Abstract
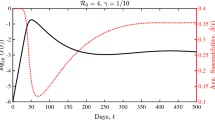
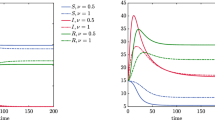
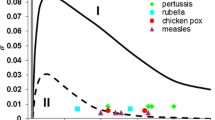
Epidemic modelling is fundamental to our understanding of biological, social and technological spreading phenomena. As conceptual frameworks for epidemiology advance, it is important they are able to elucidate empirically-observed dynamic feedback phenomena involving interactions amongst pathogenic agents in the form of syndemic and counter-syndemic effects. In this paper we model the dynamics of two types of epidemics with syndemic and counter-syndemic interaction effects in multiple possibly-overlapping populations. We derive a Markov model whose fluid limit reduces to a set of coupled SIR-type ODEs. Its numerical solution reveals some interesting multimodal behaviours, as shown in our case studies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avrachenkov, K., De Turck, K., Fiems, D., Prabhu, B.J.: Information dissemination processes in directed social networks. CoRR, abs/1311.2023 (2013)
Boukerche, A.: Epidemic Models, Algorithms, and Protocols in Wireless Sensor and Ad Hoc Networks. In: De, P., Das, S.K. (eds.) Algorithms and Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks, ch. 3. Wiley-IEEE Press (2008)
Cha, M., Kwak, H., Rodriguez, P., Ahn, Y.-Y., Moon, S.: I tube, you tube, everybody tubes: Analyzing the world’s largest user generated content video system. In: IMC 2007: Proc. 7th ACM SIGCOMM, pp. 1–14. ACM, NY (2007)
Chen, L., Ghanbarnejad, F., Cai, W., Grassberger, P.: Outbreaks of coinfections: The critical role of cooperativity. Europhysics Letters 104 (December 2013)
Daley, D.J., Kendall, D.G.: Epidemics and rumours. Nature 204, 1118 (1964)
Datta, A., Quarteroni, S., Aberer, K.: Autonomous gossiping: A self-organizing epidemic algorithm for selective information dissemination in wireless mobile ad-hoc networks. In: Bouzeghoub, M., Goble, C., Kashyap, V., Spaccapietra, S. (eds.) ICSNW 2004. LNCS, vol. 3226, pp. 126–143. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Dawkins, R.: The Selfish Gene. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1976)
De Cuypere, E., De Turck, K., Wittevrongel, S., Fiems, D.: Markovian sir model for opinion propagation. In: Proceedings of the 2013 25th International Teletraffic Congress (ITC), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2013)
Dietz, K., Heesterbeek, J.A.P.: Daniel Bernoulli’s epidemiological model revisited. Mathematical Biosciences 180, 1–21 (2002)
Ethier, S.N., Kurtz, T.G.: Markov processes – characterization and convergence. Wiley Series in Probability and Mathematical Statistics: Probability and Mathematical Statistics. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York (1986)
Gaunt, J.: Natural and Political Observations Mentioned in a following index, and made upon the Bills of Mortality (1662), http://www.neonatology.org/pdf/graunt.pdf
Getz, L.: Sustainable and responsible preventive medicine: Conceptualising ethical dilemmas arising from clinical implementation of advancing medical technology. PhD thesis. Norweigan University of Science and Technology, Trondheim (2006)
Goffman, W., Newill, V.A.: Generalization of epidemic theory: An application to the transmission of ideas. Nature 204, 225–228 (1964)
Hedetniemi, S.M., Hedetniemi, S.T., Liestman, A.L.: A survey of gossiping and broadcasting in communication networks. Networks 18(4), 319–349 (1988)
Hu, H.-W., Lee, S.-Y.: Study on influence diffusion in social network. International Journal of Computer Science and Electronics Engineering (IJCSEE) 1 (2013)
Iribarren, J.L., Moro, E.: Information diffusion epidemics in social networks. Physical Review (2009)
Jaewon, Y., Leskovec, J.: Modeling information diffusion in implicit networks. In: 2010 IEEE 10th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 599–608 (December 2010)
Karnik, A., Saroop, A., Borkar, V.: On the diffusion of messages in online social networks. Performance Evaluation 70(4), 271–285 (2013)
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G.: Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics–I. Bull. Math. Biol. 53(1-2), 33–55 (1927, 1991)
Khelil, A., Becker, C., Tian, J., Rothermel, K.: An epidemic model for information diffusion in MANETs. In: Proc. 5th ACM International Workshop on Modeling Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems, pp. 54–60 (2002)
Kwan, C., Ernst, J.: HIV and tuberculosis: a deadly human syndemic. Clinical Microbiology 24(2), 351–376 (2011)
Leibnitz, K., Hoßfeld, T., Wakamiya, N., Murata, M.: Modeling of epidemic diffusion in peer-to-peer file-sharing networks. In: Ijspeert, A.J., Masuzawa, T., Kusumoto, S. (eds.) BioADIT 2006. LNCS, vol. 3853, pp. 322–329. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Lerman, K., Ghosh, R.: Information contagion: An empirical study of the spread of news on Digg and Twitter social networks. In: Proc. 4th International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, ICWSM 2010 (2010)
Leskovec, J., Adamic, L.A., Huberman, B.A.: The dynamics of viral marketing. ACM Trans. Web 1 (May 2007)
Martcheva, M., Pilyugin, S.S.: The role of coinfection in multi-disease dynamics. SIAM Journal of Applied Mathematics 66, 843–872 (2006)
Mochalova, A., Nanopoulos, A.: On the role of centrality in information diffusion in social networks. In: Proc. ECIS 2013, p. 101 (2013)
Moss, W.J., Scott, S., Ndhlovu, Z., Monze, M., Cutts, F.T., Quinn, T.C., Griffin, D.E.: Suppression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral load during acute measles. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 28(1), 63–65 (2009)
Myers, S., Leskovec, J.: Clash of the Contagions: Cooperation and Competition in Information Diffusion. In: Proc. IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM 2012 (2012)
Netrapalli, P., Sanghavi, S.: Learning the graph of epidemic cascades. In: Proc. 12th ACM SIGMETRICS/PERFORMANCE Joint International Conference on Measurement and Modeling of Computer Systems (SIGMETRICS 2012), pp. 211–222. ACM, New York (2012)
Newman, M.E.J., Ferrario, C.R.: Interacting epidemics and coinfection on contact networks. PLoS ONE 8(8), e71321(2013)
Nika, M., Ivanova, G., Knottenbelt, W.J.: On celebrity, epidemiology and the internet. In: Proc. 7th International Conference on Performance Evaluation Methodologies and Tools (VALUETOOLS 2013), Turin, Italy (December 2013)
Parker, R.: Miasma: Pollution and Purification in Early Greek Religion. Clarendon paperbacks. Clarendon Press (1990)
Pi, S.-M., Liu, Y.-C., Chen, T.-Y., Li, S.-H.: The influence of instant messaging usage behavior on organizational communication satisfaction. In: Proc. 41st Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, HICSS 2008, p. 449. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC (2008)
Rhodes, C.J., Nekovee, M.: The opportunistic transmission of wireless worms between mobile devices. CoRR, abs/0802.2685 (2008)
Singer, M.: Introduction to Syndemics. Wiley (2009)
Snow, J.: On the Mode of Communication of Cholera. John Churchill (1855)
Weng, L., Flammini, A., Vespignani, A., Menczer, F.: Competition among memes in a world with limited attention. Scientific Reports 2(335) (2013)
Wikipedia. List of epidemics, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_epidemics
Wischhof, L., Ebner, A., Rohling, H.: Information dissemination in self-organizing intervehicle networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 6(1), 90–101 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nika, M., Fiems, D., de Turck, K., Knottenbelt, W.J. (2014). Modelling Interacting Epidemics in Overlapping Populations. In: Sericola, B., Telek, M., Horváth, G. (eds) Analytical and Stochastic Modeling Techniques and Applications. ASMTA 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8499. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08219-6_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08219-6_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-08218-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-08219-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)