Abstract
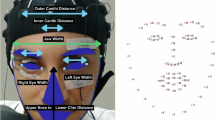
In this paper, we propose a new human implicit intent understanding model based on multi-modal information, which is a combination of eye movement data and brain wave signal obtained from eye-tracker and Electroencephalography (EEG) sensors respectively. From the eye movement data, we extract human implicit intention related to features such as fixation count and fixation duration corresponding to the areas of interest (AOI). Also, we analyze the EEG signals based on phase synchrony method. Combining the eye movement and EEG information, we train several classifiers such as support vector machine classifier, Gaussian Mixture Model and Naïve Bayesian, which can successfully identify the human’s implicit intention into two defined categories, i.e. navigational and informational intentions. Experimental results show that the human implicit intention can be better understood using multimodal information.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breazeal, C.: Social interactions in HRI: The robot view. IEEE T. Syst. Man. Cy. C: Applications and Reviews 34, 181–186 (2004)
Farrah, W., Kwang-Hyun, P., Dae-jin, K., Jin-Woo, J., Zeungnam, B.: Intention reading towards engineering applications for the elderly and people with disabilities. International Journal of ARM 7, 3–15 (2006)
Jansen, B.J., Booth, D.L., Spink, A.: Determining the informational, navigational, and transactional intent of Web queries. Inform. Process. Manag. 44, 1251–1266 (2008)
Ferreira, A., Celeste, C.W., Cheein, F.A., Bastos-Filho, T.F., Sarcinelli-Filho, M., Carelli, R.: Human-machine interfaces based on EMG and EEG applied to robotic systems. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 5, 10 (2008)
Goodrich, M.A., Schultz, A.C.: Human-robot interaction: A survey. Foundations and Trends in Human-Computer Interaction 1, 203–275 (2007)
Jaimes, A., Sebe, N.: Multimodal human-computer interaction: A survey. Comput. Vis. Image Und. 108, 116–134 (2007)
Jang, Y.M., Mallipeddi, R., Lee, S., Kwak, H.W., Lee, M.: Human intention recognition based on eyeball movement pattern and pupil size variation. Neurocomputing 128, 421–432 (2013)
Sun, J., Sun, X., Tong, S.: Phase synchronization analysis of EEG signals: An evaluation based on surrogate tests. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59, 2254–2263 (2012)
Lachaux, J.-P., Rodriguez, E., Martinerie, J., Varela, F.J.: Measuring Phase Synchrony in Brain Signals. Hum. Brain Mapp. 8, 194–208 (1999)
Suzuki, H.: Phase relationships of alpha rhythm in man. Jpn. J. Physiol. 24, 569–586 (1974)
Nunez, P.: Electrical Fields of the Brain. Oxford University Press, Mass. (1981)
Gonuguntla, V., Wang, Y., Veluvolu, K.C.: Phase Synchrony in Subject-Specific Reactive Band of EEG for Classification of Motor Imagery Tasks. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference, pp. 2784–2787 (2013)
Park, U., Veluvolu, K.C., Lee, M.: Phase synchrony for human implicit intent differentiation. In: Proceedings of 20th Annual International IEEE ICONIP Conference, pp. 427–433 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, U., Mallipeddi, R., Lee, M. (2014). Human Implicit Intent Discrimination Using EEG and Eye Movement. In: Loo, C.K., Yap, K.S., Wong, K.W., Teoh, A., Huang, K. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8834. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12637-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12637-1_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-12636-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-12637-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)