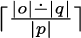Abstract
The development of sophisticated termination criteria for term rewrite systems has led to powerful and complex tools that produce (non)termination proofs automatically. While many techniques to establish termination have already been formalized—thereby allowing to certify such proofs—this is not the case for nontermination. In particular, the proof checker  was so far limited to (innermost) loops. In this paper we present an Isabelle/HOL formalization of an extended repertoire of nontermination techniques. First, we formalized techniques for nonlooping nontermination. Second, the available strategies include (an extended version of) forbidden patterns, which cover in particular outermost and context-sensitive rewriting. Finally, a mechanism to support partial nontermination proofs further extends the applicability of our proof checker.
was so far limited to (innermost) loops. In this paper we present an Isabelle/HOL formalization of an extended repertoire of nontermination techniques. First, we formalized techniques for nonlooping nontermination. Second, the available strategies include (an extended version of) forbidden patterns, which cover in particular outermost and context-sensitive rewriting. Finally, a mechanism to support partial nontermination proofs further extends the applicability of our proof checker.
This research was supported by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF): P22767 and I963.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
In the literature (e.g., in [7]) a nonterminating DP problem is also called infinite. This is the reason why in
 this property is defined as infinite-dpp.
this property is defined as infinite-dpp. - 2.
More precisely, \(n_0\) can be set to \(0\) if \(p=\varepsilon \) and to
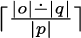
otherwise.
- 3.
Rules (i)–(iv) in [22, Definition 5], which are omitted here for brevity.
References
Arts, T., Giesl, J.: Termination of term rewriting using dependency pairs. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 236, 133–178 (2000)
Baader, F., Nipkow, T.: Term Rewriting and All That. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Blanqui, F., Koprowski, A.: \({\sf CoLoR}\): a \({\sf Coq}\) library on well-founded rewrite relations and its application to the automated verification of termination certificates. Math. Struct. Comput. Sci. 4, 827–859 (2011)
Contejean, E., Courtieu, P., Forest, J., Pons, O., Urbain, X.: Automated certified proofs with \({\sf CiME3}\). In: Proceedings of the RTA ’11. LIPIcs, vol. 10, pp. 21–30 (2011)
Emmes, F., Enger, T., Giesl, J.: Proving non-looping non-termination automatically. In: Gramlich, B., Miller, D., Sattler, U. (eds.) IJCAR 2012. LNCS(LNAI), vol. 7364, pp. 225–240. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Giesl, J., Schneider-Kamp, P., Thiemann, R.: \({\sf AProVE 1.2}\): automatic termination proofs in the dependency pair framework. In: Furbach, U., Shankar, N. (eds.) IJCAR 2006. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4130, pp. 281–286. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Giesl, J., Thiemann, R., Schneider-Kamp, P., Falke, S.: Mechanizing and improving dependency pairs. J. Autom. Reason. 37(3), 155–203 (2006)
Gramlich, B.: Abstract relations between restricted termination and confluence properties of rewrite systems. Fund. Inform. 24, 3–23 (1995)
Gramlich, B., Schernhammer, F.: Extending context-sensitivity in term rewriting. In: Proceedings of the WRS ’09. EPTCS, vol. 15, pp. 56–68 (2010)
Haftmann, F., Nipkow, T.: Code generation via higher-order rewrite systems. In: Blume, M., Kobayashi, N., Vidal, G. (eds.) FLOPS 2010. LNCS, vol. 6009, pp. 103–117. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Huffman, B., Kunčar, O.: Lifting and transfer: a modular design for quotients in Isabelle/HOL. In: Gonthier, G., Norrish, M. (eds.) CPP 2013. LNCS, vol. 8307, pp. 131–146. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Korp, M., Sternagel, C., Zankl, H., Middeldorp, A.: Tyrolean termination tool 2. In: Treinen, R. (ed.) RTA 2009. LNCS, vol. 5595, pp. 295–304. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Krauss, A.: Partial and nested recursive function definitions in higher-order logic. J. Autom. Reason. 44(4), 303–336 (2010)
Krauss, A.: Recursive definitions of monadic functions. In: Proceedings of the PAR ’10. EPTCS, vol. 43, pp. 1–13 (2010)
Lucas, S.: Context-sensitive computations in functional and functional logic programs. J. Funct. Logic Program. 1, 1–61 (1998)
Nipkow, T., Paulson, L.C., Wenzel, M. (eds.): Isabelle/HOL. LNCS, vol. 2283. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Oppelt, M.: Automatische Erkennung von Ableitungsmustern in nichtterminierenden Wortersetzungssystemen. Diploma thesis, HTWK Leipzik, Germany (2008)
Sternagel, C., Thiemann, R.: Formalizing Knuth-Bendix orders and Knuth-Bendix completion. In: Proceedings of the RTA ’13. LIPIcs, vol. 21, pp. 287–302 (2013)
Thiemann, R.: Mutually recursive partial functions. Arch. Formal Proofs, February 2014. Formal Proof Development. http://afp.sf.net/entries/Partial_Function_MR.shtml
Thiemann, R., Giesl, J., Schneider-Kamp, P.: Deciding innermost loops. In: Voronkov, A. (ed.) RTA 2008. LNCS, vol. 5117, pp. 366–380. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Thiemann, R., Sternagel, C.: Certification of termination proofs using \({\sf CeTA}\). In: Berghofer, S., Nipkow, T., Urban, C., Wenzel, M. (eds.) TPHOLs 2009. LNCS, vol. 5674, pp. 452–468. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Thiemann, R., Sternagel, C.: Loops under strategies. In: Treinen, R. (ed.) RTA 2009. LNCS, vol. 5595, pp. 17–31. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Sternagel, C., Thiemann, R.: Certification of nontermination proofs. In: Beringer, L., Felty, A. (eds.) ITP 2012. LNCS, vol. 7406, pp. 266–282. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Thiemann, R., Sternagel, C., Giesl, J., Schneider-Kamp, P.: Loops under strategies ... continued. In: Proceedings of the IWS ’10, vol. 44, pp. 51–65 (2010)
Acknowledgments
The authors are listed in alphabetical order regardless of individual contributions or seniority.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nagele, J., Thiemann, R., Winkler, S. (2014). Certification of Nontermination Proofs Using Strategies and Nonlooping Derivations. In: Giannakopoulou, D., Kroening, D. (eds) Verified Software: Theories, Tools and Experiments. VSTTE 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8471. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12154-3_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12154-3_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-12153-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-12154-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)





 this property is defined as infinite-dpp.
this property is defined as infinite-dpp.