Abstract
In reasoning about effectful computations, it often suffices to focus on the effect-free parts. We present a package for automatically lifting equations to effects modelled by applicative functors. It exploits properties of the concrete functor thanks to a modular classification based on combinators. We formalise the meta theory and demonstrate the usability of our Isabelle/HOL package with two case studies. This is a first step towards practical reasoning with effectful computations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
As lifting wraps the types of free variables in F, it does not look into abstractions, but treats them like constants. For example,
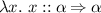 is lifted to
is lifted to  rather than
rather than 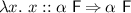 . Thus, lifting effectively operates on first-order terms.
. Thus, lifting effectively operates on first-order terms. - 2.
Hinze briefly considers functors with the combinators S and C and notes that the case with only the combinator C might be interesting, too, but omits the details.
- 3.
The following shows the equivalence (bold face denotes doubling and underlining dropping of a repetition):
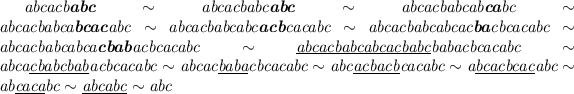 .
.
References
Berghofer, S.: Proofs, Programs and Executable Specifications in Higher Order Logic. Ph.D. thesis, Institut für Informatik, Technische Universität München (2003)
Berstel, J., Reutenauer, C.: Square-free words and idempotent semigroups. In: Lothaire, M. (ed.) Combinatorics on Words, 2nd edn., pp. 18–38. Cambridge University Press (1997)
Boutin, S.: Using reflection to build efficient and certified decision procedures. In: Abadi, M., Ito, T. (eds.) TACS 1997. LNCS, vol. 1281, pp. 515–529. Springer, Heidelberg (1997)
Bulwahn, L., Krauss, A., Haftmann, F., Erkök, L., Matthews, J.: Imperative functional programming with Isabelle/HOL. In: Mohamed, O.A., Muñoz, C., Tahar, S. (eds.) TPHOLs 2008. LNCS, vol. 5170, pp. 134–149. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Bunder, M.W.: Lambda terms definable as combinators. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 169(1), 3–21 (1996)
Church, A.: The Calculi of Lambda-Conversion. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1941)
Dijkstra, E.W.: An exercise for Dr. R.M. Burstall. In: Selected Writings on Computing: A Personal Perspective. Texts and Monographs in Computer Science, pp. 215–216. Springer, New York (1982)
Eberl, M., Hölzl, J., Nipkow, T.: A verified compiler for probability density functions. In: Vitek, J. (ed.) ESOP 2015. LNCS, vol. 9032, pp. 80–104. Springer, Heidelberg (2015)
Gammie, P., Lochbihler, A.: The Stern-Brocot tree. Archive of Formal Proofs, (2015). http://isa-afp.org/entries/Stern_Brocot.shtml, Formal proof development
Gibbons, J., Bird, R.: Be kind, rewind: a modest proposal about traversal (2012). http://www.comlab.ox.ac.uk/jeremy.gibbons/publications/backwards.pdf
Gibbons, J., Hinze, R.: Just do it: simple monadic equational reasoning. In: ICFP 2011, pp. 2–14. ACM (2011)
Graham, R.L., Knuth, D.E., Patashnik, O.: Concrete Mathematics-A Foundation for Computer Science, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1994)
Green, J.A., Rees, D.: On semi-groups in which \(x^r = x\). Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 48, 35–40 (1952)
Hinze, R.: The Bird tree. J. Func. Programm. 19(5), 491–508 (2009)
Hinze, R.: Lifting operators and laws (2010). http://www.cs.ox.ac.uk/ralf.hinze/Lifting.pdf
Homeier, P.V.: The HOL-omega logic. In: Berghofer, S., Nipkow, T., Urban, C., Wenzel, M. (eds.) TPHOLs 2009. LNCS, vol. 5674, pp. 244–259. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Huffman, B.: Transfer principle proof tactic for nonstandard analysis. In: Kanovich, M., White, G., Gottliebsen, H., Oliva, P. (eds.) NetCA 2005, pp. 18–26. Queen Mary, University of London, Dept. of Computer Science, Research report RR-05-06 (2005)
Huffman, B., Kunčar, O.: Lifting and Transfer: a modular design for quotients in Isabelle/HOL. In: Gonthier, G., Norrish, M. (eds.) CPP 2013. LNCS, vol. 8307, pp. 131–146. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Hutton, G., Fulger, D.: Reasoning about effects: seeing the wood through the trees. In: Trends in Functional Programming (TFP 2008) (2008)
Krebbers, R.: The C standard formalized in Coq. Ph.D. thesis, Radboud University (2015)
Lammich, P., Tuerk, T.: Applying data refinement for monadic programs to Hopcroft’s algorithm. In: Beringer, L., Felty, A. (eds.) ITP 2012. LNCS, vol. 7406, pp. 166–182. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Lochbihler, A.: Probabilistic functions and cryptographic oracles in higher order logic. In: Thiemann, P. (ed.) ESOP 2016. LNCS, vol. 9632, pp. 503–531. Springer, Heidelberg (2016)
Lochbihler, A., Schneider, J.: Applicative lifting. Archive of Formal Proofs (2015). http://isa-afp.org/entries/Applicative_Lifting.shtml
Marlow, S., Peyton Jones, S., Kmett, E., Mokhov, A.: Desugaring Haskell’s do-notation into applicative operations (2016). http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/simonpj/papers/list-comp/applicativedo.pdf
McBride, C., Paterson, R.: Applicative programming with effects. J. Funct. Program. 18(1), 1–13 (2008)
Nipkow, T.: More Church-Rosser proofs (in Isabelle/HOL). J. Automat. Reason. 26, 51–66 (2001)
Paulson, L.: A higher-order implementation of rewriting. Sci. Comput. Program 3(2), 119–149 (1983)
Reynolds, J.C.: Types, abstraction and parametric polymorphism. In: IFIP 1983. Information Processing, vol. 83, pp. 513–523. North-Holland/IFIP (1983)
Schropp, A., Popescu, A.: Nonfree datatypes in Isabelle/HOL. In: Gonthier, G., Norrish, M. (eds.) CPP 2013. LNCS, vol. 8307, pp. 114–130. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Tuong, F., Wolff, B.: A meta-model for the Isabelle API. Archive of Formal Proofs (2015). http://isa-afp.org/entries/Isabelle_Meta_Model.shtml
Acknowledgements
Peter Gammie triggered our interest in reasoning about applicative functors and helped with the Stern-Brocot tree. We thank Dmitriy Traytel, Joachim Breitner, and the anonymous reviewers for suggesting many textual improvements. The first author was supported by SNSF grant 153217 “Formalising Computational Soundness for Protocol Implementations”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
A Definitions of Applicative Functors
A Definitions of Applicative Functors
This appendix lists Isabelle/HOL definitions for the idioms mentioned in this paper. The definitional packages and their syntaxes are documented in the Isabelle/Isar reference manual. The proofs of the applicative laws and combinators are available online [23].
Environment (Reader)

Stream

Infinite binary tree

Non-standard numbers as used in non-standard analysis in Isabelle/HOL [17]. The type \(\alpha \) star is the quotient of the environment idiom (\(\alpha \), nat) env over equality in some free ultrafilter \(\mathcal {U}\) on nat.

Option

Zip list

Probability

Subprobability

Set

Non-empty set

Monoid, commutative monoid, idempotent monoid

The type variable \(\alpha \) must have sort monoid-add. If \(\alpha \) has sort comm-monoid-add, then monoid-ap has C. If \(\alpha \) has sort idemp-monoid-add, then monoid-ap has W.
Either

Distinct non-empty list. The function remdups removes duplicates from a list by retaining only the last occurrence of each element.

State

List

Parser. The function apfst applies a function to the first component of a tuple.

Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lochbihler, A., Schneider, J. (2016). Equational Reasoning with Applicative Functors. In: Blanchette, J., Merz, S. (eds) Interactive Theorem Proving. ITP 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9807. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-43144-4_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-43144-4_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-43143-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-43144-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


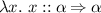 is lifted to
is lifted to  rather than
rather than 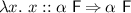 . Thus, lifting effectively operates on first-order terms.
. Thus, lifting effectively operates on first-order terms.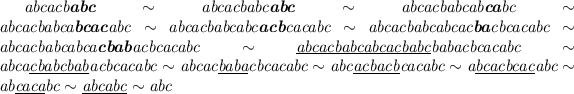 .
.