Abstract
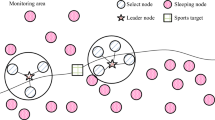
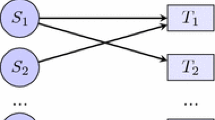
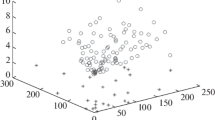
In this paper, we introduce an interesting “World Expo problem”, which aims to identify and track multiple targets in a sensor network, and propose a solution to this problem based on the mixed integer programming. Compared with traditional tracking problem in the sensor network, the World Expo problem has following two features. Firstly, the target in the network is not limited to single individuals. It can also be a group composed of multiple individuals with same path in the network, which implies that multiple targets can share the same path and be detected by the same sensor at the same time. Moreover, both the size and the number of groups are unknown. Secondly, differing from traditional sensor networks, the sensor network in the World Expo problem usually is sparse. These two features increase the difficulty in identification and tracking. To solve the aforementioned problem, we analyze the solvability of this problem and come up with a mixed integer programming based algorithm. The simulation result shows that our method has good performances and is robust to errors in the data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han, M., Xu, W., Tao, H., Gong, Y.: An algorithm for multiple object trajectory tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 864–871 (2004)
Saisan, P., Medasani, S., Owechko, Y.: Multi-view classifier swarms for pedestrian detection and tracking. In: CVPR, pp. 18 (2005)
Ali, S., Shah, M.: Floor fields for tracking in high density crowd scenes. In: Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A. (eds.) ECCV 2008, Part II. LNCS, vol. 5303, pp. 1–14. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Leibe, B., Schindler, K., Cornelis, N., Van Gool, L.: Coupled object detection and tracking from static cameras and moving vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 30(10), 1683–1698 (2008)
Pellegrini, S., Ess, A., Schindler, K., van Gool, L.: You’ll never walk alone: Modeling social behavior for multi-target tracking. In: ICCV, pp. 261–268 (2009)
Eagle, N., Pentland, A.: Reality mining: Sensing complex social system. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing 10(4), 255–268 (2006)
Celikoglu, H.B., Cigizoglu, H.K.: Public transportation trip flow modeling with generalized regression neural networks. Advances in Engineering Software 38, 71–79 (2007)
Vinciarelli, A., Pantic, M., Bourlard, H., Pentland, A.: Social signal processing: State-of-the-art and future perspectives of an emerging domain. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Vancouver, Canada, pp. 1061–1070 (2008)
Cristani, M., Murino, V., Vinciarelli, A.: Socially intelligent surveillance and monitoring: Analysing social dimensions of physical space. In: Proceedings of International Workshop on Society Intelligent Surveillance and Monitoring, San Francisco, USA, pp. 51–58 (2010)
Pickard, G., Pan, W., et al.: Time-critical social mobilization. Science 334(6055), 509–512 (2011)
Olfati-Saber, R.: Distributed kalman filtering for sensor networks. In: 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 5492–5498 (2007)
Djuric, P., Vemula, M., Bugallo, M.: Target tracking by particle filtering in binary sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 56(6), 2229–2238 (2008)
Oh, S., Sastry, S.: Tracking on a graph. In: Fourth International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN), pp. 195–202 (2005)
De, D., Song, W.Z., Xu, M., Cook, D., Huo, X.: Real-time tracking of motion trajectories from anonymous binary sensing in smart environments. In: The 32nd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (2012)
Shrivastava, N., Madhow, R.M.U., Suri, S.: Target tracking with binary proximity sensors: fundamental limits, minimal descriptions, and algorithms. In: 4th International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, pp. 251–264 (2006)
Crespi, V., Cybenko, G., Jiang, G.: The theory of trackability with applications to sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN) 4(3), 16 (2008)
Shrivastava, N., Mudumbai, R., Madhow, U., Suri, S.: Target tracking with binary proximity sensors. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN) 5(4), 30 (2009)
Lazos, L., Poovendran, R., Ritcey, J.: Analytic evaluation of target detection in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN) 5(2), 18 (2009)
Arora, A., Ramnath, R., et al.: Exscal: elements of an extreme scale wireless sensor network. In: 11th IEEE International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time Computing Systems and Applications, pp. 102–108 (2005)
Arora, A., Dutta, P., et al.: A line in the sand: a wireless sensor network for target detection, classification, and tracking. Computer Networks 46(5), 605–634 (2004)
Singh, J., Madhow, U., Kumar, R., Suri, S., Cagley, R.: Tracking multiple targets using binary proximity sensors. In: 6th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, pp. 529–538 (2007)
Wang, C., Huo, X., Song, W.Z.: An integer programming approach for multiple-target trajectory identification with binary proximity sensors. Annals of Operations Research (2012) (submitted)
Busnel, Y., Querzoni, L., Baldoni, R., Bertier, M., Kermarrec, A.: Analysis of deterministic tracking of multiple objects using a binary sensor network. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN) 42(4), 8 (2011)
Cao, L.: In-depth behavior understanding and use: the behavior informatics approach. Information Sciences 180(17), 3067–3085 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, H., Luo, D., Huo, X., Yang, X. (2013). World Expo Problem and Its Mixed Integer Programming Based Solution. In: Cao, L., et al. Behavior and Social Computing. BSIC BSI 2013 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8178. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04048-6_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04048-6_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-04047-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-04048-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)