Abstract
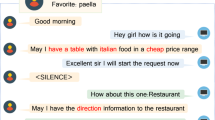
This study introduces a personalization framework for dialog systems. Our system automatically collects user-related facts (i.e. triples) from user input sentences and stores the facts in one-shot memory. The system also keeps track of changes in user interests. Extracted triples and entities (i.e. NP-chunks) are stored in a personal knowledge base (PKB) and a forgetting model manages their retention (i.e. interest). System responses can be modified by applying user-related facts to the one-shot memory. A relevance score of a system response is proposed to select responses that include high-retention triples and entities, or frequently used responses. We used Movie-Dic corpus to construct a simple dialog system and train PKBs. The retention sum of responses was increased by adopting the PKB, and the number of inappropriate responses was decreased by adopting relevance score. The system gave some personalized responses, while maintaining its performance (i.e. appropriateness of responses).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
Knowledge units consist of the same lemmas except their articles and determiners mostly have similarity >0.8.
- 3.
μ is the same as the initial value of the retention.
References
Leach, M.J.: Rapport: A key to treatment success. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 11, 262–265 (2005)
Zue, V., Seneff, S., Glass, J., Polifroni, J., Pao, C., Hazen, T., Hetherington, L.: JUPITER: A telephone-based conversational interface for weather information. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 8, 85–96 (2000)
Wei, X., Rudnicky, A.I.: An agenda-based dialog management architecture for spoken language systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE ASRU. Seattle, WA (1999)
Young, S.J., Gašić, M., Keizer, S., Mairesse, F., Schatzmann, J., Thomson, B., Yu, K.: The hidden information state model: a practical framework for POMDP-based spoken dialogue management. Comput. Speech Lang. 24(2), 150–174 (2010)
Lee, C., Jung, S., Kim, S., Lee, G.G.: Example-based dialog modeling for practical multi-domain dialog system. Speech Commun. 51(5), 466–484 (2009)
Schlangen, D., Skantze, G.: A general, abstract model of incremental dialogue processing. In: Proceedings of EACL 2009. Athens, Greece (2009)
Weizenbaum, J.: ELIZA – A computer program for the study of natural language communication between man and machine. Commun. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 9, 36–45 (1966)
Shen, X., Tan, B., Zhai, C.: Implicit user modeling for personalized search. In: Proceedings of CIKM 2005, pp. 824–831 (2005)
Qiu, F., Cho, J.: Automatic identification of user interest for personalized search. In: Proceedings of the 15th International World Wide Web Conference, WWW 2006, pp. 727–736, Edinburgh, Scotland, May 2006
Ardissono, L., Gena, C., Torasso, P., Bellifemine, F., Difino, A., Negro, B.: User modeling and recommendation techniques for personalized electronic program guides, Personalized Digital Television: Targeting Programs to Individual Viewers, pp. 3–26. Kluwer (2004)
Jiang, Y., Liu, J., Tang, M., Liu, X.F.: An effective web service recommendation method based on personalized collaborative filtering. In: ICWS, pp. 211–218 (2011)
Ebbinghaus, H.: Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology. Dover, New York (1885). (Transl. by Ruger, H.A., Bussenius, C.E., 1964)
Banchs, R.E.: Movie-DiC: a movie dialogue corpus for research and development. In: Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the ACL (2012)
F. Wu and D. S. Weld, 2010. Open information extraction using Wikipedia. In Proc. of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL ’10, pp. 118–127, Morristown, NJ, USA
Zhou, B., Zhang, B., Liu, Y., Xing, K.: User model evolution algorithm: forgetting and reenergizing user preference. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings/CPSCom), pp. 444–447
Ratnaparkhi, A.: A maximum entropy part-of-speech tagger. In: Proceedings of the Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing Conference (1996)
Collins, M.: Discriminative training methods for Hidden Markov Models: Theory and experiments with perceptron algorithms. In: EMNLP 2002
Nivre, J., Hall, J., Nilsson, J., Chanev, A., Eryigit, G., Kubler, S., Marinov, S., Andmarsi, E.: MaltParser: A language-independent system for data-driven dependency parsing. Natural Lang. Eng. 13(2), 95–135 (2007)
Zhang, Y., Nivre, J.: Transition-based dependency parsing with rich non-local features. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 188–193, Portland, Oregon, USA, June 2011
Acknowledgement
This paper was partly supported by ICT R&D program of MSIP/IITP [10044508, Development of Non-Symbolic Approach-based Human-Like Self-Taught Learning Intelligence Technology] and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by Korea government (MSIP) [NRF-2014R1A2A1A01003041].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kim, Y., Bang, J., Choi, J., Ryu, S., Koo, S., Lee, G.G. (2015). Acquisition and Use of Long-Term Memory for Personalized Dialog Systems. In: Böck, R., Bonin, F., Campbell, N., Poppe, R. (eds) Multimodal Analyses enabling Artificial Agents in Human-Machine Interaction. MA3HMI 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8757. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15557-9_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15557-9_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-15556-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-15557-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)