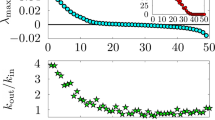
Abstract
In previous work I examined an information based complexity measure of networks with weighted links. The measure was compared with that obtained from by randomly shuffling the original network, forming an Erdös-Rényi random network preserving the original link weight distribution. It was found that real world networks almost invariably had higher complexity than their shuffled counterparts, whereas networks mechanically generated via preferential attachment did not.
In this paper, I report on a mechanical network generation system that does produce this complexity surplus. The heart of the idea is to construct the network of state transitions of a chaotic dynamical system, such as the Lorenz equation. This indicates that complexity surplus is a more fundamental trait than that of being an evolutionary system.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dehmer, M., Mowshowitz, A.: A case study of cracks in the scientific enterprise: Reinvention of information-theoretic measures for graphs. Complexity (2014), doi:10.1002/cplx.21540
Langton, C.G.: Computation at the edge of chaos: Phase transitions and emergent computation. Physica D 42, 12–37 (1990)
Li, M., Vitányi, P.: An Introduction to Kolmogorov Complexity and its Applications, 2nd edn. Springer (1997)
Lubiw, A.: Some NP-complete problems similar to graph isomorphism. SIAM Journal on Computing 10(1), 11–21 (1981), http://link.aip.org/link/?SMJ/10/11/1
Monaco, M., Ulanowicz, R.: Comparative ecosystem trophic structure of three U.S. Mid-Atlantic estuaries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 161, 239–254 (1997)
Mowshowitz, A.: Entropy and the complexity of graphs: I. an index of the relative complexity of a graph. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 30(1), 175–204 (1968)
Mowshowitz, A.: Entropy and the complexity of graphs: II. the information content of digraphs and infinite graphs. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 30(2), 225–240 (1968)
Mowshowitz, A.: Entropy and the complexity of graphs: III. graphs with prescribed information content. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 30(3), 387–414 (1968)
Mowshowitz, A.: Entropy and the complexity of graphs: IV. entropy measures and graphical structure. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 30(4), 533–546 (1968)
Small, M.: Complex networks from time series: Capturing dynamics. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems Proceedings, pp. 2509–2512 (2013)
Standish, R.K.: Network complexity of foodwebs. In: Fellerman, H., et al. (eds.) Proceedings of Artificial Life XII, pp. 337–343. MIT Press, Cambridge (2010)
Standish, R.K.: Complexity of networks (reprise). Complexity 17, 50–61, arXiv: 0911.3482 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Standish, R.K. (2015). Mechanical Generation of Networks with Surplus Complexity. In: Chalup, S.K., Blair, A.D., Randall, M. (eds) Artificial Life and Computational Intelligence. ACALCI 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8955. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14803-8_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14803-8_30
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-14802-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-14803-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)