Abstract
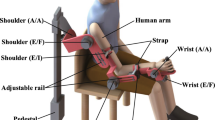
Power-assist robots are expected to work in many fields such as industry, military, medicine, etc. A lower-limb power-assist robot for physically weak persons is supposed to be used for self-rehabilitation or daily motion assist. In order to assist daily motion of the physically weak persons, the robot must estimate the motion intention of the user in real-time. Although there are several kinds of method to estimate the motion intention of the user in real-time, Electromyogram (EMG) signals are often used to estimate that since they reflect the users muscle activities. However, EMG-based real-time motion estimation is not very easy because of several reasons. In this chapter, an EMG-based control method is introduced to control the power-assist lower-limb exoskeleton robot in accordance with users motion intention. A neuro-fuzzy modifier is applied to deal with those problems. The problems of EMG-based motion estimation are cleared by applying the neuro-fuzzy modifier.
Sometimes there is a problem in the users motion even though the users motion is assisted, if the user misunderstands interaction between the users motion and a surrounding environment. In that case, the users motion should be modified to avoid an accident. In this chapter, a method of perception-assist is also introduced to automatically modify the users motion properly.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guizzo, E., Goldstein, H.: The Rise of the Body Bots. IEEE Spectrum 42(10), 42–48 (2005)
Dollar, A.M., Herr, H.: Lower Extremity Exoskeletons and Active Orthoses: Challenges and State-of-the-Art. IEEE Trans. on Robotics 24(1), 144–158 (2008)
Yang, C.J., Zhang, J.F., Chen, Y., Dong, Y.M., Zhang, Y.: A Review of Exoskeleton-type Systems and Their Key Technologies. Proc. of IMechE, Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, Part C 222, 1599–1612 (2008)
Rosen, J., Brand, M., Fuchs, M., Arcan, M.: A Myosignal-Based Powered Exoskeleton System. IEEE Trans. on System Man and Cybernetics, Part A 31(3), 210–222 (2001)
Kiguchi, K., Kariya, S., Watanabe, K., Izumi, K., Fukuda, T.: An Exoskeletal Robot for Human Elbow Motion Support. Sensor Fusion, Adaptation, and Control. IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B 31(3), 353–361 (2001)
Kiguchi, K., Tanaka, T., Fukuda, T.: Neuro-Fuzzy Control of a Robotic Exoskeleton with EMG Signals. IEEE Trans. on Fuzzy Systems 12(4), 481–490 (2004)
Kiguchi, K., Esaki, R., Fukuda, T.: Development of a Wearable Exoskeleton for Daily Forearm Motion Assist. Advanced Robotics 19(7), 751–771 (2005)
Cavallaro, E.E., Rosen, J., Perry, J.C., Burns, S.: Gravity-balancing leg orthosis and its performance evaluation. IEEE Trans. Robotics 22(6), 1228–1239 (2006)
Riener, R., Lünenburger, L., Jezernik, S., Anderschitz, M., Colombo, G., Dietz, V.: Patient-cooperative strategies for robot-aided treadmill training: first experimental results. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 13(3), 380–394 (2005)
Hogan, N.: Impedance control: an approach to manipulation, parts I, II, III. J. Dyn. Syst., Meas. Control 107, 1–23 (1985)
Blaya, J., Herr, H.: Adaptive control of a variable-impedance ankle-foot orthosis to assist drop-foot gait. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 12(1), 24–31 (2004)
Bar-Cohen, Y.: Electroactive Polymer (EAP) Actuators as Artificial Muscles - Reality, Potential and Challenges. SPIE Press (2004)
Noritsugu, T., Tanaka, T.: Application of rubber artificial muscle manipulator as a rehabilitation robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2(4), 259–267 (1997)
Buerger, S.P., Hogan, N.: Complementary stability and loop shaping for improved human-robot interaction. IEEE Trans. Robotics 23(2), 232–244 (2007)
Paluska, D., Herr, H.: Series elasticity and actuator power output. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics Autom.: ICRA 2006, pp. 1830–1833 (2006)
Kong, K., Tomizuka, M.: Flexible joint actuator for patient’s rehabilitation device. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Robot Human Interactive Commun.: ROMAN 2007, pp. 1179–1184 (2007)
Pratt, J., Krupp, B., Morse, C.: Series elastic actuators for high fidelity force control. Int. J. Ind. Robot 29(3), 234–241 (2002)
Low, K.H.: Initial experiments of a leg mechanism with a flexible geared joint and footpad. Adv. Robotics 19(4), 373–399 (2005)
Pratt, G.A., Williamson, M.W.: Series elastic actuators. In: Proc. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intell. Robotics Syst.: IROS 1995, Pittsburgh, PA, pp. 399–406 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kiguchi, K., Hayashi, Y. (2015). EMG-Based Control of a Lower-Limb Power-Assist Robot. In: Mohammed, S., Moreno, J., Kong, K., Amirat, Y. (eds) Intelligent Assistive Robots. Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, vol 106. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12922-8_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12922-8_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-12921-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-12922-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)