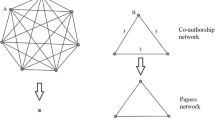
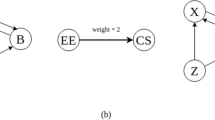
Abstract
The availability of co-authorship data from large-scale electronic databases is paving the way for new analyses on human collaboration networks. The complex network of co-authorships can identify specific features that characterise the behaviour of researchers, and impact on their production and performance. In this paper, we analyse a large sample of data regarding scientific publications from Google Scholar. The aim of our analysis is to study a fundamental aspect of co-authorship networks, i.e. the structure of authors’ ego networks. Specifically, we highlight the existence of a hierarchical organisation of these networks in a series of concentric circles, quite similar to that found in general human social networks. In addition, we highlight some properties of the correlation between the ego network structure and the authors scientific productivity, measured in terms of h-index.
This work was partially funded by the EC under the H2020-INFRAIA SoBigData (654024) project.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, A., Altmann, J., Hossain, L.: Identifying the effects of co-authorship networks on the performance of scholars: a correlation and regression analysis of performance measures and social network analysis measures. J. Inf. 5(4), 594–607 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2011.05.007
Abbasi, A., Chung, K.S.K., Hossain, L.: Egocentric analysis of co-authorship network structure, position and performance. Inf. Process. Manag. 48(4), 671–679 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2011.09.001
Arnaboldi, V., Guazzini, A., Passarella, A.: Egocentric online social networks: analysis of key features and prediction of tie strength in Facebook. Comput. Commun. 36(10–11), 1130–1144 (2013)
Doormann, C.F., Strauss, R.: A method for detecting modules in quantitative bipartite networks. Methods Ecol. Evol. 5(1), 90–98 (2013)
Dunbar, R.I.M.: Neocortex size and group size in primates: a test of the hypothesis. J. Hum. Evol. 28(3), 287–296 (1995). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0047248485710214
Dunbar, R.I.M., Arnaboldi, V., Conti, M., Passarella, A.: The structure of online social networks mirrors those in the offline world. Soc. Netw. 43, 39–47 (2015)
Gonçalves, B., Perra, N., Vespignani, A.: Modeling users’ activity on Twitter networks: validation of Dunbar’s Number. PloS One 6(8), e22656 (2011)
Guimerà, R., Uzzi, B., Spiro, J., Amaral, L.A.N.: Team assembly mechanisms determine collaboration network structure and team performance. Science 308(5722), 697–702 (2005)
Guzzo, R.A., Shea, G.P.: Group performance and and intergroup relations in organizations. In: Dunnette, M.D., Hough, L.M. (eds.) Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 2nd edn. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto (1992)
Katz, J.S., Hicks, D.: How much is a collaboration worth? A calibrated bibliometric model. Scientometrics 40(3), 541–554 (1997)
Li, E.Y., Liao, C.H., Yen, H.R.: Co-authorship networks and research impact: a social capital perspective. Res. Policy 42(9), 1515–1530 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2013.06.012
Newman, M.E.J.: The structure of scientific collaboration networks. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 98(2), 404–409 (2001). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11149952
Newman, M.E.: Coauthorship networks and patterns of scientific collaboration. PNAS 101(Suppl), 5200–5205 (2004)
Ortega, J.L.: Influence of co-authorship networks in the research impact: ego network analyses from Microsoft academic search. J. Inf. 8(3), 728–737 (2014). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2014.07.001
Sutcliffe, A., Dunbar, R.I.M., Binder, J., Arrow, H.: Relationships and the social brain: integrating psychological and evolutionary perspectives. Br. J. Psychol. 103(2), 149–68 (2012)
Wang, H., Song, M.: Clustering in one dimension by dynamic programming. R J. 3(2), 29–33 (2011)
Wiersema, M.F., Bantel, K.A.: Top management team demography and corporate strategic change. Acad. Manag. 35(1), 91–121 (2010)
Wuchty, S., Jones, B.F., Uzzi, B.: The increasing dominance of teams in production of knowledge. Science 316(5827), 1036–1039 (2007)
Zhou, W.X., Sornette, D., Hill, R.A., Dunbar, R.I.M.: Discrete hierarchical organization of social group sizes. Biol. Sci. 272(1561), 439–444 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Arnaboldi, V., Dunbar, R.I.M., Passarella, A., Conti, M. (2016). Analysis of Co-authorship Ego Networks. In: Wierzbicki, A., Brandes, U., Schweitzer, F., Pedreschi, D. (eds) Advances in Network Science. NetSci-X 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9564. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28361-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28361-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-28360-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-28361-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)