Abstract
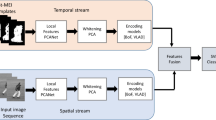
Human action recognition in video has found widespread applications in many fields. However, this task is still facing many challenges due to the existence of intra-class diversity and inter-class overlaps among different action categories. The key trick of action recognition lies in the extraction of more comprehensive features to cover the action, as well as a compact and discriminative video encoding representation. Based on this observation, in this paper we propose a hybrid feature descriptor, which combines both static descriptor and motional descriptor to cover more action information inside video clips. We also adopt the usage of VLAD encoding method to encapsulate more structural information within the distribution of feature vectors. The recognition effects of our framework are evaluated on three benchmark datasets: KTH, Weizmann, and YouTube. The experimental results demonstrate that the hybrid descriptor, facilitated with VLAD encoding method, outperforms traditional descriptors by a large margin.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jégou, H., Douze, M., Schmid, C., Pérez, P.: Aggregating local descriptors into a compact image representation. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3304–3311. IEEE (2010)
Arandjelovic, R., Zisserman, A.: All about vlad. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1578–1585. IEEE (2013)
Wang, H., Ullah, M.M., Klaser, A., Laptev, I., Schmid, C., et al.: Evaluation of local spatio-temporal features for action recognition. In: BMVC 2009-British Machine Vision Conference (2009)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2005, vol. 1, pp. 886–893. IEEE (2005)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B., Schmid, C.: Human detection using oriented histograms of flow and appearance. In: Leonardis, A., Bischof, H., Pinz, A. (eds.) ECCV 2006. LNCS, vol. 3952, pp. 428–441. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Wang, H., Klaser, A., Schmid, C., Liu, C.L.: Action recognition by dense trajectories. In: 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3169–3176. IEEE (2011)
Liu, J., Luo, J., Shah, M.: Recognizing realistic actions from videos in the wild. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2009, pp. 1996–2003. IEEE (2009)
Gorelick, L., Blank, M., Shechtman, E., Irani, M., Basri, R.: Actions as space-time shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29, 2247–2253 (2007)
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., Caputo, B.: Recognizing human actions: a local svm approach. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2004, vol. 3, pp. 32–36. IEEE (2004)
Poppe, R.: A survey on vision-based human action recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 28, 976–990 (2010)
Bobick, A.F., Davis, J.W.: The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23, 257–267 (2001)
Carlsson, S., Sullivan, J.: Action recognition by shape matching to key frames. In: Workshop on Models versus Exemplars in Computer Vision, vol. 1, p. 18 (2001)
Efros, A.A., Berg, A.C., Mori, G., Malik, J.: Recognizing action at a distance. In: Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Proceedings, pp. 726–733. IEEE (2003)
Laptev, I., Marszalek, M., Schmid, C., Rozenfeld, B.: Learning realistic human actions from movies. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2008, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2008)
Lowe, D.G.: Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: The Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer vision, vol. 2, pp. 1150–1157. IEEE (1999)
Klaser, A., Marszalek, M.: A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients (2008)
Scovanner, P., Ali, S., Shah, M.: A 3-dimensional sift descriptor and its application to action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 357–360. ACM (2007)
Willems, G., Tuytelaars, T., Van Gool, L.: An efficient dense and scale-invariant spatio-temporal interest point detector. In: Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A. (eds.) ECCV 2008, Part II. LNCS, vol. 5303, pp. 650–663. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Dollár, P., Rabaud, V., Cottrell, G., Belongie, S.: Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features. In: 2nd Joint IEEE International Workshop on Visual Surveillance and Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance, pp. 65–72. IEEE (2005)
Laptev, I., Pérez, P.: Retrieving actions in movies. In: IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2007, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2007)
Lin, Z., Jiang, Z., Davis, L.S.: Recognizing actions by shape-motion prototype trees. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 444–451. IEEE (2009)
Liu, J., Ali, S., Shah, M.: Recognizing human actions using multiple features. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2008, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2008)
Liu, J., Shah, M.: Learning human actions via information maximization. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2008, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2008)
Wang, J., Yang, J., Yu, K., Lv, F., Huang, T., Gong, Y.: Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3360–3367. IEEE (2010)
Perronnin, F., Sánchez, J., Mensink, T.: Improving the fisher kernel for large-scale image classification. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010, Part IV. LNCS, vol. 6314, pp. 143–156. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Zhou, X., Yu, K., Zhang, T., Huang, T.S.: Image classification using super-vector coding of local image descriptors. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010, Part V. LNCS, vol. 6315, pp. 141–154. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Kovashka, A., Grauman, K.: Learning a hierarchy of discriminative space-time neighborhood features for human action recognition. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2046–2053. IEEE (2010)
Yang, J., Yu, K., Gong, Y., Huang, T.: Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2009, pp. 1794–1801. IEEE (2009)
Laptev, I.: On space-time interest points. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 64, 107–123 (2005)
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: Libsvm: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2, 27 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Liu, X., Chang, M.-C., Ge, W., Chen, T.: Spatio-temporal phrases for activity recognition. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012, Part III. LNCS, vol. 7574, pp. 707–721. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Reddy, K.K., Shah, M.: Recognizing 50 human action categories of web videos. Mach. Vis. Appl. 24, 971–981 (2013)
Ikizler-Cinbis, N., Sclaroff, S.: Object, scene and actions: combining multiple features for human action recognition. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010, Part I. LNCS, vol. 6311, pp. 494–507. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Le, Q.V., Zou, W.Y., Yeung, S.Y., Ng, A.Y.: Learning hierarchical invariant spatio-temporal features for action recognition with independent subspace analysis. In: 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3361–3368. IEEE (2011)
Brendel, W., Todorovic, S.: Activities as time series of human postures. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010, Part II. LNCS, vol. 6312, pp. 721–734. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Cao, X., Zhang, H., Deng, C., Liu, Q., Liu, H.: Action recognition using 3d daisy descriptor. Mach. Vis. Appl. 25, 159–171 (2014)
Grundmann, M., Meier, F., Essa, I.: 3d shape context and distance transform for action recognition. In: 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2008, pp. 1–4. IEEE (2008)
Fathi, A., Mori, G.: Action recognition by learning mid-level motion features. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2008, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2008)
Schindler, K., Van Gool, L.: Action snippets: How many frames does human action recognition require? In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2008, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2008)
Cai, Q., Yin, Y., Man, H.: Learning spatio-temporal dependencies for action recognition, ICIP (2013)
Liu, L., Shao, L., Zhen, X., Li, X.: Learning discriminative key poses for action recognition (2013)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by NSFC (No.61272247 and 60873133), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No.13511500200), 863 (No.2008AA02Z310) in China and the European Union Seventh Frame work Programme (Grant No.247619).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xing, D., Wang, X., Lu, H. (2015). Action Recognition Using Hybrid Feature Descriptor and VLAD Video Encoding. In: Jawahar, C., Shan, S. (eds) Computer Vision - ACCV 2014 Workshops. ACCV 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9008. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16628-5_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16628-5_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-16627-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-16628-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)