Abstract
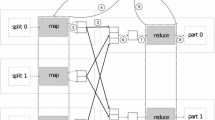
Many companies are using MapReduce applications to process very large amounts of data. Static optimization of such applications is complex because they are based on user-defined operations, called map and reduce, which prevents some algebraic optimization. In order to optimize the task allocation, several systems collect data from previous runs and predict the performance doing job profiling. However they are not effective during the learning phase, or when a new type of job or data set appears. In this paper, we present an adaptive multi-agent system for large data sets analysis with MapReduce. We do not preprocess data and we adopt a dynamic approach, where the reducer agents interact during the job. In order to decrease the workload of the most loaded reducer - and so the execution time - we propose a task re-allocation based on negotiation.
This work is part of the PartENS research project supported by the Nord-Pas de Calais region (researcher/citizen research projects).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
It is worth noticing that the negotiation is conservative.
References
Dean, J., Ghemawat, S.: MapReduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. In: Sixth Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation, pp. 137–150 (2004)
Zaharia, M., Chowdhury, M., Das, T., Dave, A., Ma, J., McCauley, M., Franklin, M.J., Shenker, S., Stoica, I.: Resilient distributed datasets: a fault-tolerant abstraction for in-memory cluster computing. In: Proceedings of the 9th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, pp. 15–28. USENIX Association (2012)
DeCandia, G., Hastorun, D., Jampani, M., Kakulapati, G., Lakshman, A., Pilchin, A., Sivasubramanian, S., Vosshall, P., Vogels, W.: Dynamo: Amazon’s highly available key-value store. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM SIGOPS Symposium on Operating Systems Principles (SOSP 2007), pp. 205–220 (2007)
Lama, P., Zhou, X.: Aroma: automated resource allocation and configuration of mapreduce environment in the cloud. In: Proceedings of the 9th Internatinal Conference on Autonomic Computing (ICAC 2012), pp. 63–72 (2012)
Verma, A., Cherkasova, L., Campbell, R.H.: Aria: automatic resource inference and allocation for mapreduce environments. In: Proceedings of the 8th Internatinal Conference on Autonomic Computing (ICAC 2011), pp. 235–244 (2011)
Kwon, Y., Balazinska, M., Howe, B., Rolia, J.: Skewtune: mitigating skew in mapreduce applications. In: Proceedings of the 2012 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, SIGMOD 2012, pp. 25–36 (2012)
Vernica, R., Balmin, A., Beyer, K.S., Ercegovac, V.: Adaptive mapreduce using situation-aware mappers. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Extending Database Technology, EDBT 2012, pp. 420–431 (2012)
Brandt, F., Conitzer, V., Endriss, U.: Computational social choice. In: Weiss, G. (ed.) Multiagent Systems, pp. 213–380. MIT Press, Cambridge (2013)
Pujol-Gonzalez, M., Cerquides, J., Meseguer, P., Rodríguez-Aguilar, J.A., Tambe, M.: Engineering the decentralized coordination of UAVs with limited communication range. In: Bielza, C., Salmerón, A., Alonso-Betanzos, A., Hidalgo, J.I., Martínez, L., Troncoso, A., Corchado, E., Corchado, J.M. (eds.) CAEPIA 2013. LNCS, vol. 8109, pp. 199–208. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Hewitt, C., Bishop, P., Steiger, R.: A universal modular actor formalism for artificial intelligence. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 235–245 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Baert, Q., Caron, A.C., Morge, M., Routier, JC. (2016). Fair Multi-agent Task Allocation for Large Data Sets Analysis. In: Demazeau, Y., Ito, T., Bajo, J., Escalona, M. (eds) Advances in Practical Applications of Scalable Multi-agent Systems. The PAAMS Collection. PAAMS 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9662. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-39324-7_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-39324-7_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-39323-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-39324-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)