Abstract
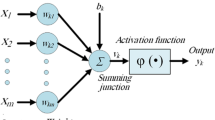
Ethiopia is located close to the equatorial belt that receives abundant solar energy. For Ethiopia, to achieve the optimum utilization of solar energy, it is necessary to evaluate the incident solar radiation over the countries of interest. Though, sophisticated and costly equipment are available but they are very limited for developing countries’ like Ethiopia. This paper is therefore tries to explore the use of artificial neural network method for predicting the daily global solar radiation in the horizontal surface using secondary data in the city of Addis Ababa. For this purpose, the meteorological data of 1195 days from one station in Addis Ababa along the years 1985–1987 were used for training testing and validating the model All independent variables (Min and Max Temperature, humidity, sunshine hour and wind speed were normalized and added to the model. Then, Back propagation (BP) Artificial Neural Network (ANN) method was applied for prediction and training respectively to determine the most suitable independent (input) variables. The results obtained by the ANN model were validated with the actual data and error values were found within acceptable limits. The findings of the study show that the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) is found to be 0.11 and correlation coefficient (R) value was obtained 0.901 during prediction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mekonnen, S.A.: Solar energy assessment in Ethiopia: modeling and measurement. Addis Ababa University Department of Environmental Science, July 2007
Kassahun, G.S.: Predictive modelling of Kaliti wastewater treatment plant performance using Artificial Neural Networks, Chemical Engineering with Specialization in Environmental Engineering, February 2012
Ethio Resource Group with Partners, Solar and Wind Energy Utilization and Project Development Scenarios, Ethiopian Rural Energy Development and Promotion Center, October 2007
Azadeh, A., Maghsoudi, A., Sohrabkhani, S.: An integrated artificial neural networks approach for predicting global radiation. Energy Convers. Manage. 50(6), 1497–1505 (2009)
Ali, R.: Estimating global solar radiation using artificial neural network and air temperature data in a semi-arid environment. Renew. Energy 35(9), 2131–2135 (2010)
Benghanem, M., Mellit, A., Alarm, S.N.: ANN-based modelling and estimation of daily global solar radiation data: a case study. Energy Convers. Manage. 50(7), 1644–1655 (2009)
Cao, J.C., Cao, S.H.: Study of forecasting solar irradiance using neural networks with preprocessing sample data by wavelet analysis. Energy 31(15), 3435–3445 (2006)
Chang, F.-J., Kao, L., Kuo, Y.-M., et al.: Artificial neural networks for estimating regional arsenic concentrations in a black foot disease area in Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 388, 65–76 (2010)
Jiang, Y.: Computation of monthly mean daily global solar radiation in China using artificial neural networks and comparison with other empirical models. Energy 34(9), 1276–1283 (2009)
Singh, K.P., Gupta, S.: Artificial intelligence based modeling for predicting the disinfection by-products in water. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 114, 122–131 (2012)
Vakili, M., Sabbagh-Yazdi, S.-R., Kalhor, K., Khosrojerdi, S.: Using Artificial Neural Networks for prediction of global solar radiation in Tehran considering particulate matter air pollution. Energy Procedia 74, 1205–1212 (2015)
Olatomiwa, L., Mekhilef, S., Shamshirband, S., Petković, D.: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy approach for solar radiation prediction in Nigeria. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 51, 1784–1791 (2015)
Jiang, H., Dong, Y., Wang, J., Li, Y.: Intelligent optimization models based on hard-ridge penalty and RBF for forecasting global solar radiation. Energy Convers. Manage. 95(1), 42–58 (2015)
Mohammadi, K., Shamshirband, S., Petković, D., Khorasanizadeh, H.: Determining the most important variables for diffuse solar radiation prediction using adaptive neuro-fuzzy methodology; case study: City of Kerman. Iran, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 53, 1570–1579 (2016)
Akarslan, E., Hocaoglu, F.O.: A novel adaptive approach for hourly solar radiation forecasting. Renew. Energy 87(1), 628–633 (2016)
Kumar, R., Aggarwal, R.K., Sharma, J.D.: Comparison of regression and artificial neural network models for estimation of global solar radiations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 52, 1294–1299 (2015)
Çelik, Ö., Teke, A., Yıldırım, H.B.: The optimized artificial neural network model with Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm for global solar radiation estimation in Eastern Mediterranean Region of Turkey. J. Cleaner Prod. 116(10), 1–12 (2016)
Eriko, I., Kenji, O., Yoichi, M.I., Makoto, A.: A neural network approach to simple prediction of soil nitrification potential: a case study in Japanese temperate forests. Ecol. Model. 219(1–2), 200–211 (2008)
Hu, J., Zhou, G., Xu, X.: Using an improved back propagation neural network to study spatial distribution of sunshine illumination from sensor network data. Ecol. Model. 26, 86–96 (2013)
Krejcar, O., Mahdal, M.: Optimized solar energy power supply for remote wireless sensors based on IEEE 802.15.4 standard. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 9 (2012). doi:10.1155/2012/305102. Article ID: 305102
Acknowledgment
This work and the contribution were supported by project “Smart Solutions for Ubiquitous Computing Environments” FIM, University of Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic (under ID: UHK-FIM-SP-2016-2102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Worki, Y., Berhan, E., Krejcar, O. (2016). Global Solar Radiation Prediction Using Backward Propagation Artificial Neural Network for the City of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. In: Nguyen, NT., Iliadis, L., Manolopoulos, Y., Trawiński, B. (eds) Computational Collective Intelligence. ICCCI 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9875. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45243-2_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45243-2_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-45242-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-45243-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)