Abstract
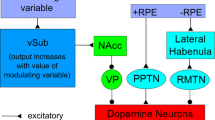
Neuromodulation is an interesting way to display different modes of functioning in a complex network. The effect of Noradrenaline has often been related to the exploration/exploitation trade-off and implemented in models by modulation of the gain of activation function. In this paper, we show that this mechanism is not sufficient for system-level networks and propose another way to implement it, exploiting reported inhibition of a striatal region by Noradrenaline. We describe here the corresponding model and report its performances in a reversal task.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aston-Jones, G., Rajkowski, J., Kubiak, P.: Conditioned responses of monkey locus coeruleus neurons anticipate acquisition of discriminative behavior in a vigilance task. Neuroscience 80(3), 697–715 (1997)
Aston-Jones, G., Cohen, J.D.: An integrative theory of locus coeruleus-norepinephrine function: adaptive gain and optimal performance. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 28(1), 403–450 (2005)
Aston-Jones, G., Rajkowski, J., Cohen, J.: Role of locus coeruleus in attention and behavioral flexibility. Biol. Psychiatry 46(9), 1309–1320 (1999)
Berridge, C.W., Waterhouse, B.D.: The locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system: modulation of behavioral state and state-dependent cognitive processes. Brain Res. Rev. 42(1), 33–84 (2003)
Bouret, S., Sara, S.J.: Network reset: a simplified overarching theory of locus coeruleus noradrenaline function. Trends Neurosci. 28(11), 574–582 (2005)
Brown, E., Gao, J., Holmes, P., Bogacz, R., Gilzenrat, M., Cohen, J.D.: Simple neural networks that optimize decisions. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 15(03), 803–826 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/s0218127405012478
Doya, K.: Metalearning and neuromodulation. Neural Netw. 15(4–6), 495–506 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0893-6080(02)00044-8
Guthrie, M., Leblois, A., Garenne, A., Boraud, T.: Interaction between cognitive and motor cortico-basal ganglia loops during decision making: a computational study. J. Neurophysiol. 109(12), 3025–3040 (2013)
Mason, S.T., Iversen, S.D.: An investigation of the role of corticalandcerebellar noradrenaline in associative motor learning in the rat. Brain Res. 134(3), 513–527 (1977). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(77)90826-5
McClure, S., Gilzenrat, M., Cohen, J.: An exploration-exploitationmodel based on norepinepherine and dopamine activity. In: Weiss, Y., Schölkopf, B.,Platt, J. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 18, pp. 867–874. MIT Press (2006). http://www.csbmb.princeton.edu/~smcclure/pdf/MGC_NIPS.pdf
Nicola, S.M., Malenka, R.C.: Modulation of synaptic transmission bydopamine and norepinephrine in ventral but not dorsal striatum. J. Neurophysiol. 79(4), 1768–1776 (1998). http://view.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9535946
O’Reilly, R.C., Frank, M.J., Hazy, T.E., Watz, B.: PVLV: the primary value and learned value Pavlovian learning algorithm. Behav. Neurosci. 121(1), 31–49 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0735-7044.121.1.31
Pauli, W.M., O’Reilly, R.C.: Attentional control of associative learning-a possible role of the central cholinergic system. Brain Res. 1202, 43–53 (2008)
Rougier, N.P., Fix, J.: DANA: distributed (asynchronous) numerical and adaptive modelling framework. Netw. Comput. Neural Syst. 23(4), 237–253 (2012)
Sadacca, B.F., Wikenheiser, A.M., Schoenbaum, G.: Toward a theoretical role for tonic norepinephrine in the orbitofrontal cortex in facilitating flexible learning. Neuroscience (2016)
Sara, S.J., Bouret, S.: Orienting and reorienting: the locus coeruleus mediates cognition through arousal. Neuron 76(1), 130–141 (2012)
Yu, A.J., Dayan, P.: Uncertainty, neuromodulation, and attention. Neuron 46(4), 681–692 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Carrere, M., Alexandre, F. (2016). A System-Level Model of Noradrenergic Function. In: Villa, A., Masulli, P., Pons Rivero, A. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2016. ICANN 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9886. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44778-0_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44778-0_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-44777-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-44778-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)