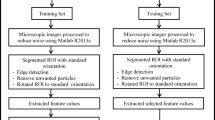
Abstract
Active Shape Models and Complex Network method are applied to the attachment hooks of several species of Gyrodactylus, including the notifiable pathogen G. salaris, to classify each species to their true species type. ASM is used as a feature extraction tool to select information from hook images that can be used as input data into trained classifiers. Linear (i.e. LDA and K-NN) and non-linear (i.e. MLP and SVM) models are used to classify Gyrodactylus species. Species of Gyrodactylus, ectoparasitic monogenetic flukes of fish, are difficult to discriminate and identify on morphology alone and their speciation currently requires taxonomic expertise. The current exercise sets out to confidently classify species, which in this example includes a species which is notifiable pathogen of Atlantic salmon, to their true class with a high degree of accuracy. The results show that Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) is the best classifier for performing the initial classification of Gyrodactylus species, with an average of 98.36%. Using MLP classifier, only one species has been misallocated. It is essential, therefore, to employ a method that does not generate type I or type II misclassifications where G. salaris is concerned. In comparison, only K-NN classifier has managed to to achieve full classification on the G. salaris.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alenäs, I.: Gyrodactylus salaris på lax i svenska vattendrag och laxproblematiken på svenska västkysten. Vann 1, 135–142 (1998) (In Swedish)
Ali, R., Hussain, A., Bron, J.E., Shinn, A.P.: Multi-stage classification of Gyrodactylus species using machine learning and feature selection techniques. Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, 457–462 (2011)
Ali, R., Hussain, A., Bron, J.E., Shinn, A.P.: The use of asm feature extraction and machine learning for the discrimination of members of the fish ectoparasite genus Gyrodactylus. Neural Information Processing 7666, 457–462 (2011)
Backes, A.R., Bruno, O.M.: Shape classification using complex network and multi-scale fractal dimension. Pattern Recognition Letters 31(1), 45–51 (2010)
Backes, A.R., Casanova, D., Bruno, O.M.: A complex network-based approach for boundary shape analysis. Pattern Recognition 42(8), 54–67 (2009)
Backes, A.R., Martinez, A.S., Bruno, O.M.: Texture analysis using graphs generated by deterministic partially self-avoiding walks. Pattern Recognition 44(8), 1684–1689 (2011)
Bakke, T.A., Cable, J., Harris, P.D.: The biology of gyrodactylid monogeneans: the “Russian-doll killers”. Advances in Parasitology 64, 161–376 (2007)
Blackledge, J.M., Dubovitskiy, A.: Object detection and classification with applications to skin cancer screening. Intelligent Systems 1(1), 34–45 (2008)
Choi, J., Chung, Y., Kim, K., Yoo, J.: Face recognition using energy probability in DCT domain, pp. 1549–1552. IEEE (2006)
Cootes, T.F., Edwards, G.J., Taylor, C.J.: Active appearance models. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 23(6), 681–685 (2001)
Cordella, L.P., Limongiello, A., Sansone, C.: Network intrusion detection by a multi-stage classification system. In: Roli, F., Kittler, J., Windeatt, T. (eds.) MCS 2004. LNCS, vol. 3077, pp. 324–333. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Du, J.X., Wang, X.F., Zhang, G.J.: Leaf shape based plant species recognition. Applied Mathematics and Computation 185(2), 883–893 (2007)
Hansen, H., Bachmann, L., Bakke, T.: Mitochondrial DNA variation of Gyrodactylus spp. (Monogenea, Gyrodactylidae) populations infecting Atlantic salmon, grayling, and rainbow trout in Norway and Sweden. Parasitology 33, 1471–1478 (2003)
Harris, P.D., Shinn, A.P., Cable, J., Bakke, T.A.: Nominal species of the genus Gyrodactylus v. Nordmann 1832 (Monogenea: Gyrodactylidae), with a list of principal host species. Systematic Parasitology 59, 1–27 (2004)
Kabir, M.F., Schmoldt, D.L., Araman, P.A., Schafer, M.E., Lee, S.M.: Classifying defects in pallet stringers by ultrasonic scanning. Wood and Fiber Science 34 (2003)
Lai, C.H., Yu, S.S., Tseng, H.Y., Tsai, M.H.: A protozoan parasite extraction scheme for digital microscope images. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 34, 122–130 (2010)
Lee, J.S., Wu, H.H., Yuan, M.Z.: Lung segmentation for chest radiograph by using adaptive active shape models. In: Int. Conf. on Information Assurance and Security, pp. 383–386 (2009)
Maini, R., Aggarwal, H.: Study and comparison of various image edge detection techniques. Image Processing 3(1), 1–60 (2009)
Meinila, M., Kuusela, J., Zietara, M.: Brief report: Primers for amplifying 820 bp of highly polymorphic mitochondrial COI gene of Gyrodactylus salaris. Hereditas 137, 72–74 (2002)
Shinn, A.P., Collins, C., García-Vásquez, A., Snow, M., Paladini, G., Lindenstrøm, T., Longshaw, M., Matĕjusová, I., Stone, D.M., Turnbull, J.F., Picon-Camacho, S.M., Vázquez Rivera, C., Duguid, R.A., Mo, T.A., Hansen, H., Olstad, K., Cable, J., Harris, P.D., Kerr, R., Graham, D., Yoon, G.H., Buchmann, K., Raynard, R., Irving, S., Bron, J.E.: Multi-centre testing and validation of current protocols for Gyrodactylus salaris (Monogenea) identification. International Journal of Parasitology 40, 1455–1467 (2010)
Shinn, A.P., Hansen, H., Bachmann, L., Bakke, T.A.: The use of morphometric characters to discriminate specimens of laboratory-reared and wild populations of Gyrodactylus salaris and G. thymalli (monogenea). Folia Parasitologica 51, 239–252 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ali, R., Jiang, B., Man, M., Hussain, A., Luo, B. (2014). Classification of Fish Ectoparasite Genus Gyrodactylus SEM Images Using ASM and Complex Network Model. In: Loo, C.K., Yap, K.S., Wong, K.W., Beng Jin, A.T., Huang, K. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8836. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12643-2_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12643-2_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-12642-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-12643-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)