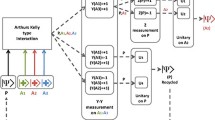
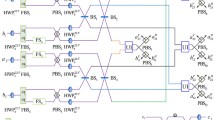
Abstract
Entanglement is a very useful phenomenon for quantum information processes. When more than one degree of freedom (DOF) is entangled, the hyperentanglement is realized. The main advantage of hyperentanglement is that of being able to encode a greater amount of information by exploiting the quantum coherence. This advantage is due to the fact that it is possible to extract information for each DOF. We propose to model a hyperentangled state through copies of a Bell state and evaluate its functionality transferring a quantum state through a classical channel. The goal is to simulate the transport of a hyperentangled state through a classical channel in the presence of a system-environment interaction. By virtue of an increased Hilbert space following the increase in the DOF, the entanglement quantifier, the so called concurrence, decays slower with the distance compared to the case of one DOF.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbieri, M., Vallone, G., Mataloni, P., De Martini, F.: Complete and deterministic discrimination of polarization bell states assisted by momentum entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 75(4), 042317 (2007)
Barbieri, M., Cinelli, C., Mataloni, P., De Martini, F.: Polarization-momentum hyperentangled states: realization and characterization. Phys. Rev. A 72(5), 052110 (2005)
Barreiro, J.T., Langford, N.K., Peters, N.A., Kwiat, P.G.: Generation of hyperentangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(26), 260501 (2005)
Barreiro, J.T., Wei, T.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Beating the channel capacity limit for linear photonic superdense coding. Nat. Phys. 4(4), 282–286 (2008)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: C. cr epeau, r. jozsa, a. peres and wk wootters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the einstein-podolsky-rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042317 (2003)
Eberly, J.H., Narozhny, N., Sanchez-Mondragon, J.: Periodic spontaneous collapse and revival in a simple quantum model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 44(20), 1323 (1980)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661 (1991)
Hillery, M., Bužek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59(3), 1829 (1999)
Hu, B.L., Zhan, Y.B.: Generation of hyperentangled states between remote noninteracting atomic ions. Phys. Rev. A 82(5), 054301 (2010)
Jaynes, E.T., Cummings, F.W.: Comparison of quantum and semiclassical radiation theories with application to the beam maser. Proc. IEEE 51(1), 89–109 (1963)
Karlsson, A., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting. Phys. Rev. A 59(1), 162 (1999)
Kwiat, P.G., Weinfurter, H.: Embedded bell-state analysis. Phys. Rev. A 58(4), R2623 (1998)
Li, X.H.: Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044304 (2010)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge University Press (2010)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement purification and concentration assisted by diamond nv centers inside photonic crystal cavities. Laser Phys. Lett. 10(11), 115201 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 88(1), 012302 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Wei, H.R., Hua, M., Li, T., Deng, F.G.: Complete hyperentangled-bell-state analysis for photon systems assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Opt. Express 20(22), 24664–24677 (2012)
Salatino, L., Mariani, L., Attanasio, C., Pagano, S., Citro, R.: Dissipative dynamics in quantum key distribution. European Phys. J. Plus 138(6), 517 (2023)
Schuck, C., Huber, G., Kurtsiefer, C., Weinfurter, H.: Complete deterministic linear optics bell state analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(19), 190501 (2006)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 81(3), 032307 (2010)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: One-step deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044305 (2010)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Complete hyperentangled-bell-state analysis for quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A 82(3), 032318 (2010)
Sheng, Y.-B., Guo, R., Pan, J., Zhou, L., Wang, X.-F.: Two-step measurement of the concurrence for hyperentangled state. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(3), 963–978 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-015-0916-1
Simon, C., Pan, J.W.: Polarization entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89(25), 257901 (2002)
Vallone, G., Ceccarelli, R., De Martini, F., Mataloni, P.: Hyperentanglement of two photons in three degrees of freedom. Phys. Rev. A 79(3), 030301 (2009)
Walborn, S., Pádua, S., Monken, C.: Hyperentanglement-assisted bell-state analysis. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042313 (2003)
Wang, T.J., Lu, Y., Long, G.L.: Generation and complete analysis of the hyperentangled bell state for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 86(4), 042337 (2012)
Wei, T.C., Barreiro, J.T., Kwiat, P.G.: Hyperentangled bell-state analysis. Phys. Rev. A 75(6), 060305 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Salatino, L., Mariani, L., Attanasio, C., Pagano, S., Citro, R. (2025). Modelling Hyperentanglement for Quantum Information Processes. In: Sergeyev, Y.D., Kvasov, D.E., Astorino, A. (eds) Numerical Computations: Theory and Algorithms. NUMTA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14478. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-81247-7_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-81247-7_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-81246-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-81247-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)