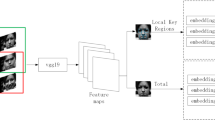
Abstract
Expressions are facial activities invoked by sets of muscle motions, which would give rise to large variations in appearance mainly around facial parts. Therefore, for visual-based expression analysis, localizing the action parts and encoding them effectively become two essential but challenging problems. To take them into account jointly for expression analysis, in this paper, we propose to adapt 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (3D CNN) with deformable action parts constraints. Specifically, we incorporate a deformable parts learning component into the 3D CNN framework, which can detect specific facial action parts under the structured spatial constraints, and obtain the discriminative part-based representation simultaneously. The proposed method is evaluated on two posed expression datasets, CK+, MMI, and a spontaneous dataset FERA. We show that, besides achieving state-of-the-art expression recognition accuracy, our method also enjoys the intuitive appeal that the part detection map can desirably encode the mid-level semantics of different facial action parts.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pantic, M., Rothkrantz, L.: Automatic analysis of facial expressions: the state of the art. IEEE T PAMI 22, 1424–1445 (2000)
Zeng, Z., Pantic, M., Roisman, G., Huang, T.: A survey of affect recognition methods: audio, visual, and spontaneous expressions. IEEE T PAMI 31, 39–58 (2009)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86, 2278–2324 (1998)
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., Yu, K.: 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE T PAMI 35, 221–231 (2013)
Klaser, A., Marszalek, M.: A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3D-gradients. In: BMVC (2008)
Zhao, G., Pietikainen, M.: Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE T PAMI 29, 915–928 (2007)
Felzenszwalb, P., Girshick, R., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D.: Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE T PAMI 32, 1627–1645 (2010)
Lucey, P., Cohn, J., Kanade, T., Saragih, J., Ambadar, Z., Matthews, I.: The extended cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): a complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In: CVPRW (2010)
Chew, S., Lucey, P., Lucey, S., Saragih, J., Cohn, J., et al.: Person-independent facial expression detection using constrained local models. In: FG (2011)
Cootes, T., Edwards, G., Taylor, C., et al.: Active appearance models. IEEE T PAMI 23, 681–685 (2001)
Cristinacce, D., Cootes, T.F.: Feature detection and tracking with constrained local models. In: BMVC (2006)
Ouyang, W., Wang, X.: Joint deep learning for pedestrian detection. In: ICCV (2013)
Nair, V., Hinton, G.: Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: ICML (2010)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS (2012)
Zhu, Z., Luo, P., Wang, X., Tang, X.: Deep learning identity preserving face space. In: ICCV (2013)
Coates, A., Ng, A., Lee, H.: An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning. In: ICAIS (2011)
Xiong, X., De la Torre, F.: Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment. In: CVPR (2013)
Bouvrie, J.: Notes on convolutional neural networks (2006)
Qian, N.: On the momentum term in gradient descent learning algorithms. Neural Netw. 12, 145–151 (1999)
Valstar, M., Pantic, M.: Induced disgust, happiness and surprise: an addition to the MMI facial expression database. In: LRECW (2010)
Valstar, M.F., Mehu, M., Jiang, B., Pantic, M., Scherer, K.: Meta-analysis of the first facial expression recognition challenge. IEEE TSMCB 42, 966–979 (2012)
Kanade, T., Cohn, J., Tian, Y.: Comprehensive database for facial expression analysis. In: FG (2000)
Ekman, P., Friesen, W.: Facial Action Coding System: A Technique for the Measurement of Facial Movement. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto (1978)
Bänziger, T., Scherer, K.R.: Introducing the geneva multimodal emotion portrayal (GEMEP) corpus. In: Scherer, K.R., Bänziger, T., Roesch, E.B. (eds.) Blueprint for Affective Computing: A Sourcebook, pp. 271–294. Oxford university Press, Oxford (2010)
Wang, Z., Wang, S., Ji, Q.: Capturing complex spatio-temporal relations among facial muscles for facial expression recognition. In: CVPR (2013)
Kanou, S., Pal, C., Bouthillier, X., Froumenty, P., Gülçehre, Ç., Memisevic, R., Vincent, P., Courville, A., Bengio, Y., Ferrari, R., et al.: Combining modality specific deep neural networks for emotion recognition in video. In: ICMI (2013)
Acknowledgement
The work is partially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China under contracts nos. 61379083, 61272321, 61272319, and the FiDiPro program of Tekes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, M., Li, S., Shan, S., Wang, R., Chen, X. (2015). Deeply Learning Deformable Facial Action Parts Model for Dynamic Expression Analysis. In: Cremers, D., Reid, I., Saito, H., Yang, MH. (eds) Computer Vision -- ACCV 2014. ACCV 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9006. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16817-3_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16817-3_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-16816-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-16817-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)