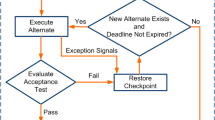
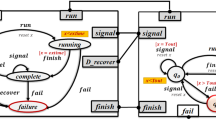
Abstract
Fast evolution of computing systems is a hot topic today that is becoming a real challenge for safety critical embedded systems. For both maintenance and functionalities reasons, over-the-air updates are very attractive for embedded systems manufacturers in many application domains. The challenge here is to maintain dependability properties when facing changes. This is exactly the definition of resilient computing we consider in this work. The implementation of resilient computing relies on fault tolerance design patterns (FTDP) that comply with various types of non-functional assumptions (behavioural assumptions, fault model assumptions, temporal assumptions, resources assumptions, etc.). Despite changes in operation, the efficiency of the fault tolerance mechanisms (instance of a FTDP) depends on the strict compliance with such assumptions. The objective of the paper is to provide a model to simplify the analysis of resilient systems, in particular focusing on adaptive fault tolerant computing. Simple measures are illustrated on evolution scenarii.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laprie, J.-C., From dependability to resilience. In: 38th IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN) (2008)
Powell, D.: Failure mode assumption and assumption coverage. In: Predictably Dependable Computing Systems (1995). ISBN 3-540-59334 (First version in Proceeding of FTCS-22)
Kim, K.H.K., Lawrence, T.F.: Adaptive fault tolerance: issues and approaches. In: Proceedings of the Second IEEE Workshop on Future Trends of Distributed Computing Systems, pp. 38–46. IEEE (1990)
Krishna, C., Koren, I.: Adaptive fault-tolerance for cyber-physical systems. In: IEEE International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), pp. 310–314 (2013)
Fraga, J., Siqueira, F., Favarim, F.: An adaptive fault-tolerant component model. In: 9th Workshop on Object- Oriented Real-Time Dependable Systems, pp. 179–186. IEEE (2003)
Lung, L.C., Favarim, F., Santos, G.T., Correia, M.: An infrastructure for adaptive fault tolerance on FT-CORBA. In: 9th International Symposium on Object and Component- Oriented Real-Time Distributed Computing. IEEE (2006)
Marin, O., Sens, P., Briot, J.-P., Guessoum, Z.: Towards adaptive fault-tolerance for distributed multi-agent systems. In: 4th European Research Seminar on Advances in Distributed Systems, pp. 195–201 (2001)
Stoicescu, M.: Architecting resilient computing systems: a component-based approach. Ph.D. thesis, National Polytechnic Institute of Toulouse (INP) (2013). www.theses.fr/en/2013INPT0120
Lauer, M., Amy, M., Fabre, J.-C., Roy, M., Excoffon, W., Stoicescu, M.: Adaptive fault tolerance mechanisms for resilient computing on ROS. In: The 17th IEEE Symposium on High Assurance Systems Engineering (HASE 2016), Orlando (FL), USA, January 2016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Excoffon, W., Fabre, JC., Lauer, M. (2016). Towards Modelling Adaptive Fault Tolerance for Resilient Computing Analysis. In: Skavhaug, A., Guiochet, J., Bitsch, F. (eds) Computer Safety, Reliability, and Security. SAFECOMP 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9922. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45477-1_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45477-1_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-45476-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-45477-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)