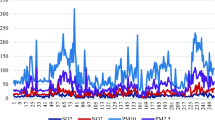
Abstract
Estimation of Particulate Matter concentration (PM1, PM2.5 and PM10) from aerosol product derived from satellite images and meteorological parameters brings a great advantage in air pollution monitoring since observation range is no longer limited around ground stations and estimation accuracy will be increased significantly. In this article, we investigate the application of Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) and Support Vector Regression (SVR) to make empirical data models for PM1/2.5/10 estimation from satellite- and ground-based data. Experiments, which are carried out on data recorded in two year over Hanoi - Vietnam, not only indicate a case study of regional modeling but also present comparison of performance between a widely used technique (MLR) and an advanced method (SVR).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Global Climate Observing System Essential Climate Variables, http://gosic.org/ios/MATRICESECVECV-matrix.htm
Balaguer, N.C.: Combining models and monitoring. A survey to elicit expert opinion on the spatial representativeness of ground based monitoring data. Fairmode activity for WG2-SG1 (2012)
Kaufman, Y.J., Tanre, D.: Algorithm for remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol from modis. In: MODIS ATBD (1997)
Remer, L.A., Tanré, D., Kaufman, Y.J.: Algorithmfor remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol from MODIS: Collection 5. In: MODIS ATBD (2004)
Nguyen, T., Mantovani, S., Bottoni, M.: Estimation of Aerosol and Air Quality Fields with PMMAPPER, An Optical Multispectral Data Processing Package. In: ISPRS TC VII Symposium 100 Years ISPRS-Advancing Remote Sensing Science, vol. XXXVIII(7A), pp. 257–261 (2010)
Campalani, P., Nguyen, T.N.T., Mantovani, S., Bottoni, M., Mazzini, G.: Validation of PM MAPPER aerosol optical thickness retrievals at 1x1 km2 of spatial resolution. In: The 19th International Conference on Proceeding of Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), pp. 1–5 (2011)
Chu, D.A., Kaufman, Y.J., Zibordi, G., Chern, J.D., Mao, J., Li, C., Holben, B.N.: Global monitoring of air pollution over land from the Earth Observing System-Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres 108(D21), 4661 (2003)
Wang, J., Chirstopher, S.A.: Intercomparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2.5 mass: Implication for air quality studies. Geophysical Research Letter 30(21), 2095 (2003)
Engel-Cox, J.A., Holloman, C.H., Coutant, B.W., Hoff, R.M.: Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of MODIS satellite sensor data for regional and urban scale air quality. Atmospheric Environment 38, 2495–2509 (2004)
Kacenelenbogen, M., Leon, J.F., Chiapello, I., Tanre, D.: Characterization of aerosol pollution events in France using ground-based and POLDER-2 satellite data. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 6, 4843–4849 (2006)
Pelletier, B., Santer, R., Vidot, J.: Retrieving of particulate matter from optical measurements: A semiparametric approach. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 112(D6208) (2007)
Schaap, M., Apituley, A., Timmermans, R.M.A., Koelemeijer, R.B.A., Leeuw, G.D.: Exploring the relation between aerosol optical depth and PM2.5 at Cabauw, the Netherlands. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 9, 909–925 (2009)
Gupta, P., Christopher, S.A., Wang, J., Gehrig, R., Lee, Y., Kumar, N.: Satellite remote sensing of particulate matter and air quality assessment over global cities. Atmospheric Environment 40, 5880–5892 (2006)
Gupta, P., Christopher, S.A.: Seven year particulate matter air quality assessment from surface and satellite measurements. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 8, 3311–3324 (2008)
Gupta, P., Christopher, S.A.: Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: Multiple regression approach. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 114(D14205) (2009)
Gupta, P., Christopher, S.A.: Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: A neural network approach. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 114(D20205) (2009)
Zha, Y., Gao, J., Jiang, J., Lu, H., Huang, J.: Monitoring of urban air pollution from MODIS aerosol data: effect of meteorological parameters. Tellus B 62(2), 109–116 (2010)
Lee, H.J., Liu, Y., Coull, B.A., Schwartz, J., Koutrakis, P.: A novel calibration ap-proach of MODIS AOD data to predict PM2.5 concentrations. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 11, 7991–8002 (2011)
Yap, X.Q., Hashim, M.: A robust calibration approach for PM10 prediction from MODIS aerosol optical depth. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 13, 3517–3526 (2013)
Yahi, H., Santer, R., Weill, A., Crepon, M., Thiria, S.: Exploratory study for estimating atmospheric low level particle pollution based on vertical integrated optical measurements. Atmospheric Environment 45, 3891–3902 (2011)
Hirtl, M., Mantovani, S., Krger, B.C., Triebnig, G., Flandorfer, C.: AQA-PM: Extension of the Air-Quality model for Austria with satellite based Particulate Matter estimates. In: European Geosciences Union, General Assembly 2013, Austria (2013)
Ichoku, C., Chu, D.A., Mattoo, S., Kaufiman, Y.J.: A spatio-temporal approach for global validation and analysis of MODIS aerosol products. Geophysical Research Letter 29(12), 1616 (2002)
Vapnik, V.: The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, Berlin (1995)
Chang, C., Lin, C.: LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nguyen, T.N.T., Ta, V.C., Le, T.H., Mantovani, S. (2014). Particulate Matter Concentration Estimation from Satellite Aerosol and Meteorological Parameters: Data-Driven Approaches. In: Huynh, V., Denoeux, T., Tran, D., Le, A., Pham, S. (eds) Knowledge and Systems Engineering. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 244. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02741-8_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02741-8_30
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-02740-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-02741-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)