Abstract
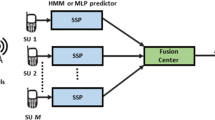
Quality of experience (QoE) of a secondary spectrum user is mainly governed by its spectrum utilization, the energy consumption in spectrum sensing and the impact of channel switching in a cognitive radio network. It can be enhanced by prediction of spectrum availability of different channels in the form of their idle times through historical information of primary users’ activity. Based on a reliable prediction scheme, the secondary user chooses the channel with the longest idle time for transmission of its data. In contrast to the existing method of statistical prediction, the use and applicability of supervised learning based prediction in various traffic scenarios have been studied in this paper. Prediction accuracy is investigated for three machine learning techniques, artificial neural network based Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), Support Vector Machines (SVM) with Linear Kernel and SVM with Gaussian Kernel, among which, the best one is chosen for prediction based opportunistic spectrum access. The results highlight the analysis of the learning techniques with respect to the traffic intensity. Moreover, a significant improvement in spectrum utilization of the secondary user with reduction in sensing energy and channel switching has been found in case of predictive dynamic channel allocation as compared to random channel selection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoyhtya, M., Pollin, S.: Improving the performance of cognitive radios through classification, learning, and predictive channel selection. Adv. Electron. Telecommun. 2, 28–38 (2011)
Azmat, F., Chen, Y., Member, S., Stocks, N., Mar, N.I.: Analysis of Spectrum Occupancy Using Machine Learning Algorithms, 0–22
Xing, X., Jing, T., Cheng, W., Huo, Y., Cheng, X.: Spectrum prediction in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 20, 90–96 (2013)
Lee, J., Park, H.-K.: Channel prediction-based channel allocation scheme for multichannel cognitive radio networks. J. Commun. Networks. 16, 209–216 (2014)
He, A., Member, S., Bae, K.K., Newman, T.R., Gaeddert, J., Member, S., Kim, K., Menon, R., Morales-tirado, L., Neel, J.J., Zhao, Y., Reed, J.H., Tranter, W.H., Fellow, L.: Survey of artificial intelligence for cognitive radios. IEEE Trans. Vech. Tech. 59, 1578–1592 (2010)
Bkassiny, M., Member, S., Li, Y., Member, S.: A Survey on Machine-Learning Techniques in Cognitive Radios, pp. 1–53
Tumuluru, V.K., Wang, P.W.P., Niyato, D.: A Neural Network Based Spectrum Prediction Scheme for Cognitive Radio (2010)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Cog. mod. 5, 3 (1988)
Burges, C.J.C.: A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining Knowl. Discov. 2(2), 121–167 (1998)
Acknowledgement
This work has been carried out as a part of the project “Mobile Broadband Service Support over Cognitive Radio Networks”, sponsored by Information Technology Research Academy (ITRA), Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Ministry of Communications & IT, Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Agarwal, A., Dubey, S., Gangopadhyay, R., Debnath, S. (2016). Secondary User QoE Enhancement Through Learning Based Predictive Spectrum Access in Cognitive Radio Networks. In: Noguet, D., Moessner, K., Palicot, J. (eds) Cognitive Radio Oriented Wireless Networks. CrownCom 2016. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 172. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40352-6_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40352-6_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-40351-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-40352-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)