Abstract
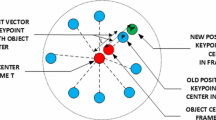
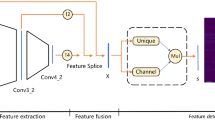
Point tracking can be regarded as a transfer and extension of keypoints representation and matching. In contrast to matching the salient points like corners or spots, which are easily detected and described by detector-based approaches, point tracking tasks are capable of handling arbitrary points on physical surfaces, including nonrigid or weakly-textured surfaces. Additionally, keypoint matching lacks a direct mechanism to handle occlusion in tracking tasks. Therefore, we propose to use a detector-free local feature-matching model based on the transformer structure to perform patch matching, incorporating occlusion prediction and introducing an uncertainty estimate for extended robustness. Besides, using a coarse-to-fine strategy, we generate coarse predictions at the patch level and refine them to obtain accurate coordinates at the sub-pixel level by motion-driven point association. After fine-tuning the model on the training set of the Perception Test benchmark, our model APM-MPAPT outperforms the competitors in the benchmark on the corresponding validation set, with promising performance improvement against the baseline.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, J., Shen, Z., Wang, Y., Bao, H., Zhou, X.: LoFTR: detector-free local feature matching with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8922–8931 (2021)
Doersch, C., et al.: Tapir: tracking any point with per-frame initialization and temporal refinement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10061–10072 (2023)
Patraucean, Vet al.: Perception test: a diagnostic benchmark for multimodal video models. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 36 (2024)
Ma, J., Jiang, X., Fan, A., Jiang, J., Yan, J.: Image matching from handcrafted to deep features: a survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 129(1), 23–79 (2021)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60, 91–110 (2004)
Bay, H., Tuytelaars, T., Van Gool, L.: Surf: speeded up robust features. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2006: 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, May 7-13, 2006. Proceedings, Part I 9, pp. 404–417. Springer (2006)
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K., Bradski, G.: ORB: an efficient alternative to sift or surf. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2564–2571. IEEE (2011)
Yi, K.M., Trulls, E., Lepetit, V., Fua, P.: Lift: learned invariant feature transform. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part VI 14, pp. 467–483. Springer (2016)
DeTone, D., Malisiewicz, T., Rabinovich, A.: Superpoint: self-supervised interest point detection and description. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 224–236 (2018)
Manuelli, L., Li, Y., Florence, P., Tedrake, R.: Keypoints into the future: self-supervised correspondence in model-based reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.05085 (2020)
Choy, C.B., Gwak, J., Savarese, S., Chandraker, M.: Universal correspondence network. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 29 (2016)
Rocco, I., Cimpoi, M., Arandjelović, R., Torii, A., Pajdla, T., Sivic, J.: Neighbourhood consensus networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 31 (2018)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Jiang, W., Trulls, E., Hosang, J., Tagliasacchi, A., Yi, K.M.: COTR: correspondence transformer for matching across images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6207–6217 (2021)
Yu, J., Chang, J., He, J., Zhang, T., Yu, J., Wu, F.: Adaptive spot-guided transformer for consistent local feature matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 21898–21908 (2023)
Huang, D., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, J., Xu, S., Wu, W., Ding, Y., Tang, F., Wang, C.: Adaptive assignment for geometry aware local feature matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5425–5434 (2023)
Zhu, X.F., Xu, T., Wu, X.J., Kittler, J.: Feature enhancement and coarse-to-fine detection for RGB-D tracking. Pattern Recogn. Lett. (2024)
Xu, T., Kang, Z., Zhu, X., Wu, X.J.: Learning adaptive spatio-temporal inference transformer for coarse-to-fine animal visual tracking: algorithm and benchmark. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1–15 (2024)
Li, Z., Snavely, N.: MegaDepth: learning single-view depth prediction from internet photos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2041–2050 (2018)
Doersch, C., et al.: Tap-vid: a benchmark for tracking any point in a video. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 13610–13626 (2022)
Harley, A.W., Fang, Z., Fragkiadaki, K.: Particle video revisited: tracking through occlusions using point trajectories. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 59–75. Springer (2022)
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Han, D., Ye, T., Han, Y., Xia, Z., Song, S., Huang, G.: Agent attention: on the integration of softmax and linear attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.08874 (2023)
Lin, T.Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollár, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2980–2988 (2017)
Greff, K., et al.: Kubric: a scalable dataset generator. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3749–3761 (2022)
Sarlin, P.E., DeTone, D., Malisiewicz, T., Rabinovich, A.: Superglue: learning feature matching with graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4938–4947 (2020)
Lindenberger, P., Sarlin, P.E., Pollefeys, M.: Lightglue: local feature matching at light speed. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 17627–17638 (2023)
Xu, T., Wu, X.J., Kittler, J.: Non-negative subspace representation learning scheme for correlation filter based tracking. In: 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 1888–1893. IEEE (2018)
Fan, H., et al.: Visdrone-sot2020: the vision meets drone single object tracking challenge results. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020 Workshops: Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part IV 16, pp. 728–749. Springer, Cham (2020)
Wen, J., Chu, H., Lai, Z., Xu, T., Shen, L.: Enhanced robust spatial feature selection and correlation filter learning for UAV tracking. Neural Netw. 161, 39–54 (2023)
Xu, T., Zhu, X.F., Wu, X.J.: Learning spatio-temporal discriminative model for affine subspace based visual object tracking. Vis. Intell. 1(1), 4 (2023)
Zhao, J., et al.: The 3rd anti-UAV workshop & challenge: methods and results. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.07290 (2023)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFE0116300). This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62106089, 62336004, 62020106012, 62332008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zang, H., Xu, T., Zhu, XF., Song, X., Wu, XJ., Kittler, J. (2025). Attention-Based Patch Matching and Motion-Driven Point Association for Accurate Point Tracking. In: Antonacopoulos, A., Chaudhuri, S., Chellappa, R., Liu, CL., Bhattacharya, S., Pal, U. (eds) Pattern Recognition. ICPR 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15316. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78444-6_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-78444-6_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-78443-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-78444-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)