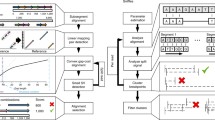
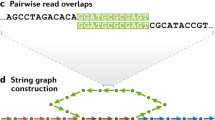
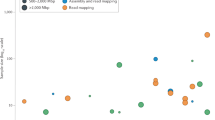
Abstract
The rapid advance of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has decreased the cost of genomic sequencing dramatically, enabling accurate variant discovery across whole genomes of many individuals. Current large-scale and cost-effective resequencing platforms produce reads of limited length, and as a result, reliable identification of variants within highly homologous regions of a target genome remains challenging.
A. Bishara and Y. Liu—contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis, G.R., Auton, A., Brooks, L.D., DePristo, M.A., Durbin, R.M., Handsaker, R.E., Kang, H.M., Marth, G.T., McVean, G.A.: An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 491(7422), 56–65 (2012)
Kuleshov, V., Xie, D., Chen, R., Pushkarev, D., Ma, Z., Blauwkamp, T., Kertesz, M., Snyder, M.: Whole-genome haplotyping using long reads and statistical methods. Nat Biotechnol 32(3), 261–266 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bishara, A. et al. (2015). Read Clouds Uncover Variation in Complex Regions of the Human Genome. In: Przytycka, T. (eds) Research in Computational Molecular Biology. RECOMB 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9029. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16706-0_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16706-0_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-16705-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-16706-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)