Abstract
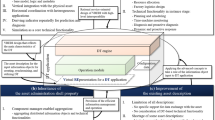
This paper presents the conceptual framework for systematic knowledge representation, storage and reuse of manufacturing information in a production scenario. This knowledge structure is designed for three levels in a manufacturing set up viz. first at the engineering objects level, second at process and finally at factory level. Virtual engineering object (VEO) deals with knowledge at the individual object/component/machine level while Virtual engineering process (VEP) represents knowledge at the process/operations level. Implementation of VEO and VEP has been already been done. This article proposes the integrated concept and architecture at facility/factory level and we termed it as Virtual Engineering Factory (VEF). It provides access to the complete production history of the factory, which is useful for decision-making activities. Moreover, we propose combined architecture for the extraction of the knowledge from different levels of manufacturing through VEF, VEP and VEO.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Posada, J., et al.: Visual computing as a key enabling technology for Industrie 4.0 and industrial internet. Comput. Graphics Appli. IEEE 35(2), 26–40 (2015)
Masood, T., et al.: Integrating through-life engineering service knowledge with product design and manufacture. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 28(1), 59–74 (2014)
Reed, N., et al.: Knowledge use in an advanced manufacturing environment. Des. Stud. 32(3), 292–312 (2011)
Sanin, C., et al.: Decisional DNA: a multi-technology shareable knowledge structure for decisional experience. Neurocomputing 88, 42–53 (2012)
Sanín, C., et al.: Application of a multi-domain knowledge structure: the decisional DNA. In: Nguyen, N., Szczerbicki, E. (eds.) Intelligent Systems for Knowledge Management, pp. 65–86. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2009)
Sanín, C., et al.: Decisional DNA: the concept and its implementation platforms. Cybern. Syst. 43(2), 67–80 (2012)
Shafiq, S.I., Sanin, C., Szczerbicki, E.: Set of experience knowledge structure (SOEKS) and decisional DNA (DDNA): past present and future. Cybern. Syst. 45(02), 200–215 (2014)
Shafiq, S.I. et al.: Using Decisional DNA to Enhance Industrial and Manufacturing Design: Conceptual Approach in Information Systems Architecture and Technology. Wrocław University of Technology, Szklarska Poreba, Wrocław, Poland (2013)
Shafiq, S.I. et al.: Decisional DNA based framework for representing virtual engineering objects. In: Nguyen, N., et al. (eds.) Intelligent Information and Database Systems, pp. 422–431. Springer International Publishing (2014)
Shafiq, S.I., et al.: Implementing virtual engineering objects (VEO) with the set of experience knowledge structure (SOEKS). Procedia Comput. Sci. 35, 644–652 (2014)
Shafiq, S.I., et al.: Virtual engineering objects (VEO): designing, developing and testing models. In: Grzech, L.B.A., Swiatek, J., Wilimowska, Z. (eds.) System Analysis Approach to the Design, Control and Decision Support, pp. 183–192. Wroclaw University of Technology Press, Wroclaw (2014)
Shafiq, S.I., et al.: Virtual Engineering Objects: Effective Way of Knowledge Representation and Decision Making. In: Barbucha, D., Nguyen, N.T., Batubara, J. (eds.) New Trends in Intelligent Information and Database Systems, pp. 261–270. Springer International Publishing (2015)
Shafiq, S.I., et al.: Virtual engineering object (VEO): toward experience-based design and manufacturing for Industry 4.0. Cybern. Syst. 46(1–2), 35–50 (2015)
Shafiq, S.I., et al.: Virtual engineering object/virtual engineering process: a specialized form of cyber physical system for Industrie 4.0. In: 19th International Conference on Knowledge Based and Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems. Procedia Computer Science, Singapore (2015, in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shafiq, S.I., Sanin, C., Szczerbicki, E., Toro, C. (2016). Decisional DNA Based Conceptual Framework for Smart Manufacturing. In: Borzemski, L., Grzech, A., Świątek, J., Wilimowska, Z. (eds) Information Systems Architecture and Technology: Proceedings of 36th International Conference on Information Systems Architecture and Technology – ISAT 2015 – Part I. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 429. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28555-9_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28555-9_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-28553-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-28555-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)