Abstract
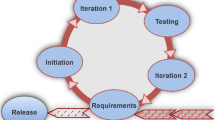
An agile business process development methodology is proposed in this research. An estimation formula is developed in order to assess the efficiency of the new methodology, to yield the required development effort for the traditional case that can be compared to the measured effort with the proposed methodology. Compared with the traditional development of processes, a savings of 27% was achieved. There are currently process development methodologies and limited adaptation work on agile approaches to process redesign. Such existing work do not define a specialized agile methodology for business process development. Existence of many actors renders this field as a complex one where specifying requirements is difficult. Agile approaches may contribute mainly to efficiently gathering desired requirements and may decrease the development time. Also the proposed methodology suggests a critical utilization of training that improves the gathering of quality requirements. Agile requirements gathering, periodic meetings, and incremental and iterative development are observed to be crucial constituents of the proposed methodology during the early studies for applying the methodology to a process in an organization.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Aalst, W.M.P., ter Hofstede, A.H.M., Weske, M.: Business Process Management: A Survey. In: BPM 2003. LNCS, vol. 2678, pp. 1–12. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Pressman, R.: Software Engineering A Practitioner’s Approach, 6th edn. McGraw Hill, New York (2005)
Agile Manifesto, http://agilemanifesto.org/principles.html (accessed January 12, 2012)
Lindstrom, L., Jeffries, R.: Extreme Programming and Agile Software Development Methodologies. Information Systems Management, 41–52 (2004) (summer)
Schwaber, K.: Agile Project Management with Scrum. Microsoft Press, Washington (2004)
Larson, S.: Applying Agile Software Development Methodologies to Business Process Redesign/Management (BPRM). In: Proceedings of the Southern Association for Information Systems Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, March 26-27 (2010)
Silva, A.R., Meziani, R., Magalhães, R., Martinho, D., Aguiar, A., Flores, N.: AGILIPO: Embedding Social Software Features into Business Process Tools. In: Rinderle-Ma, S., Sadiq, S., Leymann, F. (eds.) BPM 2009. LNBIP, vol. 43, pp. 219–230. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Bruno, G., et al.: Key Challenges for Enabling Agile BPM with Social Software. Journal of Software Maintenance and Evolution: Research and Practice 23, 297–326 (2011)
Extreme Programming, http://www.extremeprogramming.org/ (accessed January 18, 2012)
van der Aalst, W.M.P.: Three Good Reasons for Using a Petri-net-based Workflow Management System. In: IPIC 1996, Cambridge, Massachusetts, pp. 179–201 (November 1996)
Weske, M., Goesmann, T., Holten, R., Striemer, R.: Analysing, Modelling and Improving Workflow Application Development Processes. Software Process: Improvement and Practice 6(1), 35–46 (2001)
Weske, M.: Business Process Management Concepts, Languages, Architectures, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-73522-9_8
Papazoglou, M.P., van den Heuvel, W.: Business Process Development Life Cycle Methodology. Communications of the ACM 50(10) (October 2007)
Yamamoto, R., Yamamoto, K., Ohashi, K., Inomata, J.: Development of a Business Process Modeling Methodology and a Tool for Sharing Business Processes. In: Proceedings of the 12th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC 2005). IEEE (2005), doi:0-7695-2465-6/05
Smith, H.: Business Process Management—the Third Wave: Business Process Modelling Language (BPML) and its pi-calculus Foundations. Information and Software Technology 45(15), 1065–1069 (2003)
Desai, N., Mallya, A.U., Chopra, A.K., Singh, M.P.: Processes = Protocols + Policies: A Methodology for Business Process Development (2004). In: Proceedings of the 14th International World Wide Web Conference, WWW 2005 (2005)
Arkin, A., et al.: Business Process Modeling Language (BPML), Version 1.0 (2002)
Schatten, A., Schiefer, J.: Agile Business Process Management with Sense and Respond. In: IEEE International Conference on e-Business Engineering (ICEBE 2007), pp. 319–322 (2007)
Møller, C., Maack, C.J., Tan, R.D.: What is Business Process Management: A Two Stage Literature Review of an Emerging Field. In: Research and Practical Issues of Enterprise Information Systems II. IFIP International Federation for Information Processing, vol. 254, 1, pp. 19–31 (2007)
Runeson, P., Höst, M.: Guidelines for conducting and reporting case study research in software engineering. Empirical Software Engineering 14(2), 131–164 (2009)
Khan, A.I., Qurashi, R.J., Khan, U.A.: A Comprehensive Study of Commonly Practiced Heavy and Light Weight Software Methodologies. IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues 8(4(2)), 1694–814 (July 2011), www.IJCSI.org
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Çulha, D., Doğru, A. (2014). Towards an Agile Methodology for Business Process Development. In: Nanopoulos, A., Schmidt, W. (eds) S-BPM ONE - Scientific Research. S-BPM ONE 2014. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 170. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-06065-1_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-06065-1_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-06064-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-06065-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)