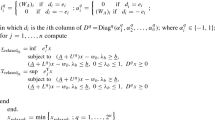Abstract
We consider a constraint programming problem described by a system of nonlinear equations and inequalities; the objective is to tightly enclose all solutions. First, we linearize the constraints to get an interval linear system of equations and inequalities. Then, we adapt techniques from interval linear programming to find a polyhedral relaxation to the solution set. The linearization depends on a selection of the relaxation center; we discuss various choices and give some recommendations. The overall procedure can be iterated and thus serves as a contractor.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Althaus, E., Becker, B., Dumitriu, D., Kupferschmid, S.: Integration of an LP solver into interval constraint propagation. In: Wang, W., Zhu, X., Du, D.-Z. (eds.) COCOA 2011. LNCS, vol. 6831, pp. 343–356. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Araya, I., Trombettoni, G., Neveu, B.: A contractor based on convex interval taylor. In: Beldiceanu, N., Jussien, N., Pinson, É. (eds.) CPAIOR 2012. LNCS, vol. 7298, pp. 1–16. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Baharev, A., Achterberg, T., Rév, E.: Computation of an extractive distillation column with affine arithmetic. AIChE J. 55(7), 1695–1704 (2009)
Beaumont, O.: Solving interval linear systems with linear programming techniques. Linear Algebra Appl. 281(1-3), 293–309 (1998)
Chen, L., Miné, A., Wang, J., Cousot, P.: Interval polyhedra: An abstract domain to infer interval linear relationships. In: Palsberg, J., Su, Z. (eds.) SAS 2009. LNCS, vol. 5673, pp. 309–325. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Collavizza, H., Delobel, F., Rueher, M.: Comparing partial consistencies. Reliab. Comput. 5(3), 213–228 (1999)
Fiedler, M., Nedoma, J., Ramík, J., Rohn, J., Zimmermann, K.: Linear optimization problems with inexact data. Springer, New York (2006)
Gerlach, W.: Zur Lösung linearer Ungleichungssysteme bei Störung der rechten Seite und der Koeffizientenmatrix. Math. Operationsforsch. Stat. Ser. Optimization 12, 41–43 (1981)
Goualard, F., Jermann, C.: A reinforcement learning approach to interval constraint propagation. Constraints 13(1), 206–226 (2008)
Granvilliers, L.: On the combination of interval constraint solvers. Reliab. Comput. 7(6), 467–483 (2001)
Hansen, E.R., Walster, G.W.: Global optimization using interval analysis, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York (2004)
Hladík, M.: Interval linear programming: A survey. In: Mann, Z.A. (ed.) Linear Programming - New Frontiers in Theory and Applications, ch. 2, pp. 85–120. Nova Science Publishers, New York (2012)
Hladík, M.: Weak and strong solvability of interval linear systems of equations and inequalities. Linear Algebra Appl. 438(11), 4156–4165 (2013)
Jansson, C.: Rigorous lower and upper bounds in linear programming. SIAM J. Optim. 14(3), 914–935 (2004)
Jaulin, L.: Reliable minimax parameter estimation. Reliab. Comput. 7(3), 231–246 (2001)
Jaulin, L., Kieffer, M., Didrit, O., Walter, É.: Applied interval analysis. With examples in parameter and state estimation, robust control and robotics. Springer, London (2001)
Kearfott, R.B.: Discussion and empirical comparisons of linear relaxations and alternate techniques in validated deterministic global optimization. Optim. Methods Softw. 21(5), 715–731 (2006)
Lebbah, Y., Lhomme, O.: Accelerating filtering techniques for numeric CSPs. Artif. Intell. 139(1), 109–132 (2002)
Lebbah, Y., Michel, C., Rueher, M.: An efficient and safe framework for solving optimization problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 199(2), 372–377 (2007)
Lebbah, Y., Michel, C., Rueher, M., Daney, D., Merlet, J.-P.: Efficient and safe global constraints for handling numerical constraint systems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42(5), 2076–2097 (2005)
Lin, Y., Stadtherr, M.A.: LP strategy for the interval-Newton method in deterministic global optimization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 43(14), 3741–3749 (2004)
Neumaier, A.: Interval methods for systems of equations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1990)
Neumaier, A., Shcherbina, O.: Safe bounds in linear and mixed-integer linear programming. Math. Program. 99(2), 283–296 (2004)
Oettli, W., Prager, W.: Compatibility of approximate solution of linear equations with given error bounds for coefficients and right-hand sides. Numer. Math. 6, 405–409 (1964)
Ratschan, S., She, Z.: Providing a basin of attraction to a target region of polynomial systems by computation of Lyapunov-like functions. SIAM J. Control Optim. 48(7), 4377–4394 (2010)
Trombettoni, G., Araya, I., Neveu, B., Chabert, G.: Inner regions and interval linearizations for global optimization. In: Burgard, W., Roth, D. (eds.) Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2011, San Francisco, California, USA. AAAI Press (2011)
Vu, X.-H., Sam-Haroud, D., Faltings, B.: Enhancing numerical constraint propagation using multiple inclusion representations. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 55(3-4), 295–354 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hladík, M., Horáček, J. (2014). Interval Linear Programming Techniques in Constraint Programming and Global Optimization. In: Ceberio, M., Kreinovich, V. (eds) Constraint Programming and Decision Making. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 539. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04280-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04280-0_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-04279-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-04280-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)