Abstract
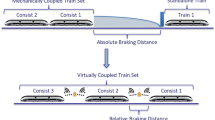
Today coupled trains have become an important bottleneck in terms of performance. Transmission through the auto-coupler is notably impaired by the contact nature and the performance of train communication backbone is much lower. Many times applications on both sides of the coupling point are incompatible, due to different implementations, versions, or retrofitting statuses. Solution comes by providing the so called virtual coupling, where the consists run together, as coupled, but without any physical connection, thus trains manufactured by different companies and with different interfaces could be virtually coupled, driven together by the leading cabin and sharing the same traffic slot. In this paper the virtual coupling is introduced together with the technologies required for its implementation which will be developed within the Shift2Rail initiative.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Example for Alstom’s TGV type “Réseau” for the compatibility with other TGV types (i.e. Paris-Brussels-Amsterdam, Paris-Brussels-Koln-Amsterdam, Duplex or POS).
References
Shift2Rail. The Rail Joint Undertaking. http://www.shift2rail.org
Shift2Rail Strategic Master Plan, Version 1.0, March 2015. http://ec.europa.eu/transport/modes/rail/doc/2015-03-31-decisionn4-2015-adoption-s2r-masterplan.pdf
Peris, E., Goikoetxea, J.: Developing the rolling stock of the future. European Railway Review 21(5) (2015)
Transportation Research Board: Transit Capacity and Quality of Service Manual. Third Edition (2013). ISBN: 978-0-309-28344-1
Filzek, B., Breuer, B.: Distance behavior on motorways with regard the active safety. SAE International. Paper# 2001-06-0066 (2001)
Meyer zu Hörste, M.: Use of broadband communication for information and control purposes in railways. In: 7th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications, ITST 2007, Sophia Antipolis, France (2007)
Rico Garcia, C., Lehner, A., Strang, T.: Channel model for train to train communication using the 400 MHz band. In: Srinivasan, V. (ed.) IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, VTC 2008 - Spring, pp. 3082–3086. eXpress Publishing (2008)
Lehner, A., Rico Garcia, C., Strang, T.: On the performance of TETRA DMO short data service in railway VANETs. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 69(4), 1647–1669 (2013)
Toubol, A., Castagnetti, F.: Marathon project for long trains with distributed traction. Transport Research Arena, Paris (2014)
Rico Garcia, C., Lehner, A., Strang, T., Rockl, M.: Comparison of collision avoidance systems and applicability to rail transport. In: 7th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications, ITST 2007, Sophia Antipolis, France (2007)
Bergenhem, C., Hedin, E., Skarin, E.: Vehicle-to-vehicle communication for a platooning system. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 48, 1222–1233 (2012)
Robinson, T., Chan, E., Coelingh, E.: Operating platoons on public motorways: an introduction to the sartre platooning programme. In: Proceedings of the 17th ITS World Congress, Busan, Korea, 25–29 October (2010)
Ronald, J.: Adaptive Cruise Control. SAE International (2006). ISBN: 978-0-7680-1792-2
Intelligent Drive next Level as part of Driving Assistance package. Mercedes-Benz. https://www.mercedes-benz.com/en/mercedes-benz/innovation/with-intelligent-drive-more-comfort-in-road-traffic/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Goikoetxea, J. (2016). Roadmap Towards the Wireless Virtual Coupling of Trains. In: Mendizabal, J., et al. Communication Technologies for Vehicles. Nets4Cars/Nets4Trains/Nets4Aircraft 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9669. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-38921-9_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-38921-9_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-38920-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-38921-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)