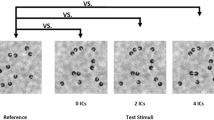
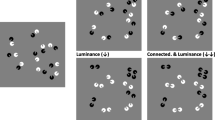
Abstract
The estimation of the cardinality of objects in a spatial environment requires a high degree of invariance. Numerous experiments showed the immense abstraction ability of the numerical cognition system in humans and other species. It eliminates almost all structures of the objects and determines the number of objects in a scene. Based on concepts and quantities like connectedness and Gaussian curvature, we provide a general solution to this problem and apply it to the numerosity estimation from visual stimuli.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allik, J., Tuulmets, T., Vos, P.G.: Size invariance in visual number discrimination. Psychological Research 53(4), 290–295 (1991)
Alvarez, G.A.: Representing multiple objects as an ensemble enhances visual cognition. Trends in Cognitive Science 15(3), 122–131 (2011)
Brannon, E.M.: The representation of numerical magnitude. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 16(2), 222–229 (2006)
Buzsáki, G., Mizuseki, K.: The log-dynamic brain: how skewed distributions affect network operations. Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2014)
Carandini, M., Heeger, D.J.: Normalization as a canonical neural computation. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 13, 51–62 (2012)
Chen, L.: The topological approach to perceptual organization. Visual Cognition 12(4), 553–637 (2005)
Clarke, B.L.: A calculus of individuals based on “connection”. Notre Dame Journal of Formal Logic 22(3), 204–218 (1981)
Dakin, S.C., Tibber, M.S., Greenwood, J.A., Kingdom, F.A.A., Morgan, M.J.: A common visual metric for approximate number and density. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 108(49), 19552–19557 (2011)
De Hevia, M.-D., Girelli, L., Bricolo, E., Vallar, G.: The representational space of numerical magnitude: Illusions of length. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 61(10), 1496–1514 (2008)
de Hevia, M.D., Girelli, L., Vallar, G.: Numbers and space: a cognitive illusion? Experimental Brain Research 168(1-2), 254–264 (2006)
Dehaene, S., Bossini, S., Giraux, P.: The mental representation of parity and number magnitude. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 122(3), 371 (1993)
Dehaene, S., Changeux, J.P.: Development of elementary numerical abilities: a neuronal model. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 5(4), 390–407 (1993)
Dehaene, S., Piazza, M., Pinel, P., Cohen, L.: Three parietal circuits for number processing. Cognitive Neuropsychology 20(3-6), 487–506 (2003)
Dillen, F., Kühnel, W.: Total curvature of complete submanifolds of euclidean space. Tohoku Mathematical Journal 57(2), 171–200 (2005)
Fias, W.: The importance of magnitude information in numerical processing: Evidence from the snarc effect. Mathematical Cognition 2(1), 95–110 (1996)
Gallistel, C.R., Gelman, R.: Preverbal and verbal counting and computation. Cognition 44(1), 43–74 (1992)
Gross, H.J., Pahl, M., Si, A., Zhu, H., Tautz, J., Zhang, S.: Number-based visual generalisation in the honeybee. PloS one, 4(1), e4263 (2009)
He, L., Zhang, J., Zhou, T., Chen, L.: Connectedness affects dot numerosity judgment: Implications for configural processing. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 16(3), 509–517 (2009)
Hegde, J., Felleman, D.: Reappraising the Functional Implications of the Primate Visual Anatomical Hierarchy. The Neuroscientist 13(5), 416–421 (2007)
Kaufman, E.L., Lord, M., Reese, T., Volkmann, J.: The discrimination of visual number. The American Journal of Psychology, 498–525 (1949)
Koenderink, J.J., van Doorn, A.: Shape and shading. The visual neurosciences, 1090–1105 (2003)
Nieder, A., Freedman, D.J., Miller, E.K.: Representation of the quantity of visual items in the primate prefrontal cortex. Science 297(5587), 1708–1711 (2002)
Oliva, A., Torralba, A.: Modeling the Shape of the Scene: A Holistic Representation of the Spatial Envelope. International Journal of Computer Vision 42(3), 145–175 (2001)
Palmer, S., Rock, I.: Rethinking perceptual organization: The role of uniform connectedness. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 1(1), 29–55 (1994)
Piazza, M., Mechelli, A., Butterworth, B., Price, C.J.: Are subitizing and counting implemented as separate or functionally overlapping processes? Neuroimage 15(2), 435–446 (2002)
Randell, D.A., Cui, Z., Cohn, A.G.: A spatial logic based on regions and connection. KR 92, 165–176 (1992)
Ranzini, M., Girelli, L.: Exploiting illusory effects to disclose similarities in numerical and luminance processing. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics 74(5), 1001–1008 (2012)
Ross, J., Burr, D.C.: Vision senses number directly. Journal of Vision 10(2), 1–8 (2010)
Starkey, P., Spelke, E.S., Gelman, R.: Numerical abstraction by human infants. Cognition 36(2), 97–127 (1990)
Stoianov, I., Zorzi, M.: Emergence of a ’visual number sense’ in hierarchical generative models. Nature Neuroscience 15(2), 194–196 (2012)
Stöttinger, E., Anderson, B., Danckert, J., Frühholz, B., Wood, G.: Spatial biases in number line bisection tasks are due to a cognitive illusion of length. Experimental Brain Research 220(2), 147–152 (2012)
Strauss, M.S., Curtis, L.E.: Infant perception of numerosity. Child Development 52(4), 1146–1152 (1981)
Suzuki, K., Horiba, I., Sugie, N.: Linear-time connected-component labeling based on sequential local operations. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 89(1), 1–23 (2003)
van Nes, F., van Eerde, D.: Spatial structuring and the development of number sense: A case study of young children working with blocks. The Journal of Mathematical Behavior 29(3), 145–159 (2010)
Walsh, V.: A theory of magnitude: common cortical metrics of time, space and quantity. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 7(11), 483–488 (2003)
Zetzsche, C., Barth, E.: Fundamental limits of linear filters in the visual processing of two-dimensional signals. Vision Research 30(7), 1111–1117 (1990)
Zetzsche, C., Barth, E.: Image surface predicates and the neural encoding of two-dimensional signal variations. In: Rogowitz, B.E., Allebach, J.P. (eds.) Proceedings SPIE, Human, Vision and Electronic Imaging: Models, Methods, and Applications, vol. 1249, pp. 160–177 (1990)
Zetzsche, C., Gadzicki, K., Kluth, T.: Statistical invariants of spatial form: From local and to numerosity. In: Proc. of the 2nd Interdisciplinary Workshop The Shape of Things, pp. 163–172. CEUR-WS.org (April 2013)
Zetzsche, C., Nuding, U.: Nonlinear and higher-order approaches to the encoding of natural scenes. Network: Computation in Neural Systems 16(2-3), 191–221 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kluth, T., Zetzsche, C. (2014). Spatial Numerosity: A Computational Model Based on a Topological Invariant. In: Freksa, C., Nebel, B., Hegarty, M., Barkowsky, T. (eds) Spatial Cognition IX. Spatial Cognition 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8684. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11215-2_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11215-2_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-11214-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-11215-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)