Abstract
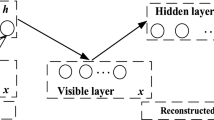
Finding suitable features has been an essential problem in computer vision. We focus on Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs), which, despite their versatility, cannot accommodate transformations that may occur in the scene. As a result, several approaches have been proposed that consider a set of transformations, which are used to either augment the training set or transform the actual learned filters. In this paper, we propose the Explicit Rotation-Invariant Restricted Boltzmann Machine, which exploits prior information coming from the dominant orientation of images. Our model extends the standard RBM, by adding a suitable number of weight matrices, associated with each dominant gradient. We show that our approach is able to learn rotation-invariant features, comparing it with the classic formulation of RBM on the MNIST benchmark dataset. Overall, requiring less hidden units, our method learns compact features, which are robust to rotations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Agarwal, A., Triggs, B.: Hyperfeatures – multilevel local coding for visual recognition. In: Leonardis, A., Bischof, H., Pinz, A. (eds.) ECCV 2006, Part I. LNCS, vol. 3951, pp. 30–43. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Arel, I., Rose, D.C., Karnowski, T.P.: Deep machine learning - a new frontier in artificial intelligence research. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 5(4), 13–18 (2010)
Cheng, D., Sun, T., Jiang, X., Wang, S.: Unsupervised feature learning using Markov deep belief network. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 260–264, No. 20120073110053. IEEE (2013)
Coates, A., Arbor, A., Ng, A.Y.: An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning. In: AISTATS, pp. 215–223 (2011)
Csurka, G., Dance, C.R., Fan, L., Willamowski, J., Bray, C.: Visual categorization with bags of keypoints. In: Proceedings of the ECCV International Workshop on Statistical Learning in Computer Vision, pp. 59–74 (2004)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE CVPR, vol. 1, pp. 886–893 (2005)
Dasarathy, B.: Nearest Neighbor (NN) Norms: NN Pattern Classification Techniques. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (1991)
Gens, R., Domingos, P.M.: Deep symmetry networks. In: NIPS, pp. 2537–2545. Curran Associates, Inc. (2014)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The Elements of Statistical Learning. Springer Series in Statistics, vol. 1, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2009)
Hinton, G.: A Practical Guide to Training Restricted Boltzmann Machines, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Hinton, G.E.: Training products of experts by minimizing contrastive divergence. Neural Comput. 14(8), 1771–1800 (2002)
Hinton, G.E., Osindero, S., Teh, Y.W.: A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 18(7), 1527–1554 (2006)
Kivinen, J.J., Williams, C.K.I.: Transformation equivariant boltzmann machines. In: Honkela, T. (ed.) ICANN 2011, Part I. LNCS, vol. 6791, pp. 1–9. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Larochelle, H., Erhan, D., Courville, A., Bergstra, J., Bengio, Y.: An empirical evaluation of deep architectures on problems with many factors of variation. In: Proceedings of the 24th ICML, pp. 473–480 (2007)
Lee, H., Battle, A., Raina, R., Ng, A.Y.: Efficient sparse coding algorithms. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 801–808 (2006)
Lee, H., Ekanadham, C., Ng, A.Y.: Sparse deep belief net model for visual area V2. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 873–880 (2008)
Lee, H., Grosse, R., Ranganath, R., Ng, A.Y.: Convolutional deep belief networks for scalable unsupervised learning of hierarchical representations. In: ICML (2009)
Lowe, D.G.: Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: ICCV (1999)
Schmidt, U., Roth, S.: Learning rotation-aware features: from invariant priors to equivariant descriptors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE CVPR, pp. 2050–2057 (2012)
Shou, Z., Zhang, Y., Cai, H.J.: A study of transformation-invariances of deep belief networks. In: IJCNN, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2013)
Sohn, K., Lee, H.: Learning invariant representations with local transformations. In: Proceedings of the 29th ICML, pp. 1311–1318 (2012)
Vapnik, V.: Statistical Learning Theory. Wiley, New York (1998)
Wei, X., Phung, S.L., Bouzerdoum, A.: Visual descriptors for scene categorization: experimental evaluation. Artif. Intell. Rev. 45(3), 1–36 (2015)
Acknowledgements
We thank NVIDIA corporation for providing us a Titan X GPU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Giuffrida, M.V., Tsaftaris, S.A. (2016). Rotation-Invariant Restricted Boltzmann Machine Using Shared Gradient Filters. In: Villa, A., Masulli, P., Pons Rivero, A. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2016. ICANN 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9887. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44781-0_57
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44781-0_57
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-44780-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-44781-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)