Abstract
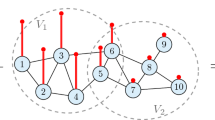
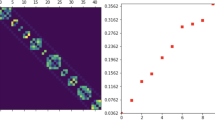
Partition of unity methods (PUMs) on graphs represent straightforward and remarkably adaptable auxiliary techniques for graph signal processing. By relying solely on the intrinsic graph structure, we propose the generation of a partition of unity through centrality measures and modularity. Subsequently, we integrate PUMs with a local graph basis function (GBF) approximation approach to achieve low-cost global interpolation schemes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavoretto, R., De Rossi, A.: Error indicators and refinement strategies for solving Poisson problems through a RBF partition of unity collocation scheme. Appl. Math. Comput. 369, 124824 (2020)
Cavoretto, R., De Rossi, A., Erb, W.: GBFPUM - A MATLAB package for partition of unity based signal interpolation and approximation on graphs. Dolomites Res. Notes Approx. 15, 25–34 (2022)
Cavoretto, R., De Rossi, A., Erb, W.: Partition of Unity Methods for Signal Processing on Graphs. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 27, Art. 66 (2021)
Erb, W.: Graph signal interpolation with positive definite graph basis functions. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 60, 368–395 (2022)
Erb, W.: Semi-Supervised Learning on Graphs with Feature-Augmented Graph Basis Functions. arXiv:2003.07646 (2020)
Fasshauer, G.E., McCourt, M.J.: Kernel-based Approximation Methods Using MATLAB, p. 536. World Scientific, Singapore (2015)
Newman, M.: Networks: An Introduction. OUP Oxford, p. 784 (2010)
Ortega, A., Frossard, P., Kovačević, J., Moura, J.M.F., Vandergheynst, P.: Graph signal processing: overview, challenges, and applications. Proc. IEEE 106(5), 808–828 (2018)
Pesenson, I.Z.: Variational splines and Paley-Wiener spaces on combinatorial graphs. Constr. Approx. 29(1), 1–21 (2009)
Rossi, R.A., Ahmed, N.K.: The Network Data Repository with Interactive Graph Analytics and Visualization. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2015). http://networkrepository.com
Schaback, R., Wendland, H.: Approximation by positive definite kernels. In: Advanced Problems in Constructive Approximation, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, pp. 203–222 (2003)
Shin, H., Park, J., Kang, D.: A graph-cut-based approach to community detection in networks. Appl. Sci. 12, 6218 (2022)
Stanković, L., Daković, L., Sejdić, E.: Introduction to graph signal processing, pp. 3–108. Springer, In Vertex-Frequency Analysis of Graph Signals (2019)
Ward, J.P., Narcowich, F.J., Ward, J.L.: Interpolating splines on graphs for data science applications. Appl. Comput. Harm. Anal. 49(2), 540–557 (2020)
Wendland, H.: Scattered Data Approximation, p. 336. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2005)
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank the reviewers for the careful reading and valuable comments on the paper. This research has been accomplished within the RITA “Research ITalian network on Approximation” and the UMI Group TAA“Approximation Theory and Applications”. This work has been supported by the INdAM–GNCS 2022 Project “Computational methods for kernel-based approximation and its applications”, code CUP\(\_\)E55F22000270001, and by the Spoke “FutureHPC & BigData” of the ICSC - National Research Center in"High-Performance Computing, Big Data and Quantum Computing", funded by European Union - NextGenerationEU. Moreover, the work has been supported by the Fondazione CRT, project 2022 “Modelli matematici e algoritmi predittivi di intelligenza artificiale per la mobilit\(\grave{\text {a}}\) sostenibile”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
De Rossi, A., Lancellotti, S., Romaniello, F. (2025). Node-Binded Communities for Interpolation on Graphs. In: Sergeyev, Y.D., Kvasov, D.E., Astorino, A. (eds) Numerical Computations: Theory and Algorithms. NUMTA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14477. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-81244-6_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-81244-6_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-81243-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-81244-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)