Abstract
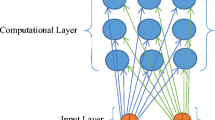
In this paper, we introduce a new approach referred to as Essential Attributes Generation (EAG) to reduce the dimensionality of multidimensional real-valued data series. We form a new representation of the original data. The approach is based on the concept of essential attributes generated by a multilayer neural network. The EAG generates a vector of real valued new attributes which form the compressed representation of the original data. The attributes are synthetic, and while not being directly interpretable, they still retain important features of the original data series. The approach has found applications to classification as well as clustering tasks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrom, K.J.: On the choice of sampling rates in parametric identification of time series. Information Sciences 1(3), 273–278 (1969)
Azzouzi, M., Nabney, I.T.: Analyzing time series structure with Hidden Markov Models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Neural Networks and Signal Processing, pp. 402–408 (1998)
Chan, K.P., Fu, A.C.: Efficient time series matching by wavelets. In: Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, pp. 126–133 (1999)
Cybenko, G.: Approximations by superpositions of sigmoidal functions. Mathematics of Control, Signals, and Systems 2(4), 303–314 (1989)
Dreyfus, G.: Neural Networks Methodology and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Faloutsos, C., Ranganathan, M., Manolopulos, Y.: Fast subsequence matching in time-series databases. SIGMOD Record 23, 519–529 (1994)
Frohlich, H., Chapelle, O., Scholkopf, B.: Feature selection for support vector machines by means of genetic algorithms. In: ICTAI, pp. 142–148 (2003)
Guyon, I., Gunn, S., Nikravesh, M., Zadeh, L. (eds.): Feature extraction foundations and applications. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Hall, M., Holmes, G.: Benchmarking attribute selection techniques for discrete class data mining. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 15(6), 1437–1447 (2003)
Inselberg, A.: Parallel Coordinates: VISUAL Multidimensional Geometry and its Applications. Springer (2009)
Jolliffe, I.T.: Principal Component Analysis. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Keogh, E., Chakrabarti, K., Pazzani, M., Mehrotra, S.: Dimensionality reduction for fast similarity search in large time series databases. J. Knowl. Inform. Syst. 3(3), 263–286 (2000)
Krawczak, M.: Multilayer Neural Systems and Generalized Net Models. Ac. Publ. House EXIT, Warsaw (2003a)
Krawczak, M.: Heuristic dynamic programming - Learning as control problem. In: Rutkowski, L., Kacprzyk, J. (eds.) Neural Networks and Soft Computing, pp. 218–223. Physica Verlag, Heidelberg (2003b)
Krawczak, M., Szkatuła, G.: Time series envelopes for classification. In: IEEE Intelligent Systems Conference, London, July 7-9 (2010)
Krawczak, M., Szkatuła, G.: A hybrid approach for dimension reduction in classification. Control and Cybernetics 40(2), 527–552 (2011)
Krawczak, M., Szkatuła, G.: Nominal Time Series Representation for the Clustering Problem. In: IEEE 6th International Conference, Intelligent Systems, Sofia, pp. 182–187 (2012)
Krawczak, M., Szkatuła, G.: An approach to dimensionality reduction in time series. Information Sciences 260, 15–36 (2014)
Lin, J., Keogh, E., Wei, L., Lonardi, S.: Experiencing SAX: a novel symbolic representation of time series. Journal Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 15(2), 107–144 (2007)
Lee, S., Kwon, D., Lee, S.: Dimensionality reduction for indexing time series based on the minimum distance. Journal of Inform. Science and Engineering 19, 697–711 (2003)
Maimon, O., Rokach, L. (eds.): Data mining and knowledge discovery handbook. Springer (2010)
Fu, T.-C.: A review on time series data mining. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 24, 164–181 (2011)
Yang, K., Shahabi, C.: On the stationarity of multivariate time series for correlation-based data analysis. In: Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 805–808 (2005)
Yi, B.K., Faloutsos, C.: Fast time sequence indexing for arbitrary norms. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Cairo, Egypt (2000)
Wnek, J., Michalski, R.S.: Hypothesis-driven Constructive Induction in AQ17-HCI: A Method and Experiments. Machine Learning 14, 139–168 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Krawczak, M., Szkatuła, G. (2014). Essential Attributes Generation for Some Data Mining Tasks. In: Rutkowski, L., Korytkowski, M., Scherer, R., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zadeh, L.A., Zurada, J.M. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing. ICAISC 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8468. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07176-3_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07176-3_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-07175-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-07176-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)