Abstract
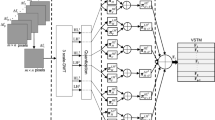
Video analysis is a major computer vision task that has received a lot of attention in recent years. The current state-of-the-art performance in video analysis is achieved with Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) that have a high energy cost and need large amounts of labeled data for training. Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) can have a significantly lower energy cost (thousands of times) than regular non-spiking networks when implemented on neuromorphic hardware [39, 40]. They have been used for video analysis with methods like 3D Convolutional Spiking Neural Networks (CSNNs). However, these networks have a significantly larger number of parameters than spiking 2D CSNNs. This not only increases their computational cost, but can also make them more difficult to implement on ultra-low power neuromorphic hardware. In this work, we use CSNNs trained in an unsupervised manner with the Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity (STDP) rule, and we introduce, for the first time, Spiking Separated Spatial and Temporal Convolutions (S3TCs). Using unsupervised STDP for feature learning reduces the amount of labeled data required for training. Factorizing a single spatio-temporal spiking convolution into a spatial and a temporal spiking convolution decreases the number of parameters of the network. We test our network with the KTH, Weizmann, and IXMAS datasets. Our results show that S3TCs successfully extract spatio-temporal information from videos and outperform spiking 3D convolutions, while preserving the output spiking activity, which usually decreases with deeper spiking networks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arunnehru, J., Chamundeeswari, G., Bharathi, S.P.: Human Action Recognition using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks with 3D Motion Cuboids in Surveillance Videos. Procedia Computer Science 133, 471–477 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.07.059
Babaiee, Z., Hasani, R.M., Lechner, M., Rus, D., Grosu, R.: On-Off Center-Surround Receptive Fields for Accurate and Robust Image Classification. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). pp. 1–21 (2021)
Baccouche, M., Mamalet, F., Wolf, C., Garcia, C., Baskurt, A.: Sequential Deep Learning for Human Action Recognition. In: International Workshop on Human Behavior Understanding (HBU). pp. 29–39 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25446-8_4
Belmonte, R., Ihaddadene, N., Tirilly, P., Bilasco, I.M., Djeraba, C.: Video-Based Face Alignment With Local Motion Modeling. In: Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). pp. 2106–2115 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2019.00228
Burkitt, A.: A Review of the Integrate-and-fire Neuron Model: I. Homogeneous Synaptic Input. Biological Cybernetics 95, 1–19 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-006-0068-6
Chakraborty, B., Holte, M., Moeslund, T., Gonzàlez, J., Roca, X.: A Selective Spatio-temporal Interest Point Detector for Human Action Recognition in Complex Scenes. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). pp. 1776–1783 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126443
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology 2, 27:1–27:27 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1145/1961189.1961199, software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm
Chen, J., Lu, Z., Liao, Q.: XSepConv: Extremely Separated Convolution for Efficient Deep Networks with Large Kernels. In: International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP). vol. 11878 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2601043
Cheni, Q., Rueckauer, B., Li, L., Delbruck, T., Liu, S.C.: Reducing Latency in a Converted Spiking Video Segmentation Network. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS51556.2021.9401667
Chollet, F.: Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In: International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp. 1251–1258 (2017)
Dampfhoffer, M., Mesquida, T., Valentian, A., Anghel, L.: Backpropagation-Based Learning Techniques for Deep Spiking Neural Networks: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems pp. 1–16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3263008
Davies, M., Srinivasa, N., Lin, T.H., Chinya, G., Cao, Y., Choday, S.H., Dimou, G., Joshi, P., Imam, N., Jain, S., Liao, Y., Lin, C.K., Lines, A., Liu, R., Mathaikutty, D., McCoy, S., Paul, A., Tse, J., Venkataramanan, G., Weng, Y.H., Wild, A., Yang, Y., Wang, H.: Loihi: A Neuromorphic Manycore Processor with On-Chip Learning. IEEE Micro 38(1), 82–99 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/MM.2018.112130359
Deng, L., Wang, G., Li, G., Li, S., Liang, L., Zhu, M., Wu, Y., Yang, Z., Zou, Z., Pei, J., Wu, Z., Hu, X., Ding, Y., He, W., Xie, Y., Shi, L.: Tianjic: A Unified and Scalable Chip Bridging Spike-Based and Continuous Neural Computation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 55(8), 2228–2246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2020.2970709
El-Assal, M., Tirilly, P., Bilasco, I.M.: A Study On the Effects of Pre-processing On Spatio-temporal Action Recognition Using Spiking Neural Networks Trained with STDP. In: International Workshop on Content-based Multimedia Indexing (CBMI) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CBMI50038.2021.9461922
El-Assal, M., Tirilly, P., Bilasco, I.M.: 2D versus 3D Convolutional Spiking Neural Networks Trained with Unsupervised STDP for Human Action Recognition. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN55064.2022.9892063
Falez, P.: Improving Spiking Neural Networks Trained with Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity for Image Recognition. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lille (2019), https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-02429539
Falez, P., Tirilly, P., Bilasco, I.M., Devienne, P., Boulet, P.: Mastering the Output Frequency in Spiking Neural Networks. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2018.8489410
Falez, P., Tirilly, P., Marius Bilasco, I., Devienne, P., Boulet, P.: Multi-layered Spiking Neural Network with Target Timestamp Threshold Adaptation and STDP. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2019.8852346
Fang, W., Yu, Z., Chen, Y., Huang, T., Masquelier, T., Tian, Y.: Deep Residual Learning in Spiking Neural Networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). vol. 34, pp. 21056–21069 (2021)
Feichtenhofer, C.: X3D: Expanding Architectures for Efficient Video Recognition. In: International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2020)
Feichtenhofer, C., Fan, H., Malik, J., He, K.: SlowFast Networks for Video Recognition. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00630
Furber, S.B., Galluppi, F., Temple, S., Plana, L.A.: The SpiNNaker Project. Proc. IEEE 102(5), 652–665 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2014.2304638
Gao, B., Zhou, Y., Zhang, Q., Zhang, S., Yao, P., Xi, Y., Liu, Q., Zhao, M., Zhang, W., Liu, Z., Li, X., Tang, J., Qian, H., Wu, H.: Memristor-based analogue computing for brain-inspired sound localization with in situ training. Nature Communications 13, 2026 (04 2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29712-8
Gorelick, L., Blank, M., Shechtman, E., Irani, M., Basri, R.: Actions as Space-Time Shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(12), 2247–2253 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2005.28
Hara, K., Kataoka, H., Satoh, Y.: Can Spatiotemporal 3D CNNs Retrace the History of 2D CNNs and ImageNet? CoRR abs/1711.09577 (2017), http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.09577
Howard, A., Sandler, M., Chen, B., Wang, W., Chen, L.C., Tan, M., Chu, G., Vasudevan, V., Zhu, Y., Pang, R., Adam, H., Le, Q.: Searching for MobileNetV3. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). pp. 1314–1324 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00140
Howard, A.G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D., Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., Adam, H.: MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. CoRR abs/1704.04861 (2017), http://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., Yu, K.: 3D Convolutional Neural Networks for Human Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(1), 221–231 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59
Lacoste, A., Luccioni, A., Schmidt, V., Dandres, T.: Quantifying the Carbon Emissions of Machine Learning. CoRR abs/1910.09700 (2019), http://arxiv.org/abs/1910.09700
Lee, C., Panda, P., Srinivasan, G., Roy, K.: Training Deep Spiking Convolutional Neural Networks With STDP-Based Unsupervised Pre-training Followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning. Frontiers in Neuroscience 12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00435
Merolla, P.A., Arthur, J.V., Alvarez-Icaza, R., Cassidy, A.S., Sawada, J., Akopyan, F., Jackson, B.L., Imam, N., Guo, C., Nakamura, Y., Brezzo, B., Vo, I., Esser, S.K., Appuswamy, R., Taba, B., Amir, A., Flickner, M.D., Risk, W.P., Manohar, R., Modha, D.S.: A Million Spiking-Neuron Integrated Circuit with a Scalable Communication Network and Interface. Science 345(6197), 668–673 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254642
Pehle, C., Billaudelle, S., Cramer, B., Kaiser, J., Schreiber, K., Stradmann, Y., Weis, J., Leibfried, A., Müller, E., Schemmel, J.: The BrainScaleS-2 Accelerated Neuromorphic System With Hybrid Plasticity. Frontiers in Neuroscience 16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.795876
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp. 4510–4520 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00474
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., Caputo, B.: Recognizing Human Actions: A Local SVM Approach. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). p. 32–36 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2004.1334462
Schuman, C.D., Potok, T.E., Patton, R.M., Birdwell, J.D., Dean, M.E., Rose, G.S., Plank, J.S.: A Survey of Neuromorphic Computing and Neural Networks in Hardware. CoRR abs/1705.06963 (2017), http://arxiv.org/abs/1705.06963
Serrano-Gotarredona, T., Masquelier, T., Prodromakis, T., Indiveri, G., Linares-Barranco, B.: STDP and STDP Variations with Memristors for Spiking Neuromorphic Learning Systems. Frontiers in Neuroscience 7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00002
Singha, A., Muralidharan, B., Rajendran, B.: Analog Memristive Time Dependent Learning Using Discrete Nanoscale RRAM Devices. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). pp. 2248–2255 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2014.6889915
Strubell, E., Ganesh, A., McCallum, A.: Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP. In: Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL). pp. 3645–3650 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P19-1355
Sun, Y., Zeng, Y., Li, Y.: Solving the Spike Feature Information Vanishing Problem in Spiking Deep Q Network With Potential Based Normalization. Frontiers in Neuroscience 16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.953368
Tavanaei, A., Ghodrati, M., Kheradpisheh, S.R., Masquelier, T., Maida, A.: Deep Learning in Spiking Neural Networks. Neural Netw. 111, 47–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.12.002
Tran, D., Wang, H., Torresani, L., Ray, J., LeCun, Y., Paluri, M.: A Closer Look at Spatiotemporal Convolutions for Action Recognition. In: International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp. 6450–6459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00675
Tran, D., Bourdev, L.D., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning Spatiotemporal Features With 3D Convolutional Networks. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.510
Weinland, D., Ronfard, R., Boyer, E.: Free viewpoint Action Recognition Using Motion History Volumes. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 104(2–3), 249–257 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2006.07.013
Zhang, J., Wang, J., Di, X., Pu, S.: High-Accuracy and Energy-Efficient Action Recognition with Deep Spiking Neural Network. In: International Conference on Neural Information Processing (ICONIP). pp. 279–292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30108-7_24
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by IRCICA (USR 3380) under the bio-inspired project, and funded by Région Hauts-de-France. Experiments presented in this paper were carried out using the Grid’5000 testbed, supported by a scientific interest group hosted by Inria and including CNRS, RENATER and several Universities as well as other organizations (see https://www.grid5000.fr).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
El-Assal, M., Tirilly, P., Bilasco, I.M. (2025). S3TC: Spiking Separated Spatial and Temporal Convolutions with Unsupervised STDP-Based Learning for Action Recognition. In: Antonacopoulos, A., Chaudhuri, S., Chellappa, R., Liu, CL., Bhattacharya, S., Pal, U. (eds) Pattern Recognition. ICPR 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15326. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78395-1_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78395-1_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-78394-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-78395-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)