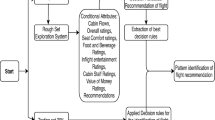
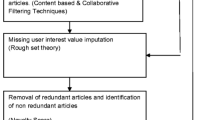
Abstract
Recommender systems are emerging as an important business tool in E-commerce. The recommendations in these systems typically rely on some sort of intelligent mechanisms that analyze previous user trends and ratings to make personalized recommendations. In this article, we examine the application of game-theoretic rough set (GTRS) model as an alternative intelligent component for recommender systems. The role of GTRS is examined by considering two important properties of recommendations. The first property is the accuracy of recommendations and the second property is the generality or support of recommendations. It is argued that making highly accurate recommendations for majority of the users is a major hindrance and difficulty for improving the performance of recommender systems. The GTRS meets this challenge by examining a tradeoff solution between the properties of accuracy and generality. Experimental results on movielen dataset suggest that the GTRS improves the two properties of recommendations compared to the standard Pawlak rough set model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grouplens research, http://www.grouplens.org
Azam, N., Yao, J.T.: Analyzing uncertainties of probabilistic rough set regions with game-theoretic rough sets. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 55(1), 142–155 (2014)
Bobadilla, J., Ortega, F., Hernando, A., Gutiérrez, A.: Recommender systems survey. Knowledge-Based Systems 46, 109–132 (2013)
Ge, M., Delgado-Battenfeld, C., Jannach, D.: Beyond accuracy: evaluating recommender systems by coverage and serendipity. In: Proceedings of the Fourth ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 257–260 (2010)
Herbert, J.P., Yao, J.T.: Game-theoretic rough sets. Fundamenta Informaticae 108(3-4), 267–286 (2011)
Herlocker, J.L., Konstan, J.A., Terveen, L.G., Riedl, J.T.: Evaluating collaborative filtering recommender systems. ACM Transactions on Information Systems 22(1), 5–53 (2004)
Leyton-Brown, K., Shoham, Y.: Essentials of Game Theory: A Concise Multidisciplinary Introduction. Morgan & Claypool Publishers (2008)
Lin, W., Alvarez, S.A., Ruiz, C.: Efficient adaptive-support association rule mining for recommender systems. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 6(1), 83–105 (2002)
Hernández del Olmo, F., Gaudioso, E.: Evaluation of recommender systems: A new approach. Expert Systems with Applications 35(3), 790–804 (2008)
Pazzani, M.J.: A framework for collaborative, content-based and demographic filtering. Artificial Intelligence Review 13(5-6), 393–408 (1999)
Su, X.Y., Khoshgoftaar, T.M.: A survey of collaborative filtering techniques. Advances in Artificial Intelligence 2009, 1–19 (2009)
Yao, J.T., Herbert, J.P.: A game-theoretic perspective on rough set analysis. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition) 20(3), 291–298 (2008)
Yao, Y.Y.: Two semantic issues in a probabilistic rough set model. Fundamenta Informaticae 108(3-4), 249–265 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Azam, N., Yao, J. (2014). Application of Game-Theoretic Rough Sets in Recommender Systems. In: Murty, M.N., He, X., Chillarige, R.R., Weng, P. (eds) Multi-disciplinary Trends in Artificial Intelligence. MIWAI 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8875. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13365-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13365-2_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-13364-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-13365-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)