. Samf: Small-area-aware multi-focus image fusion for object detection. ArXiv, abs/2401.08357, 2024
Fusiondiff: Multi-focus image fusion using denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Expert Systems with Applications, 238:121664, 2024
Pingfan Yan Guihong, Q., Zhang, D.: Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 38, 3 (2002)
Qiang Wang, Yi Shen, and Jing Jin. 19 - performance evaluation of image fusion techniques. Image Fusion, pages 469–492, 2008
C.S. Xydeas and V. Petrovi. Objective image fusion performance measure. 2000
Costas, S.: Xydeas and Vladimir S. Petrovic. Objective pixel-level image fusion performance measure. In: Dasarathy, B.V. (ed.) Sensor Fusion: Architectures. Algorithms, and Applications IV, volume 4051, pp. 89–98. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE (2000)
G. Piella and H. Heijmans. A new quality metric for image fusion. In Proceedings 2003 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. No.03CH37429), volume 3, pages III–173, 2003
Yin Chen and Rick S. Blum. A new automated quality assessment algorithm for image fusion. Image and Vision Computing, 27(10):1421–1432, 2009. Special Section: Computer Vision Methods for Ambient Intelligence
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62202205,62306203), the National Social Science Foundation of China(21 & ZD166), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China(BK20221535), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP123030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shen, T., Li, H., Cheng, C., Shen, Z., Song, X. (2025). SMFuse: Two-Stage Structural Map Aware Network for Multi-focus Image Fusion. In: Antonacopoulos, A., Chaudhuri, S., Chellappa, R., Liu, CL., Bhattacharya, S., Pal, U. (eds) Pattern Recognition. ICPR 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15322. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78312-8_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78312-8_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-78311-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-78312-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)