Abstract
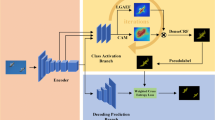
Semi-supervised semantic segmentation leverages both labeled and unlabeled images to accomplish pixel-wise classification task. Within this field, the weak-to-strong consistency regularization has been widely popularized and has become a standard approach. However, unidirectional regularization often leads to the ignorance of correct but filtered predictions and brings the noise of wrong but confident predictions. To address these inherent flaws, we fully leverage Cross-Augmentation Consensus and Conflict (CACC), including Augmentation Feedback Mechanism (AFM) and Category Threshold Controller (CTC). AFM aims to mitigate the influence of incorrect predictions with high-confidence and mine unconfident but accurate predictions by re-weighting the pixel-wise pseudo supervision and applying supplementary regularization. Concurrently, CTC adopts category-specific thresholds by considering the model’s overall performance and the varying category-specific learning difficulty. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our method, showcasing its effectiveness in improving semi-supervised semantic segmentation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The standard deviation will be provided in Sec. A in the supplementary material.
References
Chen, L.C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: ECCV. pp. 801–818 (2018)
Cordts, M., Omran, M., Ramos, S., Rehfeld, T., Enzweiler, M., Benenson, R., Franke, U., Roth, S., Schiele, B.: The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: CVPR. pp. 3213–3223 (2016)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR. pp. 248–255. Ieee (2009)
Ding, C., Zhang, J., Ding, H., Zhao, H., Wang, Z., Xing, T., Hu, R.: Decoupling with entropy-based equalization for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: IJCAI. pp. 663–671 (2023)
Everingham, M., Eslami, S.A., Van Gool, L., Williams, C.K., Winn, J., Zisserman: The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. IJCV pp. 98–136 (2015)
Fan, S., Zhu, F., Feng, Z., Lv, Y., Song, M., Wang, F.Y.: Conservative-progressive collaborative learning for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. TIP (2023)
Hariharan, B., Arbeláez, P., Bourdev, L., Maji, S., Malik, J.: Semantic contours from inverse detectors. In: ICCV. pp. 991–998. IEEE (2011)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR. pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hu, H., Wei, F., Hu, H., Ye, Q., Cui, J., Wang, L.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation via adaptive equalization learning. NeurIPS 34, 22106–22118 (2021)
Jin, Y., Wang, J., Lin, D.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation via gentle teaching assistant. NeurIPS 35, 2803–2816 (2022)
Lee, D.H., et al.: Pseudo-label: The simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: ICML. vol. 3, p. 896. Atlanta (2013)
Li, J., Dai, H., Han, H., Ding, Y.: Mseg3d: Multi-modal 3d semantic segmentation for autonomous driving. In: CVPR. pp. 21694–21704 (2023)
Li, S., He, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, W., Tan, X., Han, J., Ding, E., Wang, J.: Cfcg: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation via cross-fusion and contour guidance supervision. In: ICCV. pp. 16348–16358 (2023)
Liu, S., Zhi, S., Johns, E., Davison, A.: Bootstrapping semantic segmentation with regional contrast. In: ICLR (2021)
Liu, Y., Tian, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, F., Belagiannis, V., Carneiro, G.: Perturbed and strict mean teachers for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: CVPR. pp. 4258–4267 (2022)
Lv, X., Persello, C., Huang, X., Ming, D., Stein, A.: Deepmerge: Deep learning-based region-merging for image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.19787 (2023)
Ma, J., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Lin, L., Li, G.: Enhanced soft label for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: ICCV. pp. 1185–1195 (2023)
Oliver, A., Odena, A., Raffel, C.A., Cubuk, E.D., Goodfellow, I.: Realistic evaluation of deep semi-supervised learning algorithms. NeurIPS 31 (2018)
Pan, W., Xu, Z., Yan, J., Wu, Z., Tong, R.K.y., Li, X., Yao, J.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation meets masked modeling: Fine-grained locality learning matters in consistency regularization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.08631 (2023)
Sohn, K., Berthelot, D., Carlini, N., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Raffel, C.A., Cubuk, E.D., Kurakin, A., Li, C.L.: Fixmatch: Simplifying semi-supervised learning with consistency and confidence. NeurIPS 33, 596–608 (2020)
Sun, B., Yang, Y., Zhang, L., Cheng, M.M., Hou, Q.: Corrmatch: Label propagation via correlation matching for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.04300 (2023)
Wang, C., Xie, H., Yuan, Y., Fu, C., Yue, X.: Space engage: Collaborative space supervision for contrastive-based semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: ICCV. pp. 931–942 (2023)
Wang, H., Li, X.: Dhc: Dual-debiased heterogeneous co-training framework for class-imbalanced semi-supervised medical image segmentation. In: MICCAI. pp. 582–591 (2023)
Wang, X., Zhang, B., Yu, L., Xiao, J.: Hunting sparsity: Density-guided contrastive learning for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: CVPR. pp. 3114–3123 (2023)
Wang, Y., Wang, H., Shen, Y., Fei, J., Li, W., Jin, G., Wu, L., Zhao, R., Le, X.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation using unreliable pseudo-labels. In: CVPR. pp. 4248–4257 (2022)
Wang, Z., Zhao, Z., Xing, X., Xu, D., Kong, X., Zhou, L.: Conflict-based cross-view consistency for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: CVPR. pp. 19585–19595 (2023)
Xie, H., Wang, C., Zheng, M., Dong, M., You, S., Fu, C., Xu, C.: Boosting semi-supervised semantic segmentation with probabilistic representations. In: AAAI. pp. 2938–2946 (2023)
Xu, H., Liu, L., Bian, Q., Yang, Z.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with prototype-based consistency regularization. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 26007–26020 (2022)
Yang, L., Qi, L., Feng, L., Zhang, W., Shi, Y.: Revisiting weak-to-strong consistency in semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: CVPR. pp. 7236–7246 (2023)
Yuan, J., Ge, J., Wang, Z., Liu, Y.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with mutual knowledge distillation. In: ACMMM. pp. 5436–5444 (2023)
Yun, S., Han, D., Oh, S.J., Chun, S., Choe, J., Yoo, Y.: Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In: ICCV. pp. 6023–6032 (2019)
Zhao, Z., Long, S., Pi, J., Wang, J., Zhou, L.: Instance-specific and model-adaptive supervision for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: CVPR. pp. 23705–23714 (2023)
Zhao, Z., Yang, L., Long, S., Pi, J., Zhou, L., Wang, J.: Augmentation matters: A simple-yet-effective approach to semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In: CVPR. pp. 11350–11359 (2023)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China Under Grant No. 2024A1515011741, and partly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 62376292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cao, J., Chen, J., Huang, S., Zhang, D. (2025). Leveraging Cross-Augmentation Consensus and Conflict for Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation. In: Antonacopoulos, A., Chaudhuri, S., Chellappa, R., Liu, CL., Bhattacharya, S., Pal, U. (eds) Pattern Recognition. ICPR 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15327. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78398-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78398-2_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-78397-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-78398-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)