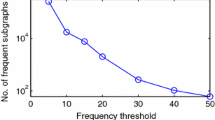
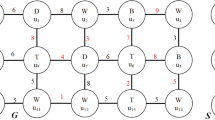
Abstract
The frequent subgraph mining has widespread applications in many different domains such as social network analysis and bioinformatics. Generally, the frequent subgraph mining refers to graph matching. Many research works dealt with structural graph matching, but a little attention is paid to semantic matching when graph vertices and/or edges are attributed. Therefore, the discovered frequent subgraphs should become more pruned by applying a new semantic filter instead of using only structural similarity in the graph matching process. In this paper, we present POSGRAMI, a new hybrid approach for frequent subgraph mining based principally on approximate graph matching. To this end, POSGRAMI first uses an approximate structural similarity function based on graph edit distance function. POSGRAMI then uses a semantic vertices similarity function based on possibilistic information affinity function. In fact, our proposed approach is a new possibilistic version of existing approach in literature named GRAMI. This paper had shown the effectiveness of POSGRAMI on some real datasets. In particular, it achieved a better performance than GRAMI in terms of processing time, number and quality of discovered subgraphs.
The author is very thankful to the executive directors and the organizers for their kind invitation to participate in the conference.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deshpande, M., Kuramochi, M., Wale, N., Karypis, G.: Frequent substructure-based approaches for classifying chemical compounds. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 17(8), 1036–1050 (2005)
Guralnik, V., Karypis, G.: A scalable algorithm for clustering sequential data. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM 2001, pp. 179–186 (2001)
Elseidy, M., Abdelhamid, E., Skiadopoulos, S., Kalnis, P.: GRAMI: frequent subgraph and pattern mining in a single large graph. PVLDB 7(7), 517–528 (2014)
McGregor, J.: Relational consistency algorithms and their application in finding subgraph and graph isomorphisms. Inf. Sci. 19(3), 229–250 (1979)
He, H., Singh, A.K.: Graphs-at-a-time: query language and access methods for graph databases, pp. 405–418. ACM (2008)
Chaoji, V., Al Hasan, M., Salem, S., Besson, J., Origami, M.J.Z.: A novel and effective approach for mining representative orthogonal graph patterns. Stat. Anal. Data Min. 1(2), 67–84 (2008)
Yan, X.: Closegraph: mining closed frequent graph patterns. In: Proceedings of the Ninth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Series. KDD 2003, pp. 286–295. ACM, New York (2003)
Benferhat, S., Dubois, D., Kaci, S., Prade, H.: Modeling positive and negative information in possibility theory. Int. J. Inf. Syst. (IJIS) 23(10), 1094–1118 (2008)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility. FuzzySets Syst. 100, 9–34 (1999)
Jenhani, I., Ben Amor, N., Elouedi, Z., Benferhat, S., Mellouli, K.: Information affinity: a new similarity measure for possibilistic uncertain information. In: Mellouli, K. (ed.) ECSQARU 2007. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4724, pp. 840–852. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Yan, X.: gSpan: Graph-based substructure pattern mining. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Series. ICDM 2002. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Moussaoui, M., Zaghdoud, M., Akaichi, J. (2016). POSGRAMI: Possibilistic Frequent Subgraph Mining in a Single Large Graph. In: Carvalho, J., Lesot, MJ., Kaymak, U., Vieira, S., Bouchon-Meunier, B., Yager, R. (eds) Information Processing and Management of Uncertainty in Knowledge-Based Systems. IPMU 2016. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 610. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40596-4_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40596-4_46
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-40595-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-40596-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)