Abstract
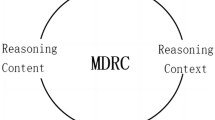
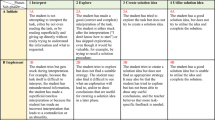
It is important for each leader to know relationship of the reason why each learner mistakes the problem of Mathematics. But, it does not exist about previous research. Therefore, in this research, we collected answers of each learner for knowing element of difficulty level in Mathematics. And we identified 10 types. 10 types are “lack of understand(problem statement, Number & Symbol, Formula, Concept)”, “circumstances of learner (inside)”, “circumstances of learner (outside)”, “Miscalculation”, “Copy miss”, “Lack of logical thinking (Deduction)” and “Lack of logical thinking (Induction)”.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker: Item Response Theory: Parameter Estimation Technique. Marcel Dekker, United States (1992)
Barbu, C.O., Beal, R.C.: Effects of Linguistic Complexity and Math Difficulty on Word Problem Solving by English Learners. International Journal of Education 2(2), 1–19 (2010)
Belton, V., Gear, T.: The legitimacy of rank reversal-A Comment. OMEGA the International Journal of Management Science 13(3), 14444 (1985)
Chalmers, D.J.: The conscious mind: In search of a fundamental theory. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1996)
Hirasihima, Y., Mori, T., Tani, T.: On the System of Numbers Considered from the Degree of Difficulty. Journal of JAPAN Society of Mathematical Education 37(10), 148–151 (1955)
Kohonen, T.: Self-Organizing Maps. Series in Information Sciences, pp. 1–521 (2000)
Maeda, M., Nishio, Y.: Research on Difficulty of Multiplication and Division Word Problems. Mathematics Education Research, 531–137 (2000)
Meece, J.L., Wigfield, A., Eccles, J.S.: Predictors of math anxiety and its influence on young adolescents’ course enrollment intentions and performance in mathematics. Journal of Educational Psychology 82(1), 60–70 (1990)
Joslyn, C., Rocha, L.: Towards semiotic agent-based models of socio-technical organizations. In: Proc. AI, Simulation and Planning in High Autonomy Systems (AIS 2000), pp. 70–79 (2000)
Hill, H.C., Ball, D.L., Schilling, S.G.: Unpacking Pedagogical Content Knowledge: Conceptualizing and Measuring Teachers’ Topic-Specific Knowledge of Students. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education 39(4), 372–400 (2008)
Jiromaru, T., Matsuo, T.: OMES: Employment support system for high education. CIEC, Computer & Education 32, 71–76 (2012)
Mogi, K.: Generation and qualia in brain. In: Suzuki, H. (ed.) Emergent and Conception of Intelligence, pp. 25–40. Ohmsha (2006)
Penrose, R.: Emperor’s New Mind. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1989)
Raghubar, K., Cirino, P., Barnes, M., et al.: Journal of Learning Disabilities, 4356–4371 (2009)
Riley, N.S., Greeno, J.G.: Developmental Analysis of Understanding Language About Quantities and of Solving Problems. Cognition and Instruction 5(1), 49–101 (1988)
Saaty, L.S.: How to Make a Decision: The Analytic Hierarchy Process. Interfaces 24(6), 19–43 (1994)
Searle, J.: The Chinese room revisited. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 5(2), 345–348 (1982)
Shimizu, H., Ide, S.: Gaps in students’ learning in elementary mathematics classes. Journal of Japan Society of Mathematical Education 85(10), 11–18 (2003)
Shojima, K.: Neural Test Theory: A Test Theory for Standardizing Qualifying Tests. The Journal of Institute of Electronics Information and Communication Engineers 92(12), 1014016 (2009)
Soga, C., Miyake, S., Wada, C.: Differences in Physiological Responses Induced by Mental Tasks with Different Difficulty Levels. The Japanese Journal of Ergonomics 45(1), 29–35 (2009)
Roberts, R.J., Varney, N.R., et al.: The neuropathology of everyday life: The frequency of partial seizure symptoms among normals. Neuropsychology 4(2), 65–85 (1990)
Tsukihara, Y., Suzuki, K., Hirose, H.: A small implementation case of the mathematics tests with the item response theory evaluation into an e-learning system. CIEC, Computer & Education 24, 70–76 (2008)
Weaver, W.: Science and complexity. American Scientist 36, 536–544 (1948)
Yamagata University Faculty of Engineering, Past entry-exam data (2013), http://www2.yz.yamagata-u.ac.jp/admission/admissiondata.html (accessed April 24, 2014)
Yoshizawa, M.: Classification of Students’ Stumbles while Learning Mathematics. Journal of Japan Society of Mathematical Education 88(3), 228 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Jiromaru, T., Kosaka, T., Matsuo, T. (2015). Elements of Difficulty Level in Mathematics. In: Lee, R. (eds) Software Engineering, Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Parallel/Distributed Computing. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 569. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10389-1_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10389-1_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-10388-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-10389-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)