Abstract
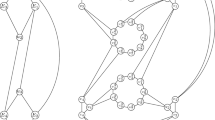
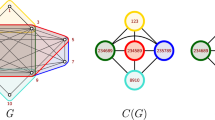
The maximum common subgraph problem is to find the largest subgraph common to two given graphs. This problem can be solved either by constraint-based search, or by reduction to the maximum clique problem. We evaluate these two models using modern algorithms, and see that the best choice depends mainly upon whether the graphs have labelled edges. We also study a variant of this problem where the subgraph is required to be connected. We introduce a filtering algorithm for this property and show that it may be combined with a restricted branching technique for the constraint-based approach. We show how to implement a similar branching technique in clique-inspired algorithms. Finally, we experimentally compare approaches for the connected version, and see again that the best choice depends on whether graphs have labels.
C. McCreesh was supported by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council [grant number EP/K503058/1].
S.N. Ndiaye and C. Solnon were supported by the ANR project SoLStiCe (ANR-13-BS02-0002-01).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akutsu, T., Tamura, T.: A polynomial-time algorithm for computing the maximum common connected edge subgraph of outerplanar graphs of bounded degree. Algorithms 6(1), 119–135 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/a6010119
Balas, E., Yu, C.S.: Finding a maximum clique in an arbitrary graph. SIAM J. Comput. 15(4), 1054–1068 (1986)
Bron, C., Kerbosch, J.: Algorithm 457: finding all cliques of an undirected graph. Commun. ACM 16(9), 575–577 (1957). http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/362342.362367
Brown, K.N., Prosser, P., Beck, C.J., Wu, C.W.: Exploring the use of constraint programming for enforcing connectivity during graph generation. In: Proceedings IJCAI Workshop on Modelling and Solving Problems with Constraints, Edinburgh, Scotland, pp. 26–31 (2005)
Bunke, H.: On a relation between graph edit distance and maximum common subgraph. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 18(8), 689–694 (1997). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8655(97)00060-3
Bunke, H., Foggia, P., Guidobaldi, C., Sansone, C., Vento, M.: A comparison of algorithms for maximum common subgraph on randomly connected graphs. In: Caelli, T.M., Amin, A., Duin, R.P.W., Kamel, M.S., de Ridder, D. (eds.) SPR 2002 and SSPR 2002. LNCS, vol. 2396, pp. 123–132. Springer, Heidelberg (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/3-540-70659-3_12
Combier, C., Damiand, G., Solnon, C.: Map edit distance vs. graph edit distance for matching images. In: Kropatsch, W.G., Artner, N.M., Haxhimusa, Y., Jiang, X. (eds.) GbRPR 2013. LNCS, vol. 7877, pp. 152–161. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Conte, D., Foggia, P., Vento, M.: Challenging complexity of maximum common subgraph detection algorithms: a performance analysis of three algorithms on a wide database of graphs. J. Graph Algorithms Appl. 11(1), 99–143 (2007). http://jgaa.info/accepted/2007/ConteFoggiaVento2007.11.1.pdf
Cook, D.J., Holder, L.B.: Substructure discovery using minimum description length and background knowledge. J. Artif. Intell. Res. (JAIR) 1, 231–255 (1994). http://dx.doi.org/10.1613/jair.43
Depolli, M., Konc, J., Rozman, K., Trobec, R., Janezic, D.: Exact parallel maximum clique algorithm for general and protein graphs. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 53(9), 2217–2228 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci4002525
Dhaenens, C., Jourdan, L., Marmion, M. (eds.): Learning and Intelligent Optimization. LNCS, vol. 8994. Springer, Switzerland (2015). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19084-6
Djoko, S., Cook, D.J., Holder, L.B.: An empirical study of domain knowledge and its benefits to substructure discovery. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 9(4), 575–586 (1997). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/69.617051
Dooms, G., Deville, Y., Dupont, P.E.: CP(Graph): introducing a graph computation domain in constraint programming. In: van Beek, P. (ed.) CP 2005. LNCS, vol. 3709, pp. 211–225. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/11564751_18
Droschinsky, A., Kriege, N., Mutzel, P.: Faster algorithms for the maximum common subtree isomorphism problem. In: Faliszewski, P., Muscholl, A., Niedermeier, R. (eds.) 41st International Symposium on Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science (MFCS 2016). Leibniz International Proceedings in Informatics (LIPIcs), vol. 58, pp. 34:1–34:14. Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik, Dagstuhl, Germany (2016, to appear)
Durand, P.J., Pasari, R., Baker, J.W., Tsai, C.C.: An efficient algorithm for similarity analysis of molecules. Internet J. Chem. 2(17), 1–16 (1999)
Ehrlich, H.C., Rarey, M.: Maximum common subgraph isomorphism algorithms and their applications in molecular science: a review. Wiley Interdisc. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 1(1), 68–79 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/wcms.5
Englert, P., Kovács, P.: Efficient heuristics for maximum common substructure search. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 55(5), 941–955 (2015). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00036
Fernández, M., Valiente, G.: A graph distance metric combining maximum common subgraph and minimum common supergraph. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 22(6/7), 753–758 (2001)
Gao, D., Reiter, M.K., Song, D.: BinHunt: automatically finding semantic differences in binary programs. In: Chen, L., Ryan, M.D., Wang, G. (eds.) ICICS 2008. LNCS, vol. 5308, pp. 238–255. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88625-9_16
Gay, S., Fages, F., Martinez, T., Soliman, S., Solnon, C.: On the subgraph epimorphism problem. Discrete Appl. Math. 162, 214–228 (2014). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dam.2013.08.008
Jégou, P.: Decomposition of domains based on the micro-structure of finite constraint-satisfaction problems. In: Fikes, R., Lehnert, W.G. (eds.) Proceedings of the 11th National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 731–736. AAAI Press/The MIT Press, 11–15 July 1993. http://www.aaai.org/Library/AAAI/1993/aaai93-109.php
Koch, I.: Enumerating all connected maximal common subgraphs in two graphs. Theor. Comput. Sci. 250(1–2), 1–30 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3975(00)00286-3
Kriege, N.: Comparing graphs. Ph.d. thesis, Technische Universität Dortmund (2015)
Levi, G.: A note on the derivation of maximal common subgraphs of two directed or undirected graphs. CALCOLO 9(4), 341–352 (1973). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02575586
Li, C., Fang, Z., Xu, K.: Combining MaxSAT reasoning and incremental upper bound for the maximum clique problem. In: 2013 IEEE 25th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Herndon, VA, USA, pp. 939–946. IEEE Computer Society, 4–6 November 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2013.143
Li, C., Jiang, H., Xu, R.: Incremental MaxSAT reasoning to reduce branches in a branch-and-bound algorithm for MaxClique. In: Dhaenens et al. [11], pp. 268–274. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19084-6_26
Lu, S.W., Ren, Y., Suen, C.Y.: Hierarchical attributed graph representation and recognition of handwritten chinese characters. Pattern Recogn. 24(7), 617–632 (1991). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0031320391900295
McCreesh, C., Prosser, P.: Multi-threading a state-of-the-art maximum clique algorithm. Algorithms 6(4), 618–635 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/a6040618
McCreesh, C., Prosser, P.: Reducing the branching in a branch and bound algorithm for the maximum clique problem. In: O’Sullivan, B. (ed.) CP 2014. LNCS, vol. 8656, pp. 549–563. Springer, Heidelberg (2014). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10428-7_40
McCreesh, C., Prosser, P.: The shape of the search tree for the maximum clique problem and the implications for parallel branch and bound. TOPC 2(1), 8 (2015). http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/2742359
McCreesh, C., Prosser, P., Trimble, J.: Heuristics and really hard instances for subgraph isomorphism problems. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2016, to appear)
McGregor, J.J.: Backtrack search algorithms and the maximal common subgraph problem. Softw. Pract. Exp. 12(1), 23–34 (1982)
Minot, M., Ndiaye, S.N., Solnon, C.: A comparison of decomposition methods for the maximum common subgraph problem. In: 27th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, ICTAI 2015, Vietri sul Mare, Italy, pp. 461–468. IEEE, 9–11 November 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2015.75
Ndiaye, S.N., Solnon, C.: CP models for maximum common subgraph problems. In: Lee, J. (ed.) CP 2011. LNCS, vol. 6876, pp. 637–644. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23786-7_48
Nikolaev, A., Batsyn, M., Segundo, P.S.: Reusing the same coloring in the child nodes of the search tree for the maximum clique problem. In: Dhaenens et al. [11], pp. 275–280. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19084-6_27
Petit, T., Régin, J.-C., Bessière, C.: Specific filtering algorithms for over-constrained problems. In: Walsh, T. (ed.) CP 2001. LNCS, vol. 2239, pp. 451–463. Springer, Heidelberg (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10479-011-1019-8
Piva, B., de Souza, C.C.: Polyhedral study of the maximum common induced subgraph problem. Ann. OR 199(1), 77–102 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10479-011-1019-8
Prosser, P.: Exact algorithms for maximum clique: a computational study. Algorithms 5(4), 545–587 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/a5040545
Prosser, P., Unsworth, C.: A connectivity constraint using bridges. In: Brewka, G., Coradeschi, S., Perini, A., Traverso, P. (eds.) Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence, ECAI 2006. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, vol. 141, August 29–September 1, 2006, Riva del Garda, Italy, Including Prestigious Applications of Intelligent Systems (PAIS), pp. 707–708. IOS Press (2006)
Raymond, J.W., Willett, P.: Maximum common subgraph isomorphism algorithms for the matching of chemical structures. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 16(7), 521–533 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/A:1021271615909
Sabin, D., Freuder, E.C.: Contradicting conventional wisdom in constraint satisfaction. In: Borning, A. (ed.) PPCP 1994. LNCS, vol. 874, pp. 10–20. Springer, Heidelberg (1994)
Santo, M.D., Foggia, P., Sansone, C., Vento, M.: A large database of graphs and its use for benchmarking graph isomorphism algorithms. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 24(8), 1067–1079 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8655(02)00253-2
Segundo, P.S., Lopez, A., Batsyn, M.: Initial sorting of vertices in the maximum clique problem reviewed. In: Pardalos, P.M., Resende, M.G.C., Vogiatzis, C., Walteros, J.L. (eds.) LION 2014. LNCS, vol. 8426, pp. 111–120. Springer, Switzerland (2014). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09584-4_12
Segundo, P.S., Lopez, A., Pardalos, P.M.: A new exact maximum clique algorithm for large and massive sparse graphs. Comput. OR 66, 81–94 (2016). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2015.07.013
Segundo, P.S., Matía, F., Rodríguez-Losada, D., Hernando, M.: An improved bit parallel exact maximum clique algorithm. Optim. Lett. 7(3), 467–479 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11590-011-0431-y
Segundo, P.S., Nikolaev, A., Batsyn, M.: Infra-chromatic bound for exact maximum clique search. Comput. OR 64, 293–303 (2015). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2015.06.009
Segundo, P.S., Rodríguez-Losada, D., Jiménez, A.: An exact bit-parallel algorithm for the maximum clique problem. Comput. OR 38(2), 571–581 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2010.07.019
Segundo, P.S., Tapia, C.: Relaxed approximate coloring in exact maximum clique search. Comput. OR 44, 185–192 (2014). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2013.10.018
Shasha, D., Wang, J.T.L., Giugno, R.: Algorithmics and applications of tree and graph searching. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-first ACM SIGMOD-SIGACT-SIGART Symposium on Principles of Database Systems, PODS 2002, NY, USA, pp. 39–52 (2002). http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/543613.543620
Suters, W.H., Abu-Khzam, F.N., Zhang, Y., Symons, C.T., Samatova, N.F., Langston, M.A.: A new approach and faster exact methods for the maximum common subgraph problem. In: Wang, L. (ed.) COCOON 2005. LNCS, vol. 3595, pp. 717–727. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/11533719_73
Tomita, E., Kameda, T.: An efficient branch-and-bound algorithm for finding a maximum clique with computational experiments. J. Global Optim. 37(1), 95–111 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10898-006-9039-7
Tomita, E., Seki, T.: An efficient branch-and-bound algorithm for finding a maximum clique. In: Calude, C.S., Dinneen, M.J., Vajnovszki, V. (eds.) DMTCS 2003. LNCS, vol. 2731. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45066-1_22
Tomita, E., Sutani, Y., Higashi, T., Takahashi, S., Wakatsuki, M.: A simple and faster branch-and-bound algorithm for finding a maximum clique. In: Rahman, M.S., Fujita, S. (eds.) WALCOM 2010. LNCS, vol. 5942, pp. 191–203. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11440-3_18
Vismara, P., Valery, B.: Finding maximum common connected subgraphs using clique detection or constraint satisfaction algorithms. In: An, L.T.H., Bouvry, P., Tao, P.D. (eds.) MCO 2008. CCIS, vol. 14, pp. 358–368. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-87477-5_39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
McCreesh, C., Ndiaye, S.N., Prosser, P., Solnon, C. (2016). Clique and Constraint Models for Maximum Common (Connected) Subgraph Problems. In: Rueher, M. (eds) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming. CP 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9892. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44953-1_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44953-1_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-44952-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-44953-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)