Abstract
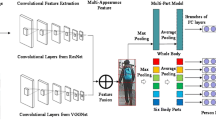
Human-specified appearance features are widely used for person re-identification at present, such as color and texture histograms. Often, these features are limited by the subjective appearance of pedestrians. This paper presents a new representation to re-identification that incorporates data-driven features to improve the reliability and robustness in person matching. Firstly, we utilize a deep learning network, namely PCA Network, to learn data-driven features from person images. The features mine more discriminative cues from pedestrian data and compensate the drawback of human-specified features. Then the data-driven features and common human-specified features are combined to produce a final representation of each image. The so-obtained enriched Data-driven Representation (eDR) has been validated through experiments on two person re-identification datasets, demonstrating that the proposed representation is effective for person matching. That is, the data-driven features facilitate more accurate re-identification when they are fused together with the human-specified features.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, C., Gong, S., Loy, C.C., et al.: Person Re-identification: What Features are Important? In: European Conference on Computer Vision, Workshops and Demonstrations, pp. 391–401. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Park, U., Jain, A.K., Kitahara, I., et al.: Vise: Visual Search Engine Using Multiple Networked Cameras. In: IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition, vol. 3, pp. 1204–1207 (2006)
Farenzena, M., Bazzani, L., Perina, A., et al.: Person Re-identification by Symmetry-Driven Accumulation of Local Features. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2360–2367 (2010)
Schwartz, W.R., Davis, L.S.: Learning Discriminative Appearance-Based Models Using Partial Least Squares. IEEE Transactions on Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 322–329 (2009)
Mignon, A., Jurie, F.: PCCA: A New Approach for Distance Learning from Sparse Pairwise Constraints. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2666–2672 (2012)
Gray, D., Tao, H.: Viewpoint Invariant Pedestrian Recognition with an Ensemble of Localized Features. In: Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A. (eds.) ECCV 2008, Part I. LNCS, vol. 5302, pp. 262–275. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Gheissari, N., Sebastian, T.B., Hartley, R.: Person Reidentification Using Spatiotemporal Appearance. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 2, pp. 1528–1535 (2006)
Wang, X., Doretto, G., Sebastian, T., et al.: Shape and Appearance Context Modeling. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Zheng, W.S., Gong, S., Xiang, T.: Associating Groups of People. In: British Machine Vision Conference, London (2009)
Zheng, W.S., Gong, S., Xiang, T.: Re-identification by Relative Distance Comparison. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 35(3), 653–668 (2013)
Chan, T.H., Jia, K., Gao, S., et al.: PCANet: A Simple Deep Learning Baseline for Image Classification? arXiv preprint arXiv:1404.3606 (2014)
Ess, A., Leibe, B., Van Gool, L.: Depth and Appearance for Mobile Scene Analysis. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Pedagadi, S., Orwell, J., Velastin, S., Boghossian, B.: Local Fisher Discriminant Analysis for Pedestrian Re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3318–3325 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, X., Gao, J., Chang, X., Mai, Y., Zheng, WS. (2014). Person Re-identification with Data-Driven Features. In: Sun, Z., Shan, S., Sang, H., Zhou, J., Wang, Y., Yuan, W. (eds) Biometric Recognition. CCBR 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8833. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12484-1_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12484-1_58
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-12483-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-12484-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)