Abstract
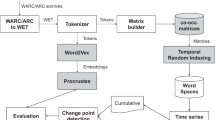
The semantic meanings of words are always changing with time. In this paper, we focus on semantic shifts, a certain type of semantic change, which indicates the meaning changes of a bunch of words that are influenced by social trends in specific time period. By training distributed word representation spaces for segmented time periods in diachronic corpus and mapping them into a universal semantic space, the semantic shifts of a certain cluster of words can be reflected as an offset vector in the universal space.
Further study shows that this semantic shift vector can be used as standard pattern to trace the words which have the similar semantic shift between other time periods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, P.: Times may change, but we will always have money: Diachronic variation in recent british english. Journal of English Linguistics 39(1), 65–88 (2011)
Bengio, Y., Ducharme, R., Vincent, P., Janvin, C.: A neural probabilistic language model. The Journal of Machine Learning Research 3, 1137–1155 (2003)
Fisher, W.D.: On grouping for maximum homogeneity. Journal of the American Statistical Association 53(284), 789–798 (1958)
Gabrielatos, C., McEnery, T., Diggle, P.J., Baker, P.: The peaks and troughs of corpus-based contextual analysis. International Journal of Corpus Linguistics 17(2), 151–175 (2012)
He, S., Zou, X., Xiao, L., Hu, J.: Construction of diachronic ontologies from people’s daily of fifty years. In: Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, pp. 3258–3263 (2014)
Kruszewski, G., Baroni, M.: Dead parrots make bad pets: exploring modifier effects in noun phrases. In: Lexical and Computational Semantics (* SEM 2014), p. 171 (2014)
Kulkarni, V., Al-Rfou, R., Perozzi, B., Skiena, S.: Statistically significant detection of linguistic change. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.3315 (2014)
Michel, J.B., Shen, Y.K., Aiden, A.P., Veres, A., Gray, M.K., Pickett, J.P., Hoiberg, D., Clancy, D., Norvig, P., Orwant, J., et al.: Quantitative analysis of culture using millions of digitized books. Science 331(6014), 176–182 (2011)
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J.: Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781 (2013)
Mikolov, T., Le, Q.V., Sutskever, I.: Exploiting similarities among languages for machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1309.4168 (2013)
Mikolov, T., Yih, W.T., Zweig, G.: Linguistic regularities in continuous space word representations. In: HLT-NAACL, pp. 746–751 (2013)
Rohrdantz, C., Hautli, A., Mayer, T., Butt, M., Keim, D.A., Plank, F.: Towards tracking semantic change by visual analytics. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies: Short Papers. Association for Computational Linguistics, vol. 2, pp. 305–310 (2011)
Sun, N., Chen, T., Xiao, L., Hu, J.: Diachronic deviation features in continuous space word representations. In: Sun, M., Liu, Y., Zhao, J. (eds.) NLP-NABD 2014 and CCL 2014. LNCS, vol. 8801, pp. 23–33. Springer, Heidelberg (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mou, W., Sun, N., Zhang, J., Yang, Z., Hu, J. (2015). Politicize and Depoliticize: A Study of Semantic Shifts on People’s Daily Fifty Years’ Corpus via Distributed Word Representation Space. In: Lu, Q., Gao, H. (eds) Chinese Lexical Semantics. CLSW 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9332. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27194-1_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27194-1_43
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-27193-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-27194-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)