Abstract
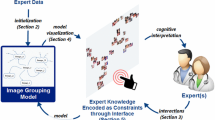
Image grouping in knowledge-rich domains is challenging, since domain knowledge and expertise are key to transform image pixels into meaningful content. Manually marking and annotating images is not only labor-intensive but also ineffective. Furthermore, most traditional machine learning approaches cannot bridge this gap for the absence of experts’ input. We thus present an interactive machine learning paradigm that allows experts to become an integral part of the learning process. This paradigm is designed for automatically computing and quantifying interpretable grouping of dermatological images. In this way, the computational evolution of an image grouping model, its visualization, and expert interactions form a loop to improve image grouping. In our paradigm, dermatologists encode their domain knowledge about the medical images by grouping a small subset of images via a carefully designed interface. Our learning algorithm automatically incorporates these manually specified connections as constraints for re-organizing the whole image dataset. Performance evaluation shows that this paradigm effectively improves image grouping based on expert knowledge.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Primary morphology terms (PRI) and 8 other categories of terms were identified by 2 highly trained dermatologists as thought units in an annotation study to label the stages in diagnostic reasoning [17]. Used here in this interface, these thought units can disclose the influence of each category of terms on the medical image grouping.
- 2.
We do not define image similarity for domain experts to not restrict them by layperson definitions. We use t-SNE only as a feature projection technique for low dimensional visualization.
References
Aronson, A.R.: Effective mapping of biomedical text to the UMLS Metathesaurus: the MetaMap program. In: American Medical Informatics Association Annual Symposium Proceedings, pp. 17–21. AMIA (2001)
Belkin, M., Niyogi, P.: Laplacian eigenmaps and spectral techniques for embedding and clustering. NIPS 14, 585–591 (2001)
Cai, D., Bao, H., He, X.: Sparse concept coding for visual analysis. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2905–2910. IEEE (2011)
Choo, J., Lee, C., Reddy, C.K., Park, H.: UTOPIAN: user-driven topic modeling based on interactive nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 19(12), 1992–2001 (2013)
Choo, J., Lee, H., Kihm, J., Park, H.: iVisClassifier: an interactive visual analytics system for classification based on supervised dimension reduction. In: IEEE Symposium on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), pp. 27–34. IEEE (2010)
Crossno, P.J., Dunlavy, D.M., Shead, T.M.: LSAView: A tool for visual exploration of latent semantic modeling. In: IEEE Symposium on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), pp. 83–90. IEEE (2009)
El-Hamdouchi, A., Willett, P.: Comparison of hierarchic agglomerative clustering methods for document retrieval. Comput. J. 32(3), 220–227 (1989)
Gao, S., Tsang, I.W., Chia, L.-T., Zhao, P.: Local features are not lonely-Laplacian sparse coding for image classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3555–3561. IEEE (2010)
Guo, X., Li, R., Alm, C., Yu, Q., Pelz, J., Shi, P., Haake, A.: Infusing perceptual expertise, domain knowledge into a human-centered image retrieval system: a prototype application. In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, pp. 275–278. ACM (2014)
Guo, X., Yu, Q., Alm, C.O., Calvelli, C., Pelz, J.B., Shi, P., Haake, A.R.: From spoken narratives to domain knowledge: mining linguistic data for medical image understanding. Artif. Intell. Med. 62(2), 79–90 (2014)
Guo, X., Yu, Q., Li, R., Alm, C.O., Haake, A.R.: Fusing multimodal human expert data to uncover hidden semantics. In: Proceedings of the 7th Workshop on Eye Gaze in Intelligent Human Machine Interaction: Eye-Gaze and Multimodality, pp. 21–26. ACM (2014)
Holzinger, A.: Human-Computer Interaction and Knowledge Discovery (HCI-KDD): what is the benefit of bringing those two fields to work together? In: Cuzzocrea, A., Kittl, C., Simos, D.E., Weippl, E., Xu, L. (eds.) CD-ARES 2013. LNCS, vol. 8127, pp. 319–328. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Hu, Y., Boyd-Graber, J., Satinoff, B., Smith, A.: Interactive topic modeling. Mach. Learn. 95(3), 423–469 (2014)
Lee, H., Battle, A., Raina, R., Ng, A.Y.: Efficient sparse coding algorithms. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 801–808 (2006)
Lee, H., Kihm, J., Choo, J., Stasko, J., Park, H.: iVisClustering: an interactive visual document clustering via topic modeling. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 31, pp. 1155–1164. Wiley Online Library (2012)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
McCoy, W., Alm, C.O., Calvelli, C., Li, R., Pelz, J.B., Shi, P., Haake, A.: Annotation schemes to encode domain knowledge in medical narratives. In: Ide, N., Xia, F. (eds.) Proceedings of the 6th Linguistic Annotation Workshop, pp. 95–103. Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg (2012)
Vaidyanathan, P., Pelz, J., Li, R., Mulpuru, S., Wang, D., Shi, P., Calvelli, C., Haake, A.: Using human experts’ gaze data to evaluate image processing algorithms. In: Hemami, S., Pappas, T.N. (eds.) \(10^{th}\) IVMSP Workshop: Perception and Visual Signal Analysis, pp. 129–134. IEEE (2011)
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(2579–2605), 85 (2008)
Zheng, M., Bu, J., Chen, C., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Qiu, G., Cai, D.: Graph regularized sparse coding for image representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(5), 1327–1336 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by NIH grant 1R21 LM010039-01A1 and NSF grant IIS-0941452. We would like to thank the participating physicians, the reviewers; and Logical Images, Inc. for images. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official views of the NIH or the NSF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guo, X. et al. (2016). An Expert-in-the-loop Paradigm for Learning Medical Image Grouping. In: Bailey, J., Khan, L., Washio, T., Dobbie, G., Huang, J., Wang, R. (eds) Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. PAKDD 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9651. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31753-3_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31753-3_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-31752-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-31753-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)