Abstract
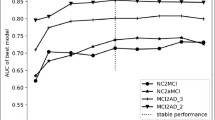
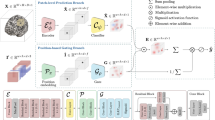
There has been significant interest in approaches that utilize local intensity patterns within patches to derive features for disease classification. Several existing methods explore the patch relationship between different subjects for classification. Other methods utilize the patch relationship within the same subject to aid classification. In this paper, we proposed a new approach to extract different types of features by utilizing the patch relationships within and between subjects. Specifically, features are first extracted by exploiting the patch relationship between subjects. Then, the relationship among patches within the same subject is modeled as a network and features are derived from the constructed network. Finally, these two different types of features are integrated into one framework for identifying mild cognitive impairment (MCI) subjects who will progress to Alzheimer’s disease. Using the standardized ADNI database, the proposed method can achieve an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 81.3 % in discriminating patients with stable MCI and progressive MCI in a 10-fold cross validation, demonstrating that the integration of patch relationship between and within subjects can aid the prediction of MCI to AD conversion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, D.E., Yaffe, K.: The projected effect of risk factor reduction on Alzheimer’s disease prevalence. Lancet Neurol. 10(9), 819–828 (2011)
Coupé, P., Eskildsen, S.F., Manjón, J.V., Fonov, V., Collins, D.L.: Simultaneous segmentation and grading of hippocampus for patient classification with Alzheimer’s disease. In: Fichtinger, G., Martel, A., Peters, T. (eds.) MICCAI 2011, Part III. LNCS, vol. 6893, pp. 149–157. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Coupé, P., Eskildsen, S.F., Manjon, J.V., Fonov, V.S., Pruessner, J.C., Allard, M., Collins, D.L.: Scoring by nonlocal image patch estimator for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage: Clin. 1(1), 141–152 (2012)
Cuingnet, R., Gerardin, E., Tessieras, J., Auzias, G., Lehéricy, S., Habert, M.O., Chupin, M., Benali, H., Colliot, O.: Automatic classification of patients with Alzheimer’s disease from structural MRI: a comparison of ten methods using the ADNI database. Neuroimage 56(2), 766–781 (2011)
Gray, K.R., Wolz, R., Heckemann, R.A., Aljabar, P., Hammers, A., Rueckert, D.: Multi-region analysis of longitudinal FDG-PET for the classification of Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 60(1), 221–229 (2012)
Grundman, M., Petersen, R.C., Ferris, S.H., Thomas, R.G., Aisen, P.S., Bennett, D.A., Foster, N.L., Jack, Jr., C.R., Galasko, D.R., Doody, R., et al.: Mild cognitive impairment can be distinguished from Alzheimer disease and normal aging for clinical trials. Arch. Neurol. 61(1), 59 (2004)
Haury, A.C., Gestraud, P., Vert, J.P.: The influence of feature selection methods on accuracy, stability and interpretability of molecular signatures. PLoS ONE 6(12), e28210 (2011)
Jack, C.R., Bernstein, M.A., Fox, N.C., Thompson, P., Alexander, G., Harvey, D., Borowski, B., Britson, P.J., Whitwell, J.L., Ward, C., et al.: The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI): MRI methods. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 27(4), 685–691 (2008)
Keihaninejad, S., Zhang, H., Ryan, N.S., Malone, I.B., Modat, M., Cardoso, M.J., Cash, D., Fox, N.C., Ourselin, S.: An unbiased longitudinal analysis framework for tracking white matter changes using diffusion tensor imaging with application to Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 72, 153–163 (2013)
Liu, M., Zhang, D., Shen, D.: Hierarchical fusion of features and classifier decisions for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 35, 1305–1319 (2013)
Moradi, E., Pepe, A., Gaser, C., Huttunen, H., Tohka, J.: ADNI: machine learning framework for early MRI-based Alzheimer’s conversion prediction in MCI subjects. NeuroImage 104, 398–412 (2015)
Nyu, L.G., Udupa, J.K.: On standardizing the MR image intensity scale. Magn. Reson. Med. 42(6), 1072 (1999)
Rueckert, D., Sonoda, L.I., Hayes, C., Hill, D.L.G., Leach, M.O., Hawkes, D.J.: Nonrigid registration using free-form deformations: application to breast MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 18(8), 712–721 (1999)
Tong, T., Wolz, R., Coupé, P., Hajnal, J.V., Rueckert, D.: Segmentation of MR images via discriminative dictionary learning and sparse coding: application to hippocampus labeling. NeuroImage 76, 11–23 (2013)
Tong, T., Wolz, R., Gao, Q., Hajnal, J.V., Rueckert, D.: Multiple instance learning for classification of dementia in brain MRI. Med. Image Anal. 18(5), 808–818 (2014)
Wee, C.Y., Yap, P.T., Li, W., Denny, K., Browndyke, J.N., Potter, G.G., Welsh-Bohmer, K.A., Wang, L., Shen, D.: Enriched white matter connectivity networks for accurate identification of MCI patients. Neuroimage 54(3), 1812–1822 (2011)
Wee, C.Y., Yap, P.T., Shen, D.: Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment using cortical morphological patterns. Hum. Brain Mapp. 34(12), 3411–3425 (2013)
Wolz, R., Julkunen, V., Koikkalainen, J., Niskanen, E., Zhang, D.P., Rueckert, D., Soininen, H., Lotjonen, J.: Multi-method analysis of MRI images in early diagnostics of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 6(10), e25446 (2011)
Wu, G., Wang, Q., Zhang, D., Nie, F., Huang, H., Shen, D.: A generative probability model of joint label fusion for multi-atlas based brain segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 18(6), 881–890 (2014)
Wyman, B.T., Harvey, D.J., et al.: Standardization of analysis sets for reporting results from ADNI MRI data. Alzheimer’s Dement. 9(3), 332–337 (2013)
Young, J., Modat, M., Cardoso, M.J., Mendelson, A., Cash, D., Ourselin, S.: Accurate multimodal probabilistic prediction of conversion to Alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. NeuroImage Clin. 2, 735–745 (2013)
Zhou, L., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Yap, P.T., Shen, D.: Hierarchical anatomical brain networks for MCI prediction: revisiting volumetric measures. PLoS ONE 6(7), e21935 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tong, T., Gao, Q. (2015). Extraction of Features from Patch Based Graphs for the Prediction of Disease Progression in AD. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Hussain, A. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Methodologies. ICIC 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9226. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22186-1_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22186-1_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-22185-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-22186-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)