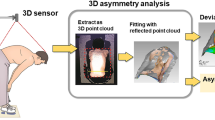
Abstract
The paper proposes an automatic method to screen and assess scoliosis, especially for the early-stage cases. Compared to state-of-art methods based on professional medical images such as radiographs and 3-D surface images, this method only requires 2-D digital images containing human back. The method reaches comparable results with manual results marked on the same images by clinicians, so it provides a feasible and convenient way for potential scoliosis patients to detect scoliosis and for patients to monitor the dynamic changes on scoliosis at home.
C. Zhang—This work is supported by Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program(founded by Tsinghua University Scientific Research Development, No. 20141081231).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajemba, P.O., Durdle, N.G., Raso, V.J.: Characterizing torso shape deformity in scoliosis using structured splines models. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56(6), 1652–1662 (2009)
Allen, S., Parent, E., Khorasani, M., Hill, D.L., Raso, J.V.: Validity and reliability of active shape models for the estimation of cobb angle in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Digit. Imaging 21(2), 208–218 (2008)
Cobb, J.R.: Outline for the study of scoliosis. Instr. Course Lect. 5, 261–275 (1948)
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1(4), 321–331 (1988)
Kim, H.S., Ishikawa, S., Ohtsuka, Y., Shimizu, H., Shinomiya, T., Viergever, M.A.: Automatic scoliosis detection based on local centroids evaluation on moire topographic images of human backs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 20(12), 1314–1320 (2001)
Liu, J., Liu, Y.: Curved reflection symmetry detection with self-validation. In: Kimmel, R., Klette, R., Sugimoto, A. (eds.) ACCV 2010, Part IV. LNCS, vol. 6495, pp. 102–114. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Morrissy, R.T., Goldsmith, G.S., Hall, E.C., Kehl, D., Cowie, G.H.: Measurement of the cobb angle on radiographs of patients who have. J. Bone Joint. Surg. Am. 72, 320–327 (1990)
Ramirez, L., Durdle, N.G., Raso, V.J., Hill, D.L.: A support vector machines classifier to assess the severity of idiopathic scoliosis from surface topography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 10(1), 84–91 (2006)
Colombo, A.S., Saad, K.R., João, S.M.A.: Reliability and validity of the photogrammetry for scoliosis evaluation: a crosssectional prospective study. J. Manipulative Physiol. Ther. 32(6), 423–430 (2009)
Stolinski, L., Czaprowski, D., Kozinoga, M., Korbel, K., Janusz, P., Tyrakowski, M., Kono, K., Suzuki, N., Kotwicki, T.: Analysis of anterior trunk symmetry index (atsi) in healthy school children based on 2D digital photography: normal limits for age 7–10 years. Scoliosis 8(Suppl 2), P10 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pan, W., Hou, G., Zhang, C. (2015). Automatic Methods for Screening and Assessing Scoliosis by 2-D Digital Images. In: He, X., et al. Intelligence Science and Big Data Engineering. Image and Video Data Engineering. IScIDE 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9242. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23989-7_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23989-7_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-23987-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-23989-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)