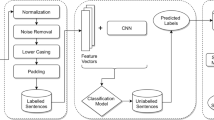
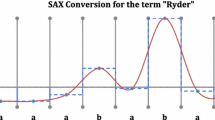
Abstract
Micro-blog forums, such as Twitter, constitute a powerful medium today that people use to express their thoughts and intentions on a daily, and in many cases, hourly, basis. Extracting ‘Real-Time Intention’ (RTI) of a user from such short text updates is a huge opportunity towards web personalization and social networking around dynamic user context. In this paper, we propose novel ensemble approaches for learning and classifying RTI expressions from micro-blogs, based on a wide spectrum of linguistic and statistical features of RTI expressions (viz. high dimensionality, sparseness of data, limited context, grammatical in-correctness, etc.). We demonstrate our approach achieves significant improvement in accuracy, compared to word-level features used in many social media classification tasks. Further, we conduct experiments to study the run-time performance of such classifiers for integration with a variety of applications. Finally, a prototype implementation using an Android-based user device demonstrates how user context (intention) derived from social media sites can be consumed by novel social networking applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J.: Recognizing intentions from natural language utterances. In: Brady, M., Berwick, R.C. (eds.) Computational Models of Discourse, pp. 107–166. MIT Press, Cambridge (1983)
Banerjee, N., et al.: User interests in social media sites: an exploration with micro-blogs. In: International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM) (2009)
Banerjee, N., et al.: Towards analyzing micro-blogs for detection and classification of real-time intentions. In: ICWSM (2012)
Banerjee, N., et al.: R-U-In? - exploiting rich presence and converged communications for next-generation activity-oriented social networking. In: International Conference on Mobile Data Management Systems (MDM), Services and Middleware (2009)
Chalamalla, A.K., et al.: Identification of class specific discourse patterns. In: ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (2008)
Chen, Z., et al.: User intention modeling inweb applications using data mining. World Wide Web: Internet and Web Inf. Syst. 5, 181–191 (2002)
Dietterich, T.G.: Ensemble methods in machine learning. In: Kittler, J., Roli, F. (eds.) MCS 2000. LNCS, vol. 1857, pp. 1–15. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Han, J., et al.: Mining frequent patterns without candidate generation (2000)
Han, J., et al.: Data Mining Concepts and Techniques, Chap. 6, 2nd edn, pp. 318–327. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (2006)
Hastie, T., et al.: The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2009)
Liu, R.-L., et al.: Incremental context mining for adaptive document classification. In: KDD, pp. 599–604 (2002)
Martineau, J., et al.: Delta TFIDF: an improved feature space for sentiment analysis. In: AAAI Internatonal Conference on Weblogs and Social Media (2009)
Nasukawa, T., et al.: Text analysis and knowledge mining system. IBM Syst. J. 40(4), 967–984 (2001)
Rakotomamonjy, A., et al.: SimpleMKL. J. Mach. Learn. Res. (JMLR) 9, 2491–2521 (2008)
Sakaki, T., et al.: Earthquake shakes twitter users: real-time event detection by social sensors. In: WWW (2010)
Varma, M., et al.: Morje generality in efficient multiple kernel learning. In: ICML (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Banerjee, N., Chakraborty, D., Joshi, A., Mittal, S., Rai, A., Ravindran, B. (2014). Detection of Real-Time Intentions from Micro-blogs. In: Stojmenovic, I., Cheng, Z., Guo, S. (eds) Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking, and Services. MobiQuitous 2013. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 131. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11569-6_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11569-6_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-11568-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-11569-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)