Abstract
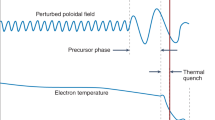
The L-H transition is a remarkable self-organization phenomenon that occurs in Magnetically Confined Nuclear Fusion (MCNF) devices. For research reasons, it is relevant to create models able to determine the confinement regime the plasma is in by using, from the wide number of measured signals in each discharge, just a reduce number of them. Also desirable is that a general model, applicable not only to one device but to all of them, is reached. From a data-driven modelling point of view it implies the careful —and hopefully, automatic— selection of the phenomenon’s related signals to input them into an equation able to determine the confinement mode. Using a supervised machine learning method, it would also require the tuning of some internal parameters. This is an optimization problem, tackled in this study with Genetic Algorithms (GAs). The results prove that reliable and universal laws that describe the L-H transition with more than a ~98,60% classification accuracy can be attained using only 3 input signals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wagner, F., et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 1453–1456 (1984)
Chankin, A.V.: Fusion. Plasma Phys. Control 39, 1059 (1997)
Rogister, A.L.: Fusion. Plasma Phys. Control 36, A219 (1994)
Scott, B., et al.: In: Proc. 16th Int. Conf. on Fusion Energy (Montreal, Canada, 1996), vol 2, 649. IAEA, Vienna (1996)
Shaing, K.C., Crume, E.C.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 2369 (1989)
Vega, J., et al.: Nucl. Fusion 49, 085023. doi:10.1088/0029-5515/49/8/085023
Rattá, G.A., et al.: Fusion Engineering and Design 83(2–3), 467–470, April 2008
Murari, A., et al.: Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 623(2), 850–854 (November 11, 2010)
Yao, K., Huang, Y.: 39th EPS Conference & 16th Int. Congress on Plasma Physics (2012)
http://efdasql.ipp.mpg.de/threshold/Public/ThresholdDbInfo/ThresholdvarDB2_3.htm
Mitchell, M.: MIT Press. (1996) ISBN 780585030944
Alander, J.T.: Proceedings CompEuro, Computer Systems and Software Engineering, 6th Annual European Computer Conference, pp. 65–70 (1992)
De Jong, K.A., Spears, W.M.: Parallel Problem Solving from Nature. LNCS, vol. 496, pp. 38-47. Springer, Heidelberg (1991)
Liu, Z.X., et al: Nucl. Fusion 53, 073041 (2013)
Maingi, R., et al: Nucl. Fusion 45, 1066 (2005)
Joachims, T.: Advances in Kernel Methods - Support Vector Learning. MIT-Press (1999)
MATLAB and Statistics Toolbox. The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, Massachusetts, United States
Briggs, T.: MATLAB/MEX Interface to SVMlight. http://sourceforge.net/projects/mex-svm/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rattá, G.A., Vega, J. (2015). Confinement Regime Identification Using Artificial Intelligence Methods. In: Gammerman, A., Vovk, V., Papadopoulos, H. (eds) Statistical Learning and Data Sciences. SLDS 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9047. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17091-6_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17091-6_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-17090-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-17091-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)