Abstract
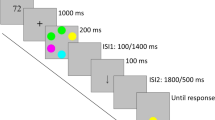
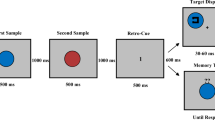
This paper reports experiments investigating the effect of presentation on visual working memory (VWM) when set-size increases. The capacity of VWM is limited to approximately four items (Luck & Vogel, 1997) and increasing set-size impairs the performance in visual tasks. Also, the performance in visuospatial tasks was better in the simultaneous presentation than in the sequential presentation. However, it is possible that large set-size in the simultaneous presentation caused overload in visual processing, and also, there is a possibility to increase interference among stimuli.Therefore, we speculated that performance in a simultaneous presentation would show a sharper decrease than in a partitioned presentation, which divides stimuli into two halves in order to reduce visual processing load and interference among stimuli when number of stimuli increases. Thus, the experiments with two types of set-size and two types of presentations (simultaneous and partitioned) were performed.The experiment examined whether a probe item was old or novel after seeing 4 or 8 items that appeared at random locations. These items were displayed either in simultaneous or in a partitioned manner. The results revealed a significant interaction between set-size and presentation. In a small set-size condition, performance was better in the simultaneous presentation than in the partitioned presentation. However, no difference was found between performances for both presentations in the large set-size condition, as it was influenced by the partitioned presentation. The results proposed that the partitioned presentation was more stable method to show items than the simultaneous presentation when set-size is large.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belopolsky, A.V., Kramer, A.F., Theeuwes, J.: Prioritization by transients in visual search. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 12(1), 93–99 (2005)
Donk, M., Theeuwes, J.: Visual marking beside the mark: Prioritizing selection by abrupt onsets. . Perception & Psychophysics 63(5), 891–900 (2001)
Duncan, J., Humphreys, G.W.: Visual search and stimulus similarity. Psychological Review 96(3), 433–458 (1989)
Egeth, H.E., Virzi, R.A., Garbart, H.: Searching for conjunctively defined targets. . Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 10(1), 32 (1984)
Eriksen, C.W., Yeh, Y.Y.: Allocation of attention in the visual field. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 11(5), 583 (1985)
Friedman-Hill, S., Wolfe, J.M.: Second-order parallel processing: Visual search for the odd item in a subset. Journal of Experimental Psychology-Human Perception and Performance 21(3), 531–550 (1995)
Jiang, Y., Olson, I.R., Chun, M.M.: Organization of visual short-term memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 26(3), 683 (2000)
Lecerf, T., De Ribaupierre, A.: Recognition in a visuospatial memory task: The effect of presentation. . European Journal of Cognitive Psychology 17(1), 47–75 (2005)
Luck, S.J., Vogel, E.K.: The capacity of visual working memory for features and conjunctions. Nature 390(6657), 279–281 (1997)
McCormick, P.A., Klein, R.: The spatial distribution of attention during covert visual orienting. Acta Psychologica 75(3), 225–242 (1990)
Palmer, J.: Attention in visual search: Distinguishing four causes of a set-size effect. . Current Directions in Psychological Science 4(4), 118–123 (1995)
Posner, M.I.: Orienting of attention. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 32(1), 3–25 (1980)
Sàenz, M., Buraĉas, G.T., Boynton, G.M.: Global feature-based attention for motion and color. Vision Research 43(6), 629-637 (2003)
Trick, L.M., Pylyshyn, Z.W.: What enumeration studies can show us about spatial attention: evidence for limited capacity preattentive processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 19(2), 331 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kim, DH., Kim, SH., Han, K. (2014). The Effect of Presentation on Visual Working Memory. In: Stephanidis, C. (eds) HCI International 2014 - Posters’ Extended Abstracts. HCI 2014. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 434. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07857-1_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07857-1_61
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-07856-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-07857-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)