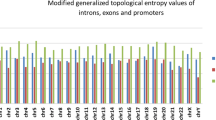
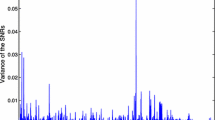
Abstract
In recent studies [1-3], lots of hidden homology in DNA genome are not found by current comparative tools despite decades of research. Many scholars modeled the genome as a monotonous string, which limits and probably obstructs the discovery of some significant patterns. We propose an information-coding-based model called DNA As X (DAX) to improve the sensitivity in comparative genomic studies by integrating the principles and concepts of other disciplines including information coding theory and signal processing into genome analysis. The proposed DNA As X model uses character-analysis-free (CAF) techniques, where X is the intermediate for analysis that can be digit, code, signal, vector, tree, graph network and so on. It provides novel and comprehensive perspectives to further analyze and recognize the critical patterns hidden in DNA genomes. Comparing with traditional character-analysis-based (CAB) methods, DAX not only enriches the tools and the knowledge library of computational biology but also extends the domain from 1-D character string analysis to 2-D spatial/temporal domain. Furthermore, by applying the DAX model to the issue of exon prediction as an evaluation, we illustrate the insights behind this model. The experimental results show that the DAX methodology can improve the sensitivity in genome analysis by using the novel information-coding techniques.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frith, M.C.: A new repeat-masking method enables specific detection of homologous sequences. Nucleic Acids Research 39(4), e23 (2011)
Frith, M.C., Noé, L.: Improved search heuristics find 20 000 new alignments between human and mouse genomes. Nucleic Acids Research 42(7), e59 (2014)
Trimble, W., Keegan, K., D’Souza, M., Wilke, A., Wilkening, J., Gilbert, J., Meyer, F.: Short-read reading-frame predictors are not created equal: sequence error causes loss of signal. BMC Bioinformatics 13(1), 183 (2012)
Djebali, S., Davis, C.A., Merkel, A., Dobin, A., Lassmann, T., Mortazavi, A.M., Schlesinger, F.: Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489(7414), 101–108 (2012)
ENCODE. An integrated encyclopedia of dna elements in the human genome. Nature 489(7414), 57–74 (September 2012)
Hiller, M., Schaar, B.T., Bejerano, G.: Hundreds of conserved non-coding genomic regions are independently lost in mammals. Nucleic Acids Research (2012)
Klimke, W., O’Donovan, C., White, O., Brister, J.R., Clark, K., Fedorov, B., Tatusova, T.: Solving the problem: Genome annotation standards before the data deluge. Standards in Genomic Sciences 5(1), 168–193 (2011)
Li, H., Homer, N.: A survey of sequence alignment algorithms for next-generation sequencing. Briefings in Bioinformatics 11(5), 473–483 (2010)
Wu, X., Cai, Z., Wan, X.-F., Hoang, T., Goebel, R., Lin, G.: Nucleotide composition string selection in HIV-1 subtyping using whole genomes. Bioinformatics 23(14), 1744–1752 (2007)
Cai, Z., Goebel, R., Salavatipour, M., Lin, G.: Selecting dissimilar genes for multi-class classification, an application in cancer subtyping. BMC Bioinformatics 8(1), 206 (2007)
Tesorero, R.A., Yu, N., Wright, J.O., Svencionis, J.P., Cheng, Q., Kim, J.-H., Cho, K.H.: Novel regulatory small rnas in streptococcus pyogenes. PLoS One 8(6), e64021(2013)
Guo, X., Meng, Y., Yu, N., Pan, Y.: Cloud computing for detecting high-order genome-wide epistatic interaction via dynamic clustering. BMC Bioinformatics 15(1), 102 (2014)
Yang, K., Cai, Z., Li, J., Lin, G.: A stable gene selection in microarray data analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 7(1), 228 (2006)
Cai, Z., Duan, Y., Li, Y., Lin, G., Ozden, M., Wan, X.F.: Ipminer: a progenitor gene identifier for influenza a virus. Influenza Other Respi. Viruses 5(suppl. 1), 413–415 (2011)
Silverman, B.D., Linsker, R.: A measure of DNA periodicity. Journal of Theoretical Biology 118(3), 295–300 (1986)
Voss, R.F.: Evolution of long-range fractal correlations and 1/ f noise in dna base sequences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3805–3808 (1992)
Cristea, P.D.: Genetic signal representation and analysis. In: Proc. SPIE, vol. 4623, pp. 77–84 (2002)
Rosen, G.L.: Signal Processing for BiBiological-inspired Gradient Source Localization and DNA Sequence Analysis. PhD thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering (August 2006)
Chakravarthy, N., Spanias, A., Iasemidis, L.D., Tsakalis, K.: Autoregressive modeling and feature analysis of DNA sequences. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing 2004(1), 952689 (2004)
Kent, W.J., Sugnet, C.W., Furey, T.S., Roskin, K.M., Pringle, T.H., Zahler, A.M., Haussler, D.: UCSC genome browser. Genome Res 12(6), 996–1006 (2002)
Kauer, G., Blöcker, H.: Applying signal theory to the analysis of biomolecules. Bioinformatics 19(16), 2016–2021 (2003)
Rosen, G.L.: Examining coding structure and redundancy in DNA. IEEE Engineerin. In: Medicine and Biology Magazine, Special Issue on Communication Theory, Coding Theory, and Molecular Biology 62–68 (January/February 2006)
Yoon, B.J.: Hidden markov models and their applications in biological sequence analysis. Current Genomic 10, 402–415 (2009)
Blahut, R.E.: Algebraic Codes for Data Transmission, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Breslauer, K.J., Frank, R.: Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 83(11), 3746–3750 (1986)
Crick, F.: Codon and anticodon pairing: the wobble hypothesis. Journal of Molecular Biology 19, 548–555 (1966)
Lin, S., Costello, D.J.: Error control coding: fundamentals and applications, vol. 114. Pearson-Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (2004)
Dubchak, I., Poliakov, A., Kislyuk, A., Brudno, M.: Multiple whole-genome alignments without a reference organism. Genome Res. 19, 682–689 (2009)
Batzoglou, S., Pachter, L., Mesirov, J.P., Berger, B., Lander, E.S.: Human and mouse gene structure: Comparative analysis and application to exon prediction. Genome Res. 10, 950–958 (2000)
Brudno, M., Do, C.B., Cooper, G.M., Kim, M.F., Davydov, E., Green, E.D., Sidow, A., Batzoglou, S.: LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: efficient tools for large-scale multiple alignment of genomic DNA. Genome Res., 13 (April 2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yu, N., Guo, X., Gu, F., Pan, Y. (2015). DNA AS X: An Information-Coding-Based Model to Improve the Sensitivity in Comparative Gene Analysis. In: Harrison, R., Li, Y., Măndoiu, I. (eds) Bioinformatics Research and Applications. ISBRA 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9096. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19048-8_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19048-8_31
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-19047-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-19048-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)