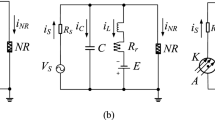
Abstract
Neurons as active unities are connected one with the others by synapses in an electronic way. Each neuron as N port electronic medium scatters input waves and transmits output waves to other neurons. By voltage waves each neuron interacts with the others in a complex way. Scattering processes create dependence among neurons. We show that a multi pendulum mechanical system can be a simple model to represent complex dependence among neurons. With the multi pendulum synchronization we show that a suitable geometry and geodesic dynamic can be found. We know that neuron network is an electronic network for which power is a metric (electronic distance ) in the space of the currents or in the space of the voltages. The power of electronic system is given by the impedance matrix or by admittance matrix that model the type of electronic geometry and entanglement. In conclusion multi pendulum , quantum entanglement and electronic system are useful models to show in a geometric way how neural dynamic can be controlled by conceptual reference transformation ( geometry change ) and why synchronic processes are possible in the neural network dynamics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kozma, R., Freeman, W.J.: Intermittent spatial – temporal desynchronization and sequenced synchrony in ECoG signal. Interdisciplinary J. Chaos 18, 037131 (2008)
Resconi, G., Srini, V.P.: Electrical Circuit As A Morphogenetic System. GEST International Transactions on Computer Science and Engineering 53(1), 47–92 (2009)
Mead, C.: Neuromoprhic Electronic Systems. Proceeding of the IEEE 78(10) (1990)
Torralba, A.B.: Analogue Architectures for Vision Cellular Neural Networks and Neuromorphic Circuits, Doctorat thesis, Institute national Polytechnique Grenoble, Laboratory of Images and Signals (1999)
Resconi, G.: Ignazio Licata Adv. Studies Theor. Phys. 10, 479–513 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Resconi, G., Kozma, R. (2015). Geometric Syncronisation by Multi-pendulum and Electronic Models of Neurodynamics. In: Madani, K., Correia, A., Rosa, A., Filipe, J. (eds) Computational Intelligence. IJCCI 2012. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 577. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11271-8_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11271-8_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-11270-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-11271-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)