Abstract
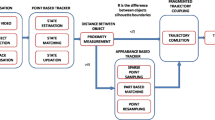
Successful multi-object tracking requires consistently maintaining object identities and real-time performance. This task becomes more challenging when objects are indistinguishable from one another. This paper presents a Bayesian framework for maintaining the identities of multiple objects. Our semi-independent joint motion model (SIMM) solves the coalescence and identity switching problem in real time. This joint motion model is a non-parametric mixture model that simultaneously captures linear motion and repulsive motion. Linear motion is a constant velocity model, while repulsive motion is described by a repulsive potential in MRF. By maintaining multimodality from multiple motion models, we can infer the appropriate motion model using image evidence and consequently avoid many identity switching errors. Moreover, we develop a new sampling method that does not suffer from the curse of dimensionality because of the availability of high-quality samples. Experimental results show that our approach can track numerous objects in real time and maintain identities under difficult situations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrieu, C., De Freitas, N., Doucet, A., Jordan, M.: An introduction to MCMC for machine learning. Mach. Learn. 50, 5–43 (2003)
Andriyenko, A., Schindler, K., Roth, S.: The Discrete-continuous optimization for multi-target tracking. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2012)
Bazzani, L., Cristani, M., Murino, V.: Decentralized particle filter for joint individual-group tracking. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2012)
Breitenstein, M.D., Reichlin, F., Leibe, B., Koller-Meier, E., Van Gool, L.: Online multiperson tracking-by-detection from a single, uncalibrated camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33, 1820–1833 (2011)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2005)
Dicle, C., Camps, O.I., Sznaier, M.: The way they move: tracking multiple targets with similar appearance. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (2013)
Hess, R., Fern, A.: Discriminatively trained particle filters for complex multi-object tracking. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2009)
Isard, M., Blake, A.: A mixed-state condensation tracker with automatic model-switching. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (1998)
Khan, Z., Balch, T., Dellaert, F.: Efficient particle filter-based tracking of multiple interacting targets using an MRF-based motion model. In: International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (2003)
Khan, Z., Balch, T., Dellaert, F.: MCMC-based particle filtering for tracking a variable number of interacting targets. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27, 1805–1819 (2005)
Kwon, J., Lee, K.M.: Visual tracking decomposition. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2010)
Lanz, O.: Approximate bayesian multibody tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28, 1436–1449 (2006)
Leibe, B., Schindler, K., Cornelis, N., Van Gool, L.: Coupled object detection and tracking from static cameras and moving vehicles. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 30, 1683–1698 (2008)
Lerner, U., Parr, R.: Inference in hybrid networks: Theoretical limits and practical algorithms. In: Proceedings of the Seventeenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (2001)
Liu, J., Carr, P., Collins, R.T., Liu, Y.: Tracking sports players with context-conditioned motion models. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2013)
Milan, A., Schindler, K., Roth, S.: Detection-and trajectory-level exclusion in multiple object tracking. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2013)
MacCormick, J., Blake, A.: A probabilistic exclusion principle for tracking multiple objects. Int. J. Comput. Vision 39, 57–71 (2000)
Oh, S., Rehg, J., Balch, T., Dellaert, F.: Learning and inferring motion patterns using parametric segmental switching linear dynamic systems. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 77, 103–124 (2008)
Okuma, K., Taleghani, A., de Freitas, N., Little, J.J., Lowe, D.G.: A boosted particle filter: multitarget detection and tracking. In: Pajdla, T., Matas, J.G. (eds.) ECCV 2004. LNCS, vol. 3021, pp. 28–39. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Pellegrini, S., Ess, A., Schindler, K., Van Gool, L.: You’ll never walk alone: Modeling social behavior for multi-target tracking. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (2009)
Perera, A., Srinivas, C., Hoogs, A., Brooksby, G., Hu, W.: Multi-object tracking through simultaneous long occlusions and split-merge conditions. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2006)
Pitt, M., Shephard, N.: Filtering via simulation: auxiliary particle filters. Int. j. comput. vis. 94, 590–599 (1999)
Qu, W., Schonfeld, D., Mohamed, M.: Real-time distributed multi-object tracking using multiple interactive trackers and a magnetic-inertia potential model. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 9, 511–519 (2007)
Segal, A.V., Reid, I.: Latent data association: bayesian model selection for multi-target tracking. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (2013)
Vermaak, J., Doucet, A., Prez, P.: Maintaining multimodality through mixture tracking. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (2003)
Vermaak, J., Godsill, S., Perez, P.: Monte carlo filtering for multi target tracking and data association. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 41, 309–332 (2005)
Wu, B., Nevatia, R.: Detection and tracking of multiple, partially occluded humans by bayesian combination of edgelet based part detectors. Int. J. Comput. Vision 75, 247–266 (2007)
Xing, J., Ai, H., Lao, S.: Multi-object tracking through occlusions by local tracklets filtering and global tracklets association with detection responses. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2009)
Yang, B., Nevatia, R.: Multi-target tracking by online learning of non-linear motion patterns and robust appearance models. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2012)
Yu, T., Wu, Y.: Collaborative tracking of multiple targets. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2004)
Yu, T., Wu, Y.: Decentralized multiple target tracking using netted collaborative autonomous trackers. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2005)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61001195) and Technology Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province of China (2010JY0078). We would like to thank anonymous reviewers of this paper for helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shen, L., You, Z., Liu, Q. (2015). Real-Time Tracking of Multiple Objects by Linear Motion and Repulsive Motion. In: Cremers, D., Reid, I., Saito, H., Yang, MH. (eds) Computer Vision -- ACCV 2014. ACCV 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9006. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16817-3_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16817-3_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-16816-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-16817-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)